What is the influence of multivalent ions (SO4, Mg2+, Ca2+) on wettability and interfacial tension in low salinity flooding?
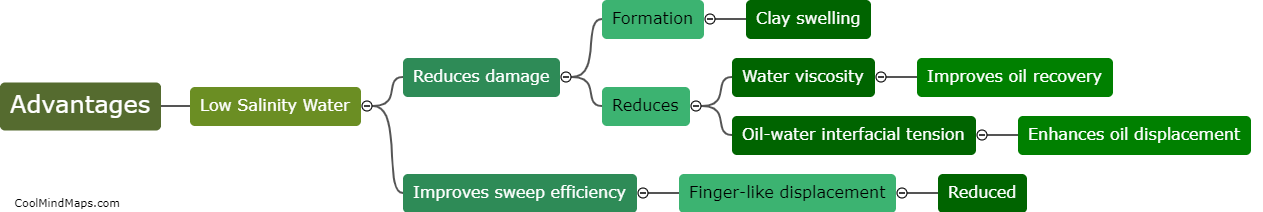
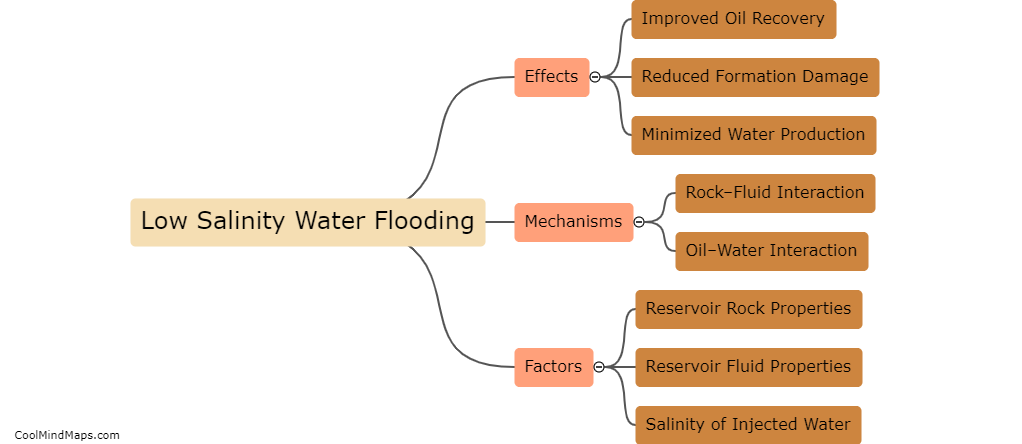
Multivalent ions, such as SO4, Mg2+, and Ca2+, have a significant influence on wettability and interfacial tension in low salinity flooding. Low salinity flooding is a technique used in enhanced oil recovery to improve the displacement of oil by water. These multivalent ions alter the surface properties of the reservoir rocks and affect the wetting behavior of oil and water on these surfaces. Specifically, these ions can change the wettability from oil-wet to water-wet, enhancing water imbibition and improving oil recovery. Additionally, the presence of multivalent ions can lower the interfacial tension between oil and water, allowing for easier displacement and mobilization of the trapped oil. Understanding the influence of these multivalent ions is crucial for optimizing low salinity flooding operations and maximizing oil recovery from reservoirs.
This mind map was published on 20 December 2023 and has been viewed 38 times.