What are the steps involved in protein synthesis?
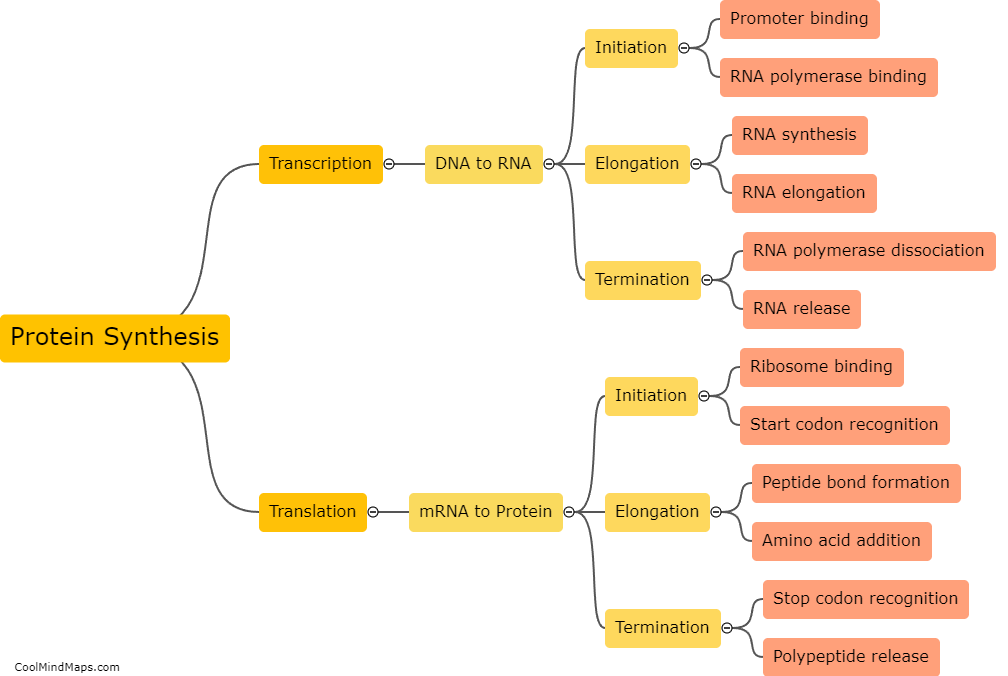
Protein synthesis is a complex biological process that involves several sequential steps. It begins with the transcription of DNA, where an enzyme called RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary mRNA molecule based on the DNA template. Once the mRNA molecule is formed, it undergoes a modification process called RNA splicing, where non-coding regions called introns are removed, and the remaining coding regions called exons are joined together. After splicing, the mature mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm, where it binds to a ribosome. The second step, known as translation, begins with the initiation phase. In this phase, the ribosome recognizes a specific sequence called the start codon on the mRNA, and an initiator tRNA molecule carrying the amino acid methionine is attracted to it. The ribosome then proceeds to the elongation phase, where successive tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids based on their anticodon sequence and bond them together to form a polypeptide chain. Finally, when a termination codon is encountered, the ribosome releases the completed polypeptide and mRNA molecule. This process of transcription and translation ensures the synthesis of functional proteins, which play crucial roles in various biological functions.
This mind map was published on 11 September 2023 and has been viewed 98 times.