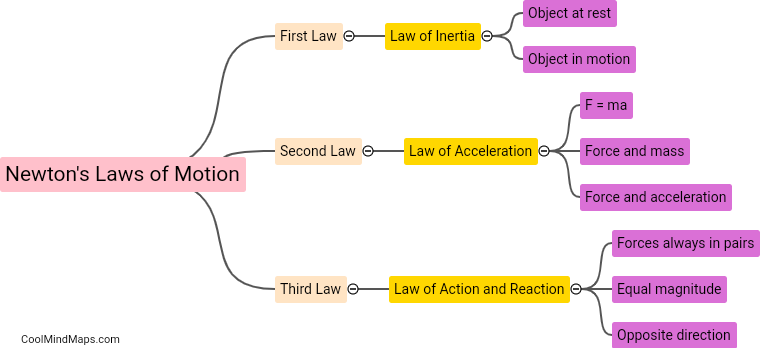
What are the three laws of motion by Newton?
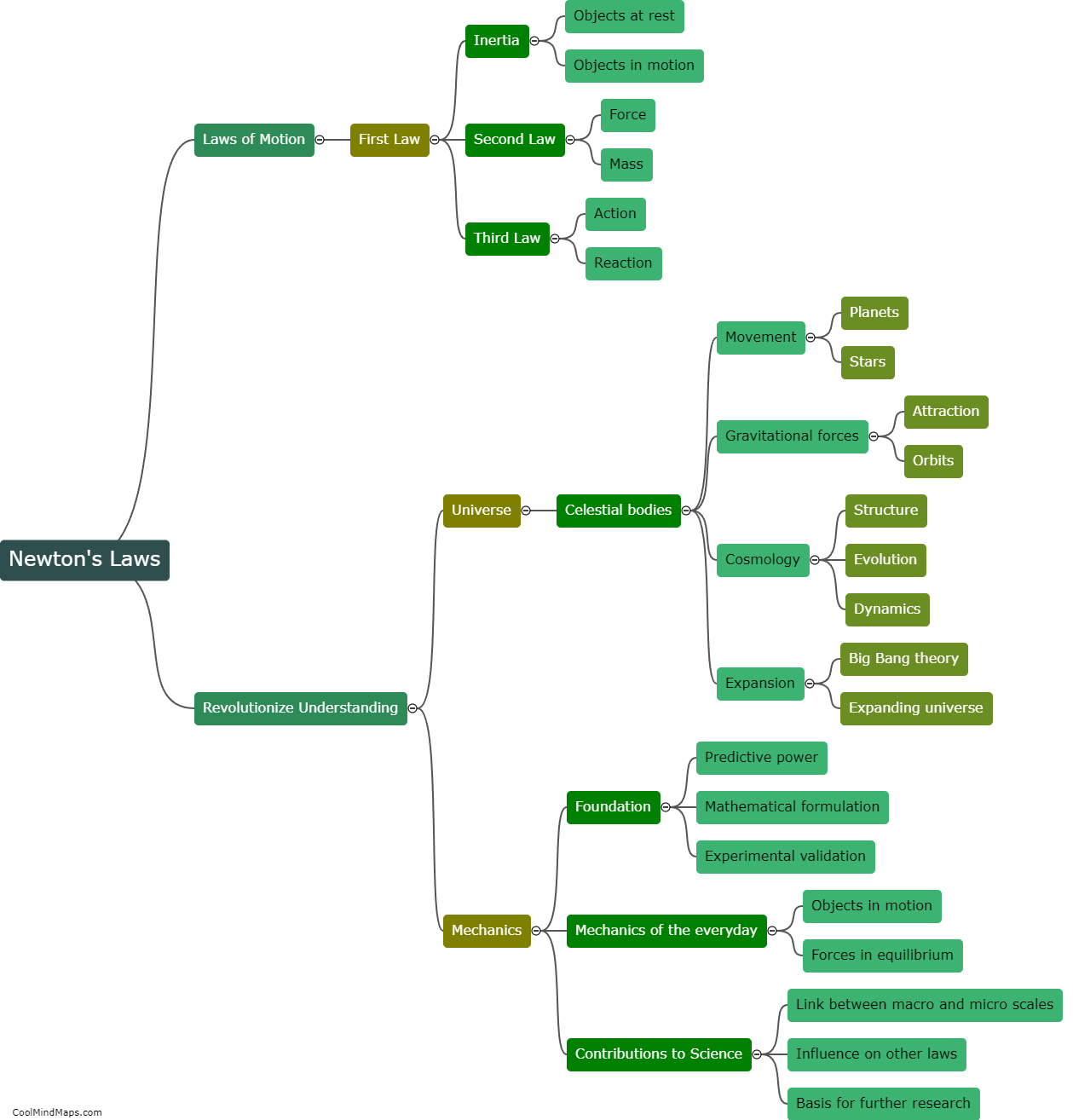
The three laws of motion by Sir Isaac Newton form the foundation of classical mechanics. The first law, known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force. The second law, often referred to as the force equation, states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. F = ma, where F represents force, m is mass, and a denotes acceleration. The third law, known as the law of action and reaction, states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude in the opposite direction on the first object. These laws provide a comprehensive framework to understand and analyze the motion of objects in various physical scenarios.
This mind map was published on 13 September 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.