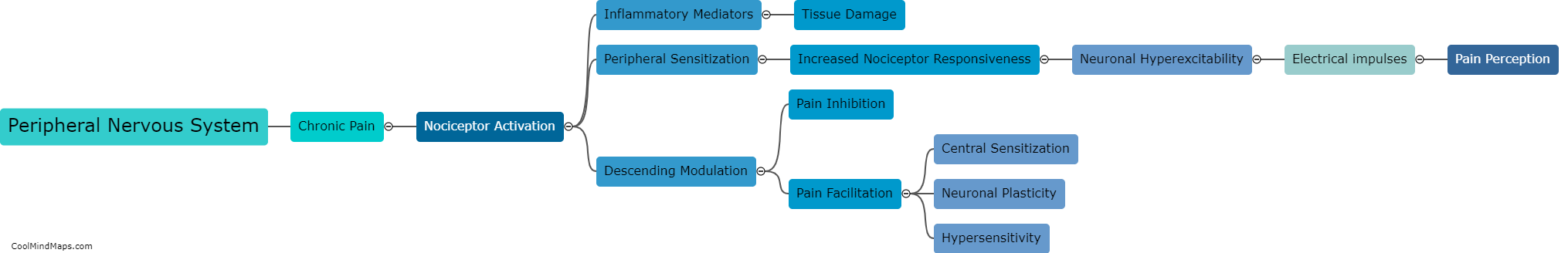
How does the peripheral nervous system contribute to chronic pain?
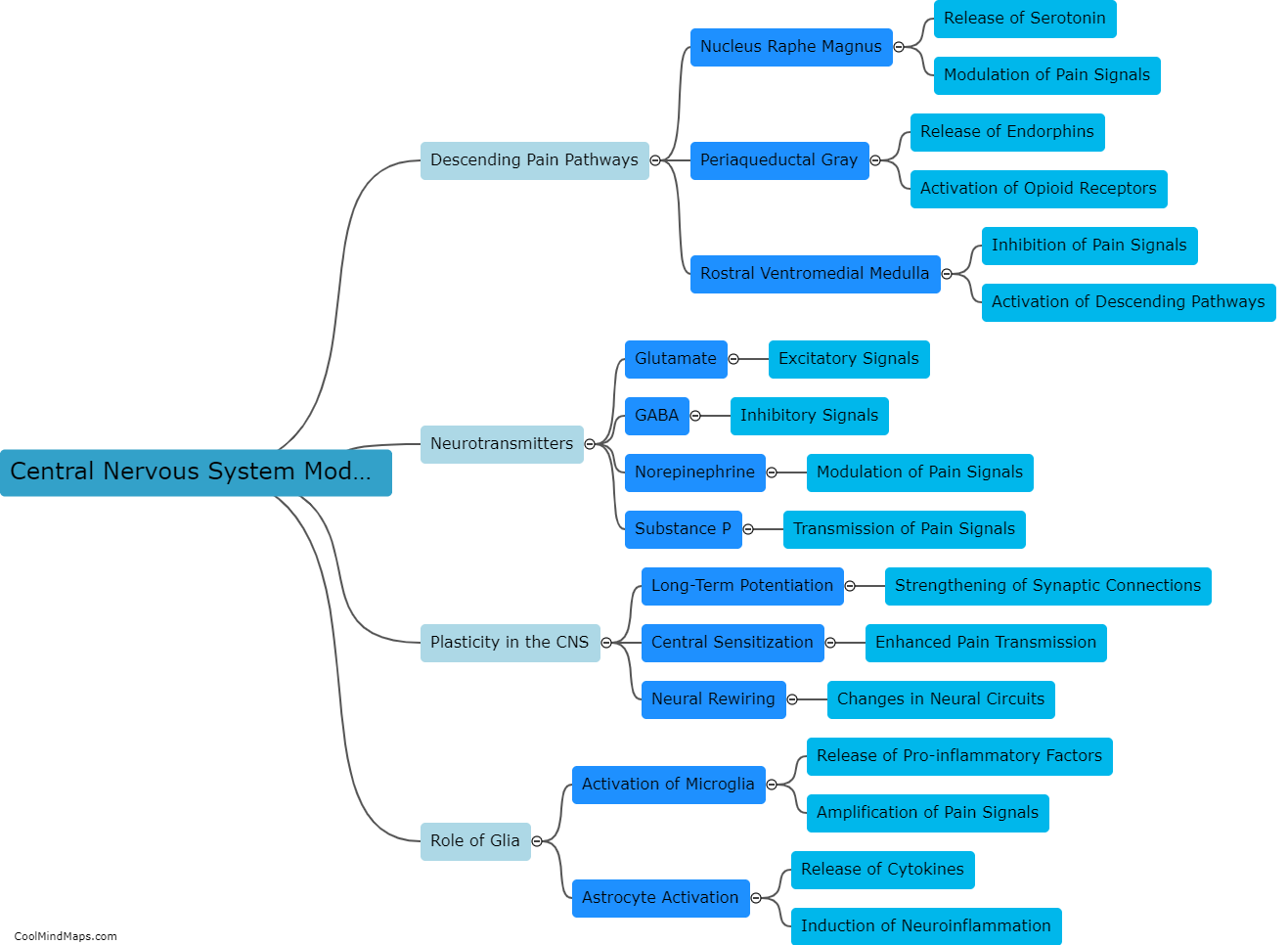
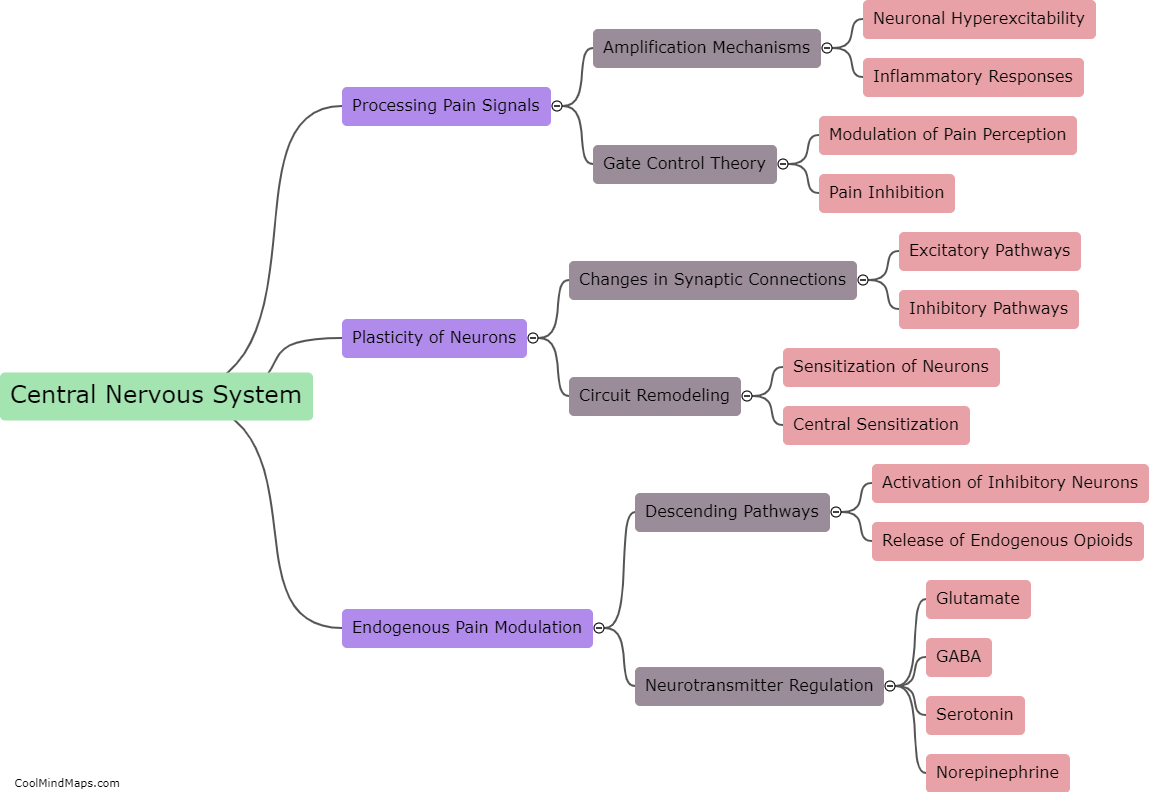
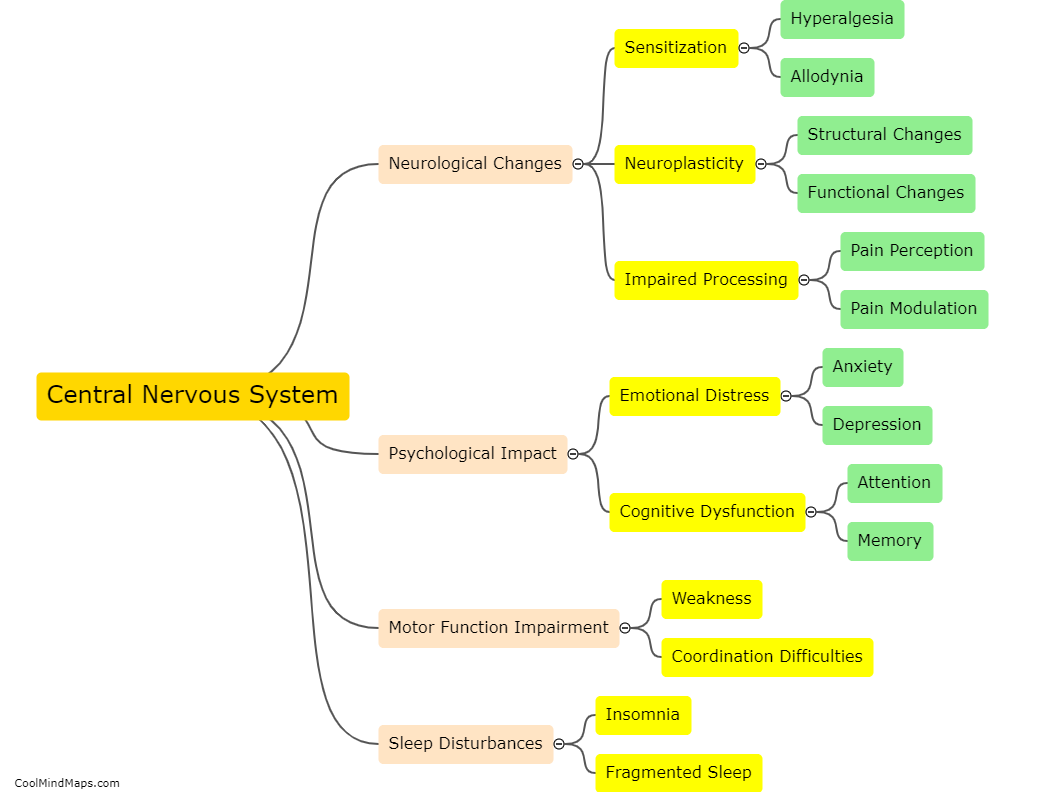
