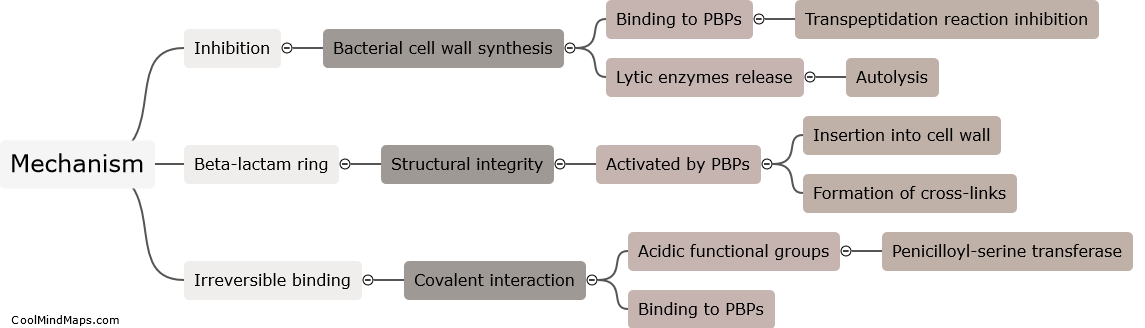
What is the mechanism of action of penicillin?
Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic that belongs to the class of beta-lactam antibiotics. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, which are crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the bacteria. Penicillin works by binding to and inhibiting an enzyme called transpeptidase, which is responsible for the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains in the bacterial cell wall. By disrupting this process, penicillin weakens the bacterial cell wall, leading to osmotic lysis and ultimately, the death of the bacteria. This mechanism of action is specific to bacteria, as human cells do not have cell walls and are not affected by penicillin. Overall, penicillin's ability to target bacterial cell walls makes it a potent and effective treatment for various bacterial infections.
This mind map was published on 29 November 2023 and has been viewed 95 times.