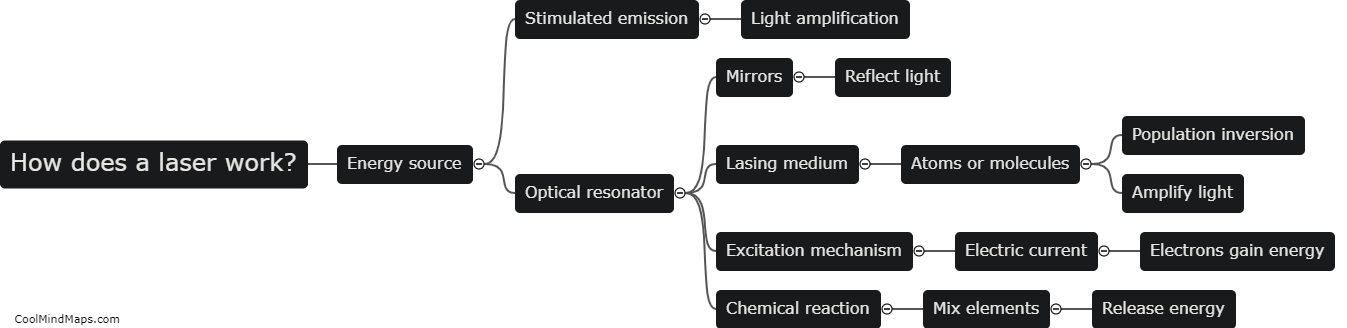
How does a laser work?
A laser, short for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, operates on the principles of stimulated emission and amplification of light. It starts with a gain medium, such as a crystal or gas, that is excited by an external energy source, such as electrical discharge or optical pumping. The excitation causes electrons in the gain medium to jump to a higher energy level. As these excited electrons return to their ground state, they release photons with specific wavelengths. This process of stimulated emission creates a chain reaction where the emitted photons stimulate surrounding excited electrons to emit photons of the same wavelength and phase, resulting in a coherent beam of light. This beam is further amplified as it passes through multiple mirrors or optical components in the laser cavity. The final output is a highly focused and intense beam of light with characteristics determined by the properties of the gain medium. Lasers find applications in various fields, including telecommunications, medicine, industry, and research.
This mind map was published on 15 November 2023 and has been viewed 134 times.