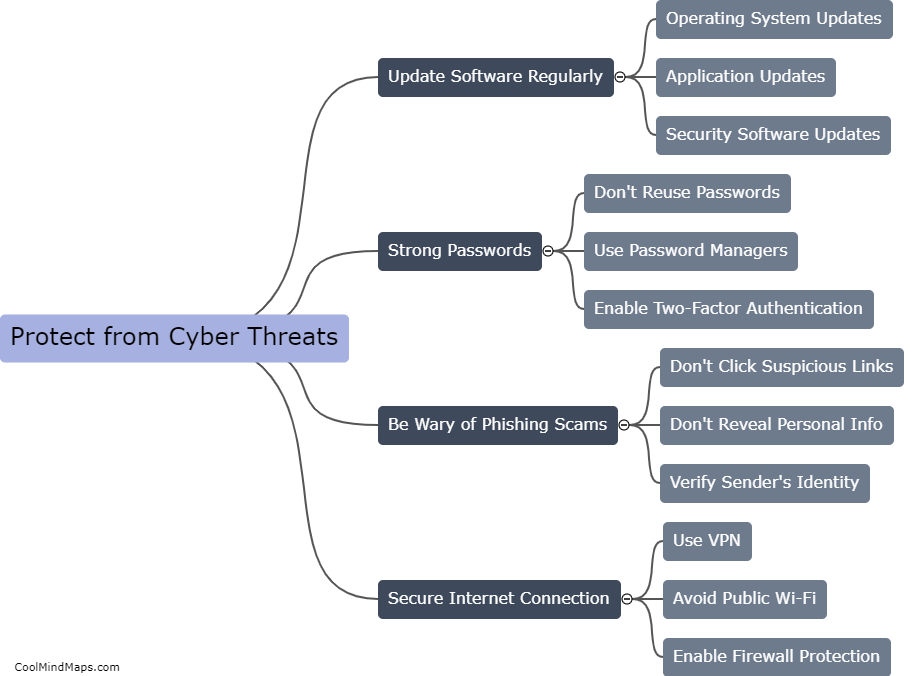
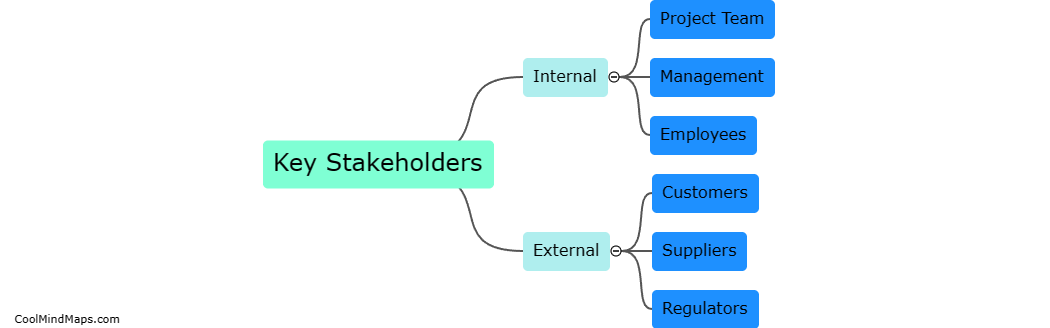
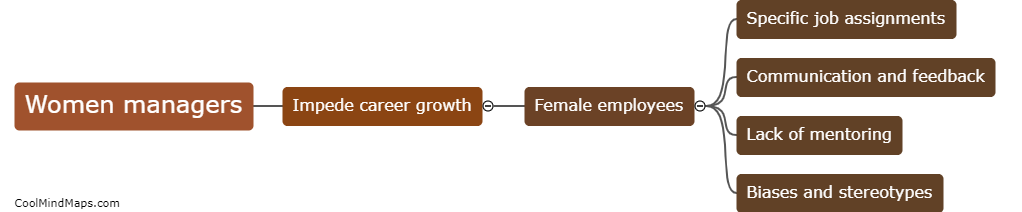
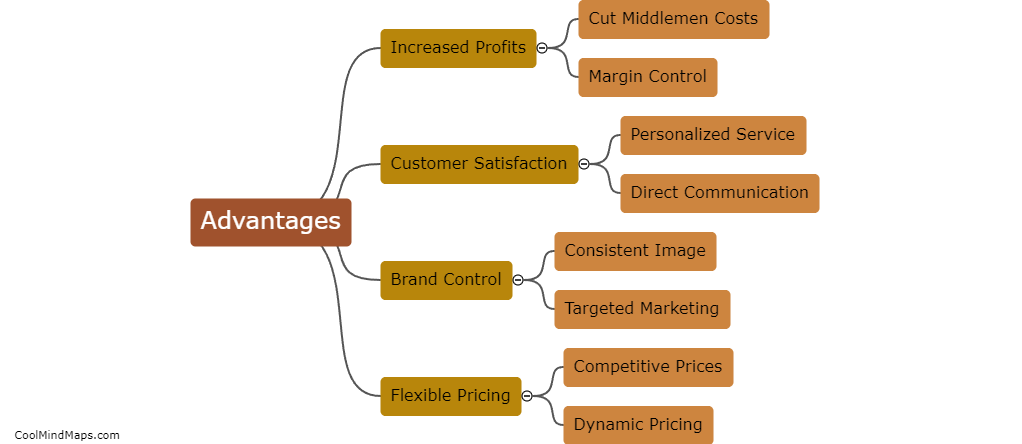
What is the function of the p53 protein?
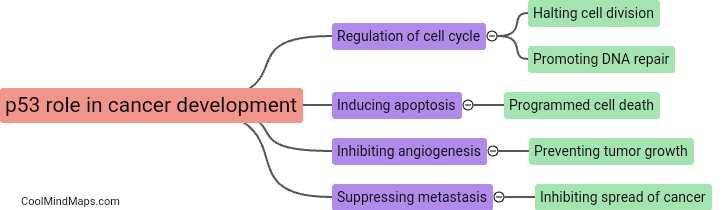
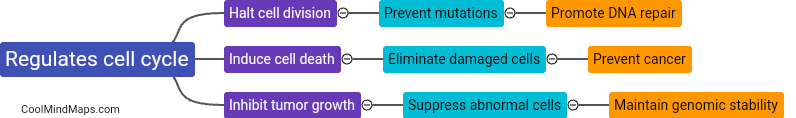
The p53 protein, often referred to as the "guardian of the genome," plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and apoptosis. It acts as a tumor suppressor by monitoring DNA damage and initiating either repair mechanisms or programmed cell death if the damage is too severe. In essence, p53 helps maintain genetic stability by preventing the replication of damaged DNA and the formation of potentially cancerous cells. Its function is essential in protecting the integrity of our genetic material and ensuring proper cell growth and division.
This mind map was published on 9 May 2024 and has been viewed 83 times.