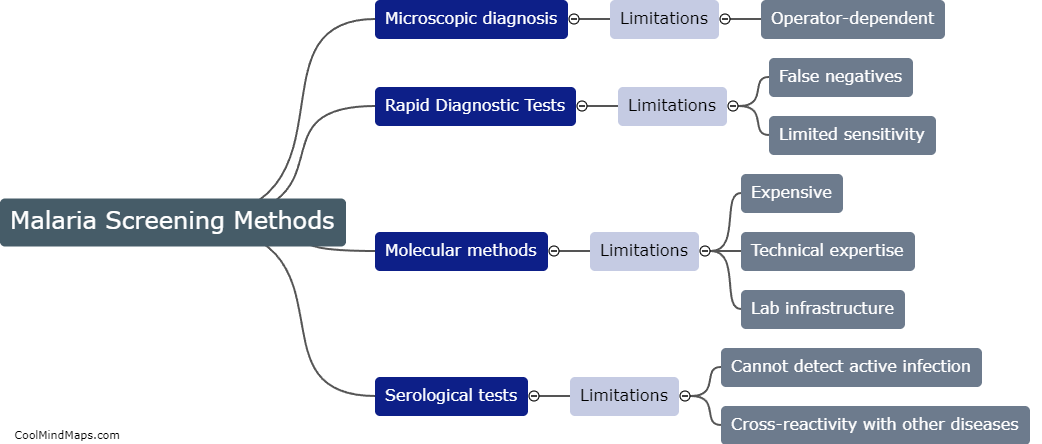
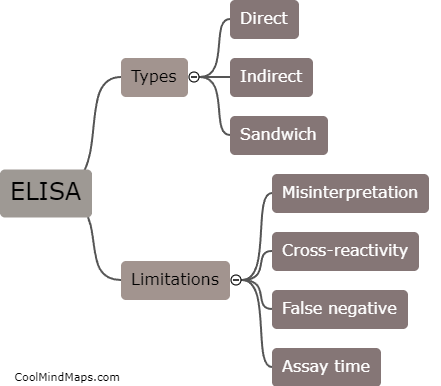
What is Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and its limitations?
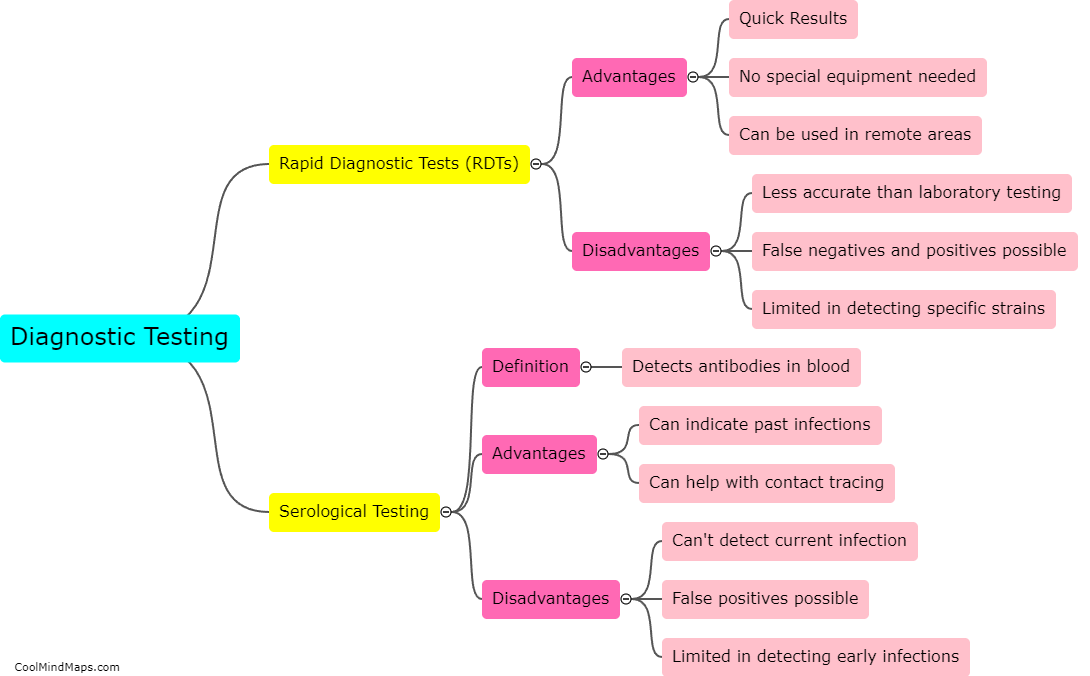
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a technique used to detect and measure the presence of antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves coating a microplate with a specific antigen or antibody, binding the target molecule in the sample to a primary antibody, and detecting the complex with a secondary enzyme-linked antibody. While ELISA is widely used in research and diagnosis of infectious diseases, it has several limitations, including the need for expensive equipment and reagents, sensitivity issues with low concentrations of target molecules, and potential for cross-reactivity with related molecules. Nevertheless, ELISA remains a valuable tool in scientific research and clinical diagnostics.
This mind map was published on 25 June 2023 and has been viewed 107 times.