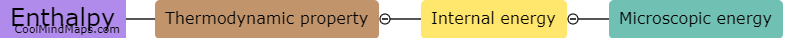What is internal energy in chemistry?
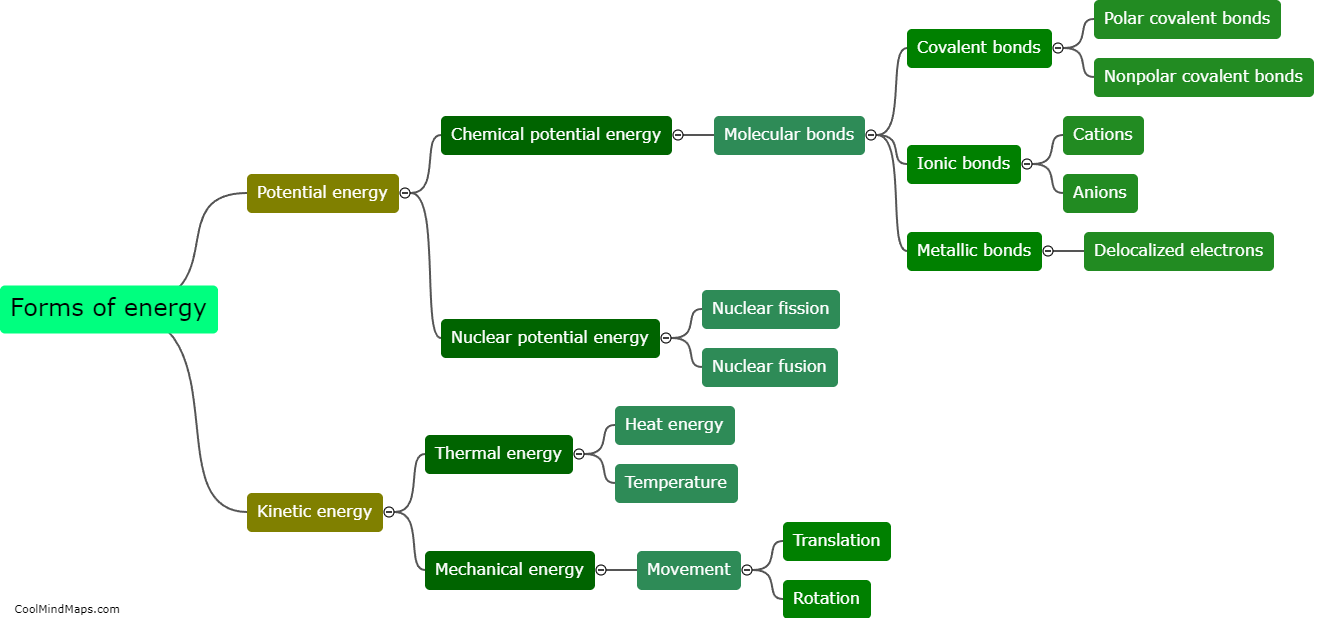
In chemistry, internal energy refers to the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles within a substance. It represents the total energy associated with the microscopic motion and interactions of atoms and molecules. Internal energy is a fundamental concept that helps explain various thermodynamic processes, such as heat transfer and chemical reactions. It is influenced by factors like temperature, pressure, and the composition of the system. Understanding and manipulating internal energy is essential for studying and predicting the behavior of substances and designing processes in fields ranging from energy production to material science.
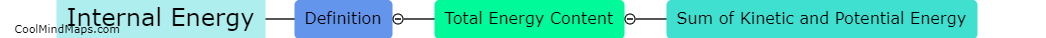
This mind map was published on 7 September 2023 and has been viewed 147 times.