How does Rheumatic fever progress to Rheumatic heart disease?
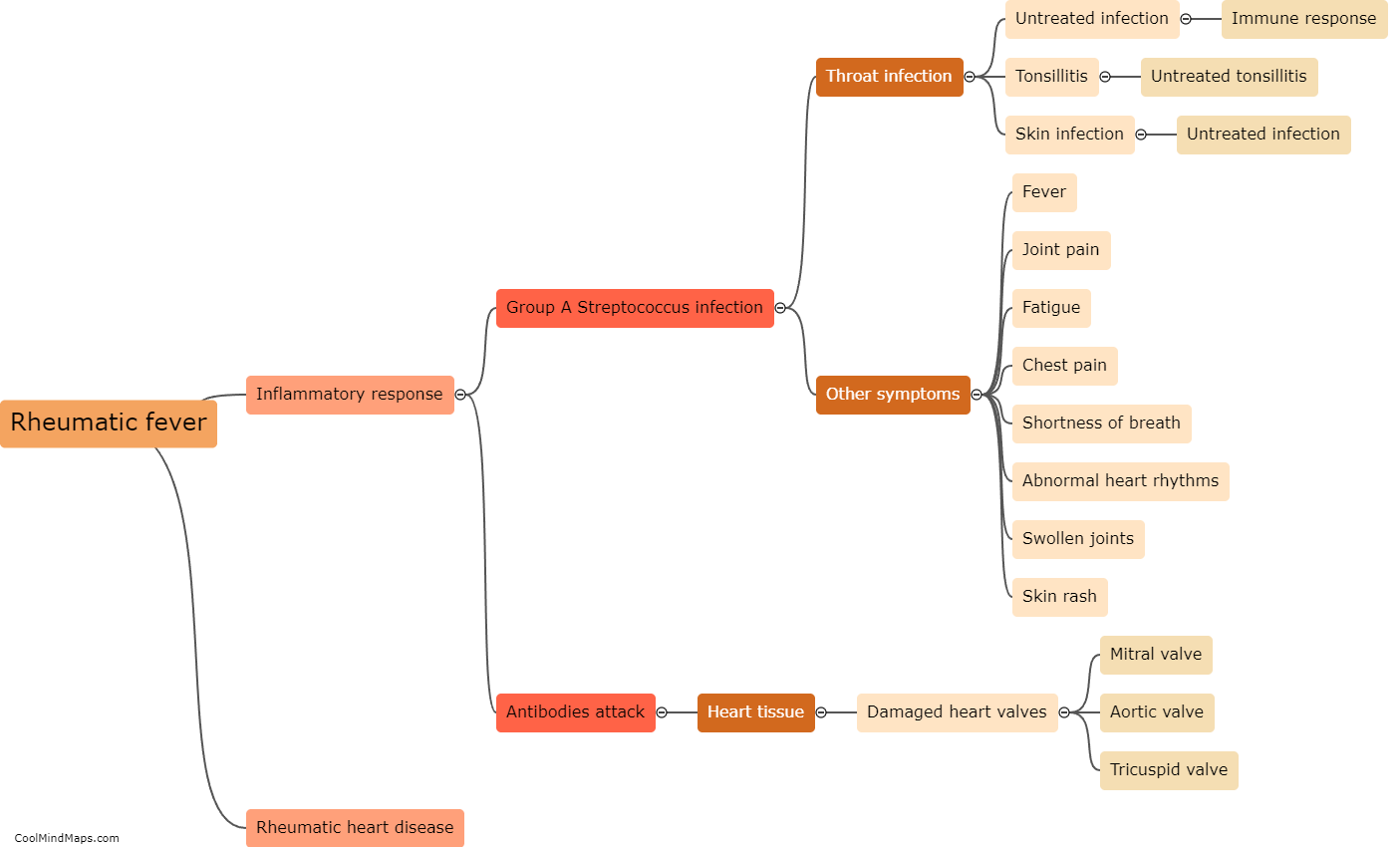
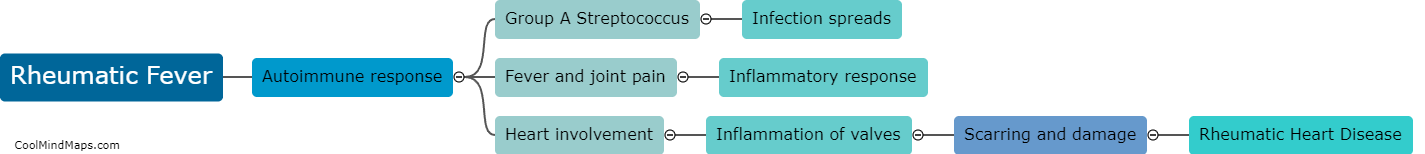
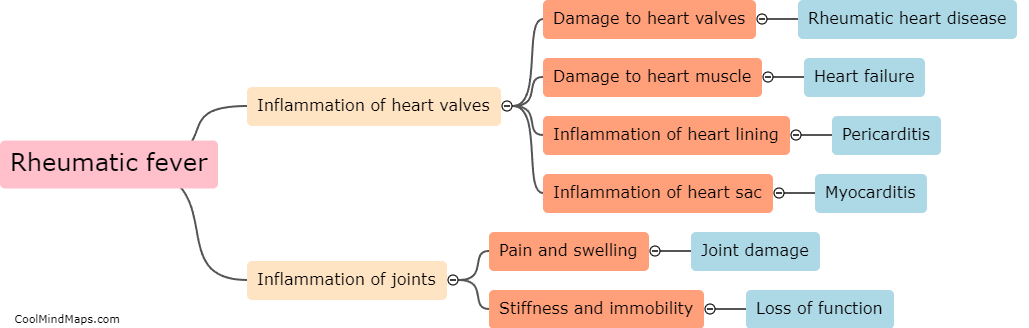
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop following an untreated or incompletely treated streptococcal infection, particularly in children. If left untreated or poorly managed, rheumatic fever can progress to chronic scarring and damage of the heart valves, leading to rheumatic heart disease (RHD). The development of RHD occurs due to an abnormal immune response to the streptococcal infection, where the body's immune system not only fights off the bacteria but also targets healthy tissues, including the heart. Over time, this immune response causes inflammation in the heart valves, resulting in their thickening and scarring. As the disease progresses, the damaged valves become less effective, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations. Early diagnosis, proper management of streptococcal infections, and timely administration of antibiotic treatment for rheumatic fever can significantly reduce the risk of developing RHD.
This mind map was published on 17 October 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.