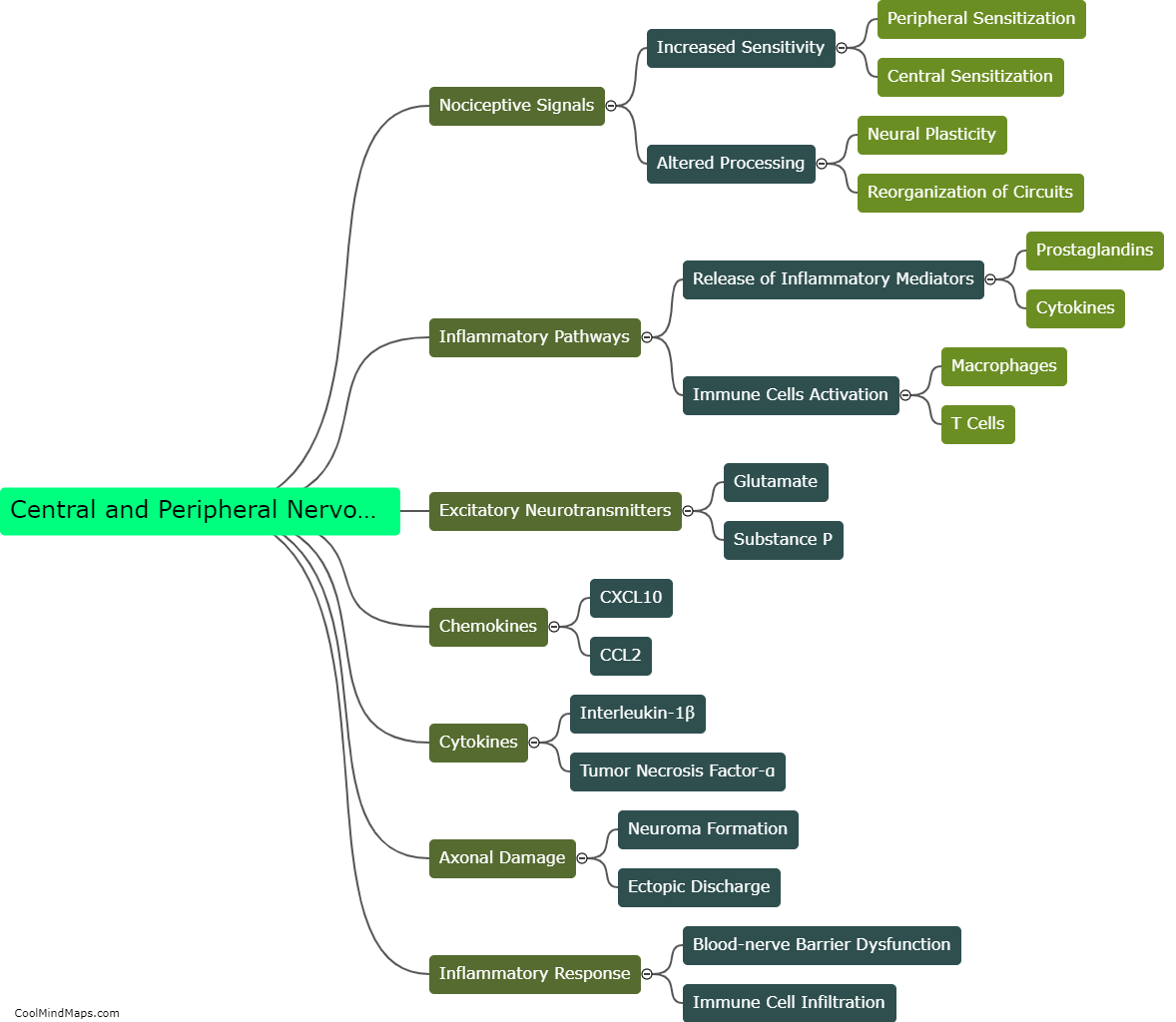
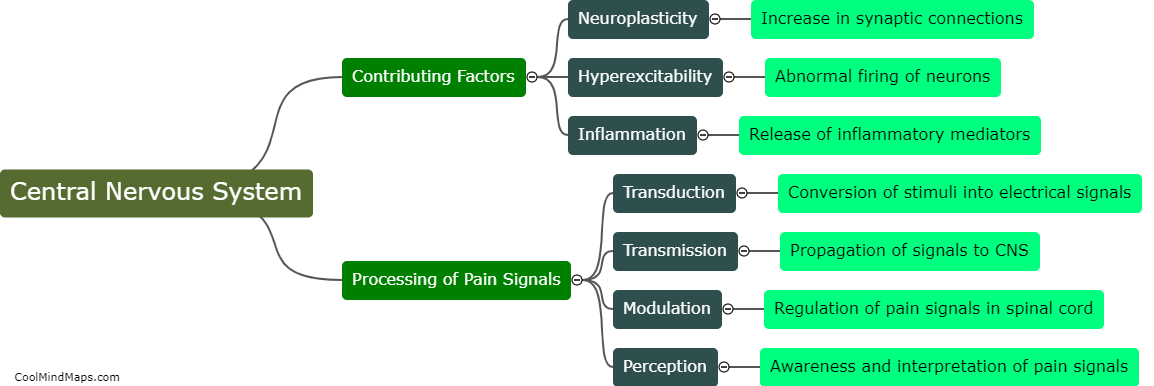
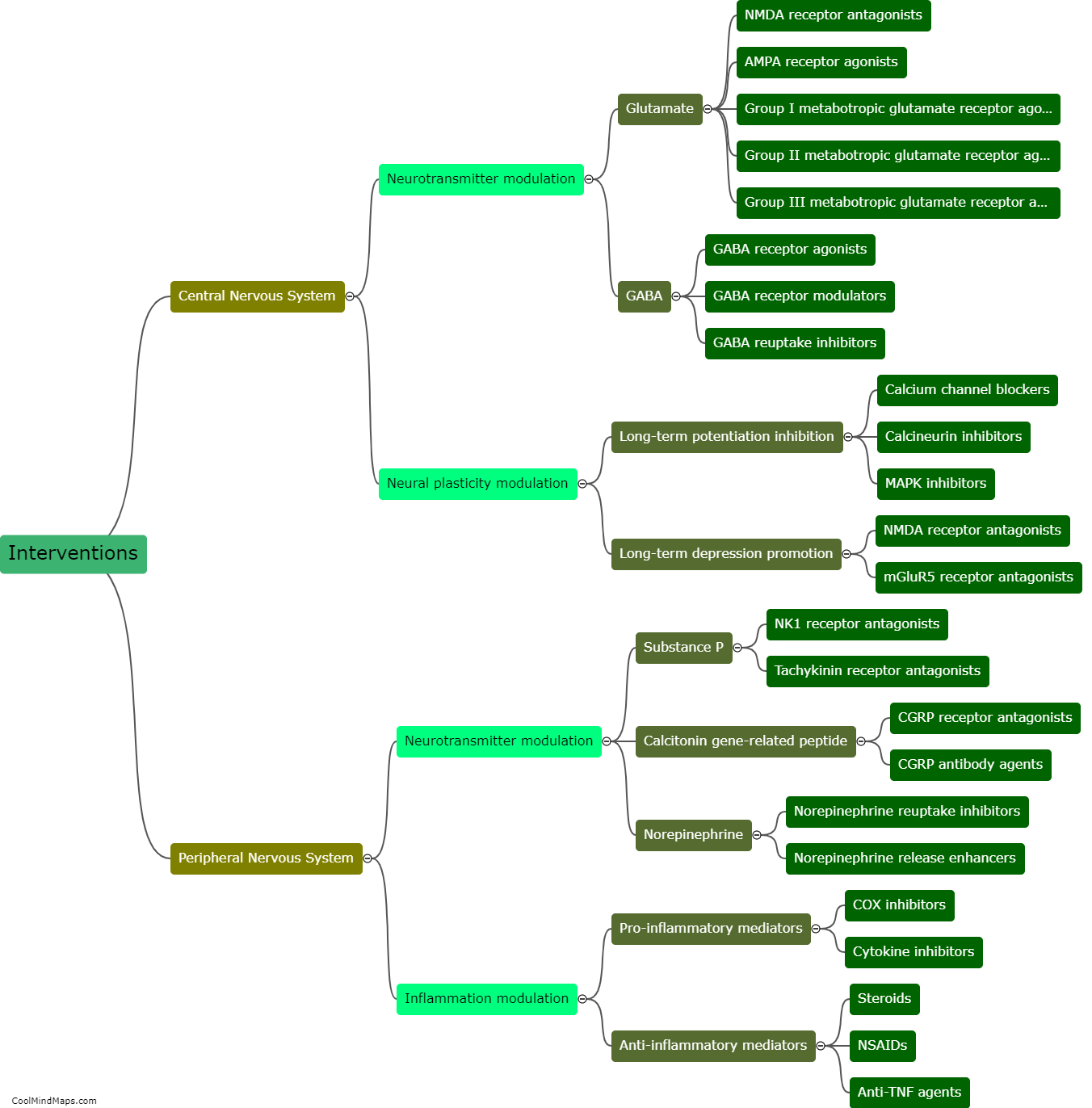
The peripheral nervous system plays a crucial role in chronic pain. When an injury or disease occurs, specialized nerve fibers called nociceptors detect and transmit pain signals to the spinal cord and brain. In the case of chronic pain, these nociceptors are sensitized and become hyperactive, leading to an amplified and prolonged pain response. This can occur due to various factors, including inflammation, nerve damage, or dysfunction in the peripheral nerves. Additionally, the peripheral nervous system also contributes to chronic pain through mechanisms such as neuroplasticity, where the nerves undergo structural and functional changes that enhance pain transmission. Understanding the role of the peripheral nervous system in chronic pain is vital for developing effective treatments and managing the condition more efficiently.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.