What is sensory transduction?
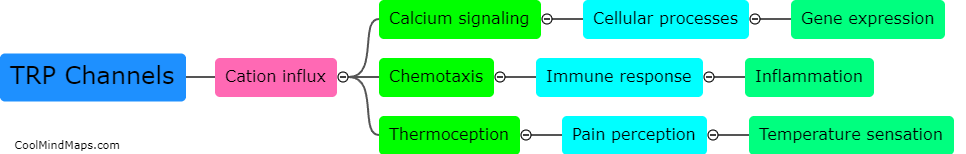
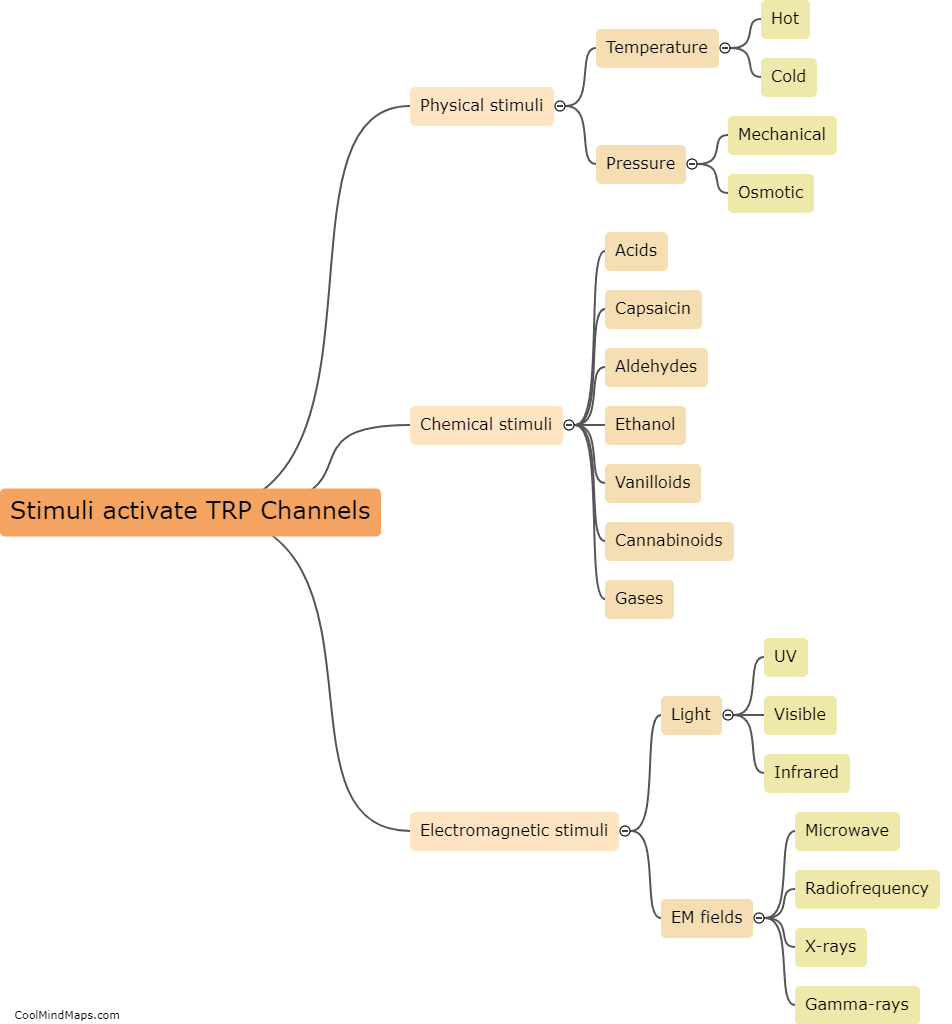
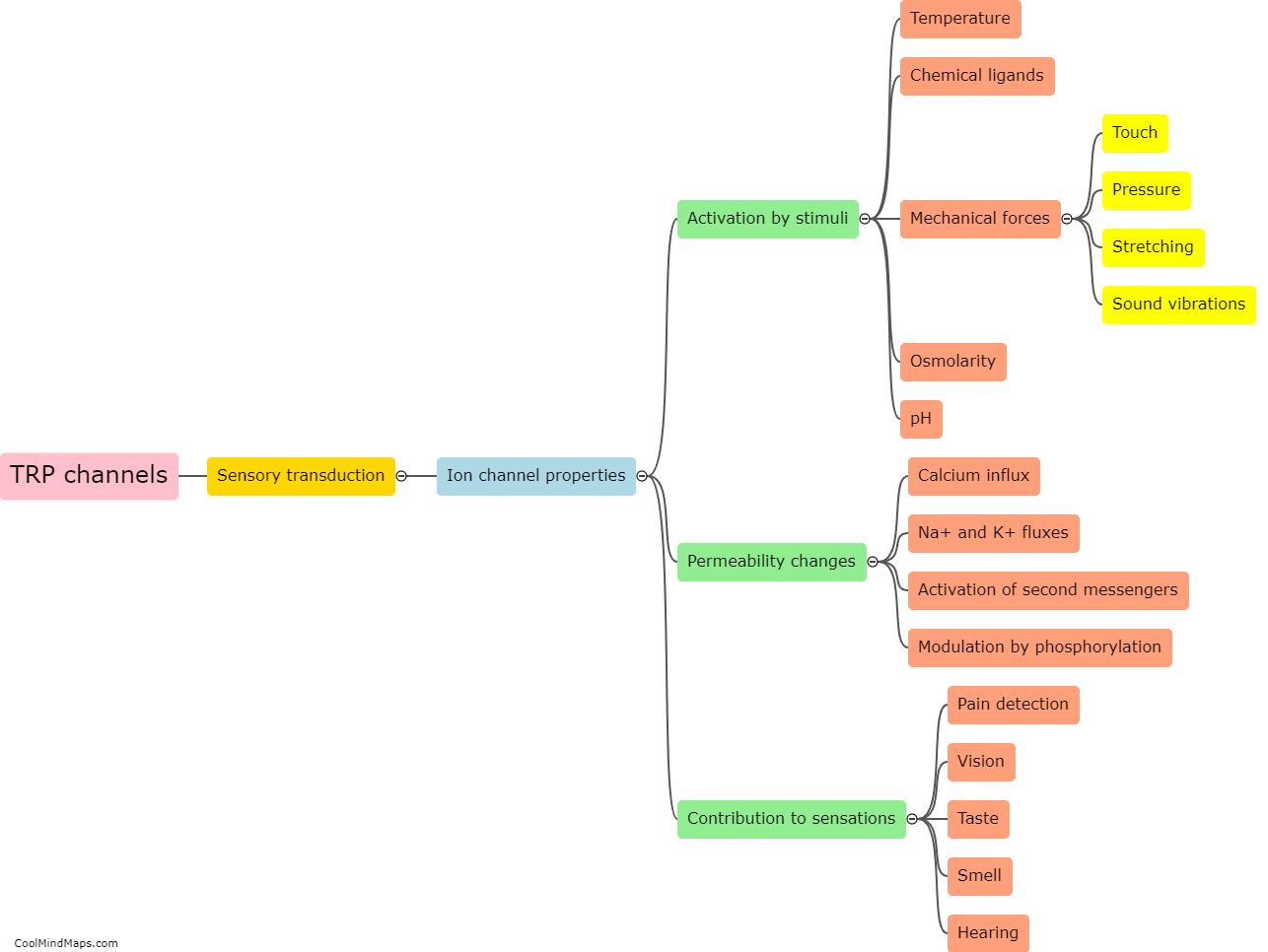
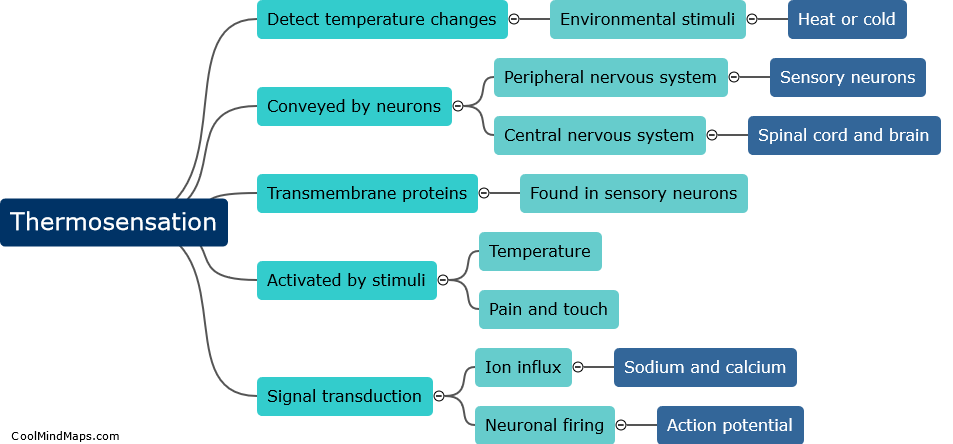
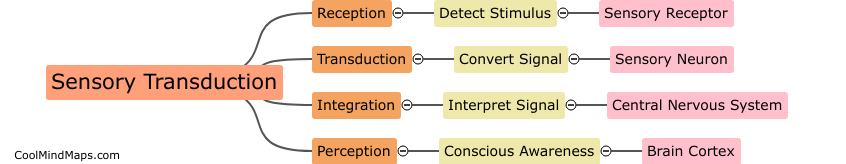
Sensory transduction is the process by which sensory stimuli (such as light, sound waves, or chemicals) are converted into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. This process occurs in specialized cells called sensory receptors, which are responsible for detecting different types of stimuli. Each sensory receptor has specific molecules, called receptors, that are activated by specific stimuli. Once activated, these receptors trigger a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the generation of electrical signals that can be transmitted to the brain via nerve fibers. Sensory transduction is a fundamental process that underlies our ability to perceive and interact with the world around us.
This mind map was published on 22 June 2023 and has been viewed 102 times.