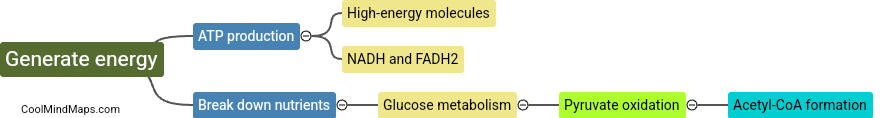
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle?
The purpose of the Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This series of chemical reactions takes place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and is essential for the production of high-energy molecules that power cellular processes. Additionally, the Krebs cycle also serves to generate reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and FADH2, which are necessary for the electron transport chain to produce even more ATP molecules. Overall, the Krebs cycle is a crucial component of aerobic respiration and plays a central role in metabolism.
This mind map was published on 26 July 2024 and has been viewed 73 times.