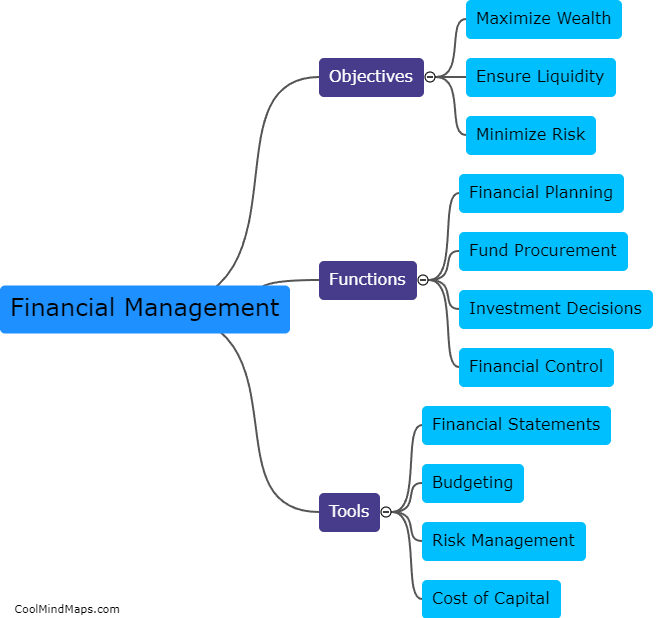
What are the Brazilian government branches?
The Brazilian government system follows the principles of separation of powers and has three main branches: the Executive, Legislative, and Judiciary. The Executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws and is headed by the President who is assisted by ministers and other high-ranking officials. The Legislative branch is responsible for making laws and is divided into two chambers: the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. The Judiciary branch is responsible for interpreting and enforcing the laws and is composed of various courts and judges. Each branch has distinct functions and operates independently, but they also work together to maintain a balanced and effective government.
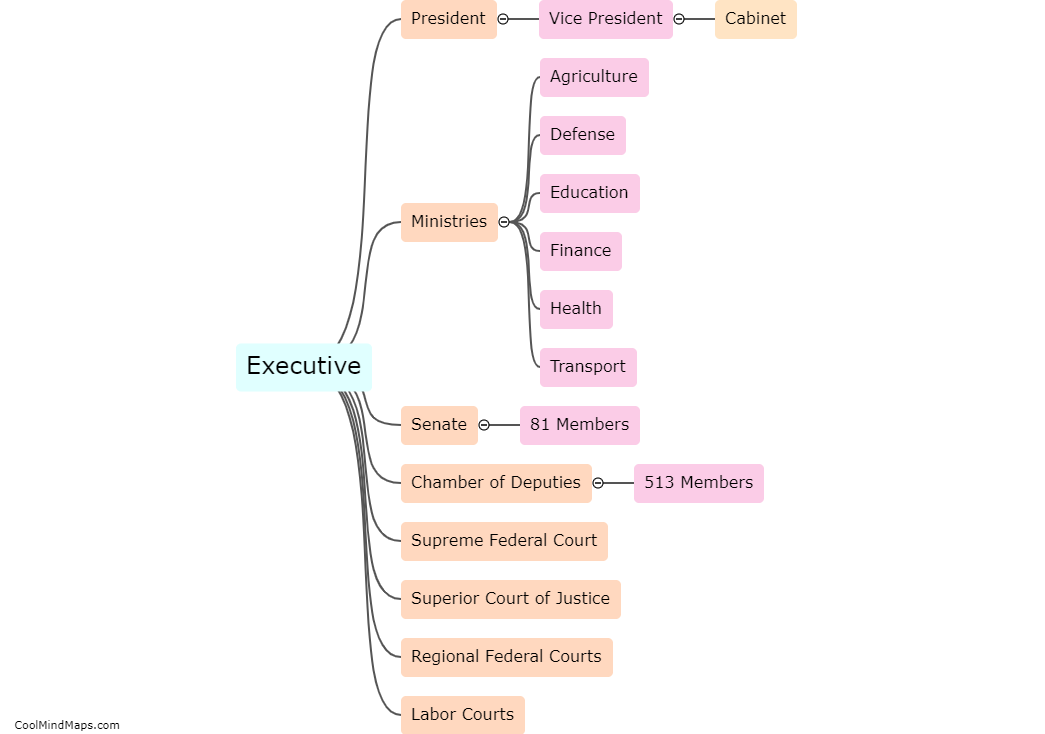
This mind map was published on 16 May 2023 and has been viewed 129 times.