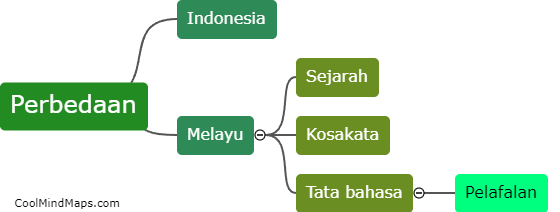
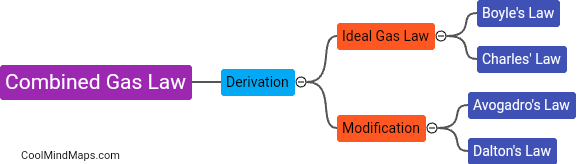
What are the characteristics of the ideal gas?
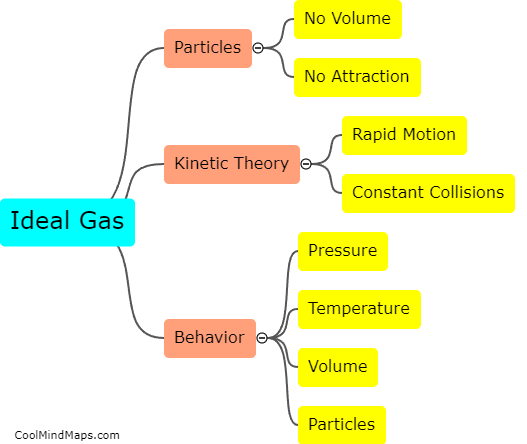
The ideal gas is a theoretical model used in physics and chemistry to describe the behavior of gases. It is characterized by several key characteristics. Firstly, an ideal gas is assumed to consist of a large number of particles that are constantly in motion, colliding with each other and the walls of the container they are in. These particles are considered to be point masses with no volume or intermolecular forces. Secondly, an ideal gas obeys the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are related by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. Thirdly, an ideal gas exhibits predictable behavior, with its properties being determined solely by its temperature, pressure, and volume. These properties include the ability to be compressed or expanded easily, and the fact that different gases at the same temperature and pressure will have the same number of molecules per unit volume. While real gases often deviate from these ideal characteristics, the ideal gas serves as a useful simplification for understanding the behavior of gases in many situations.
This mind map was published on 10 November 2023 and has been viewed 79 times.