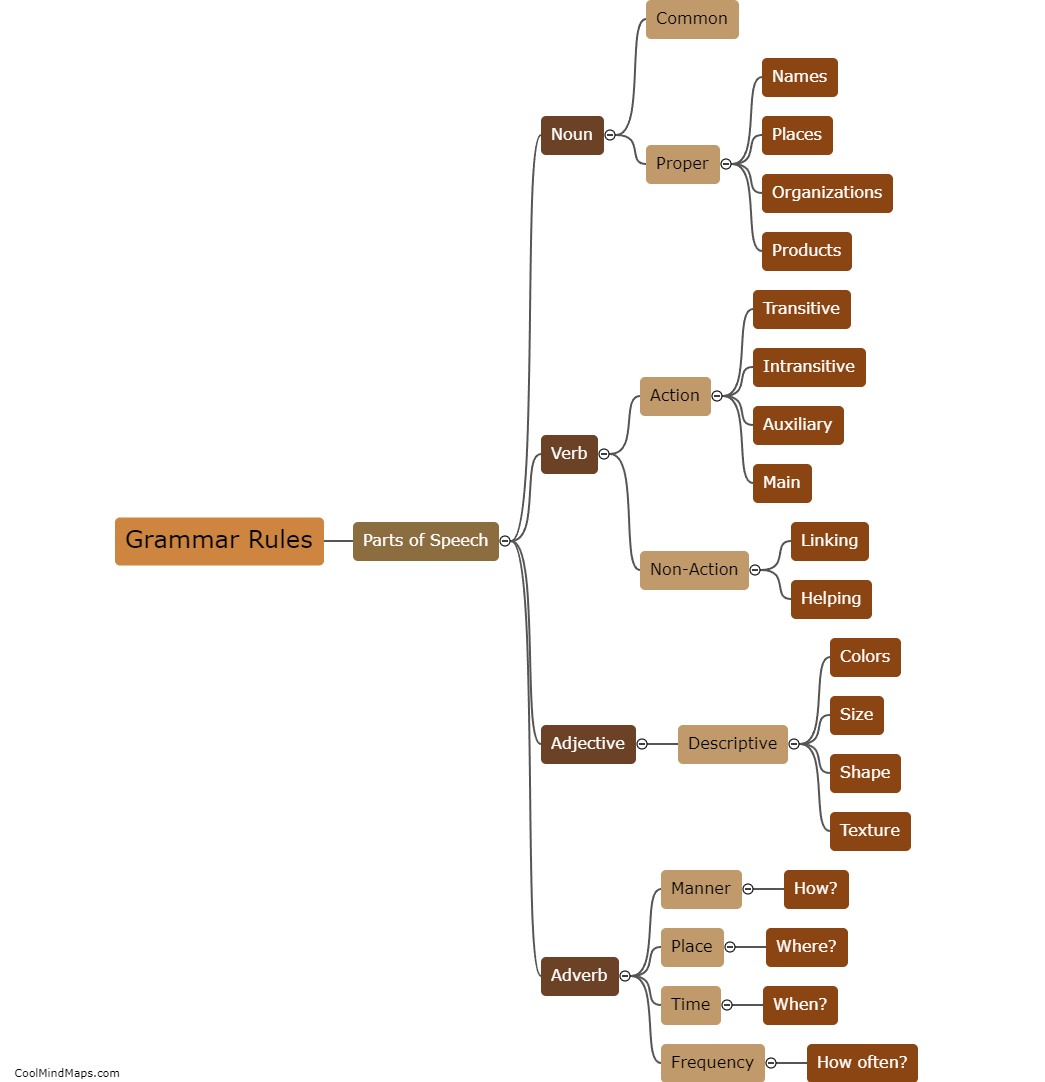
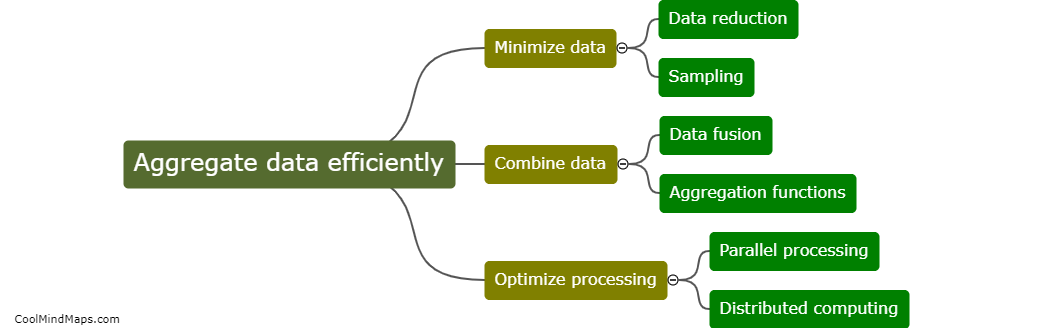
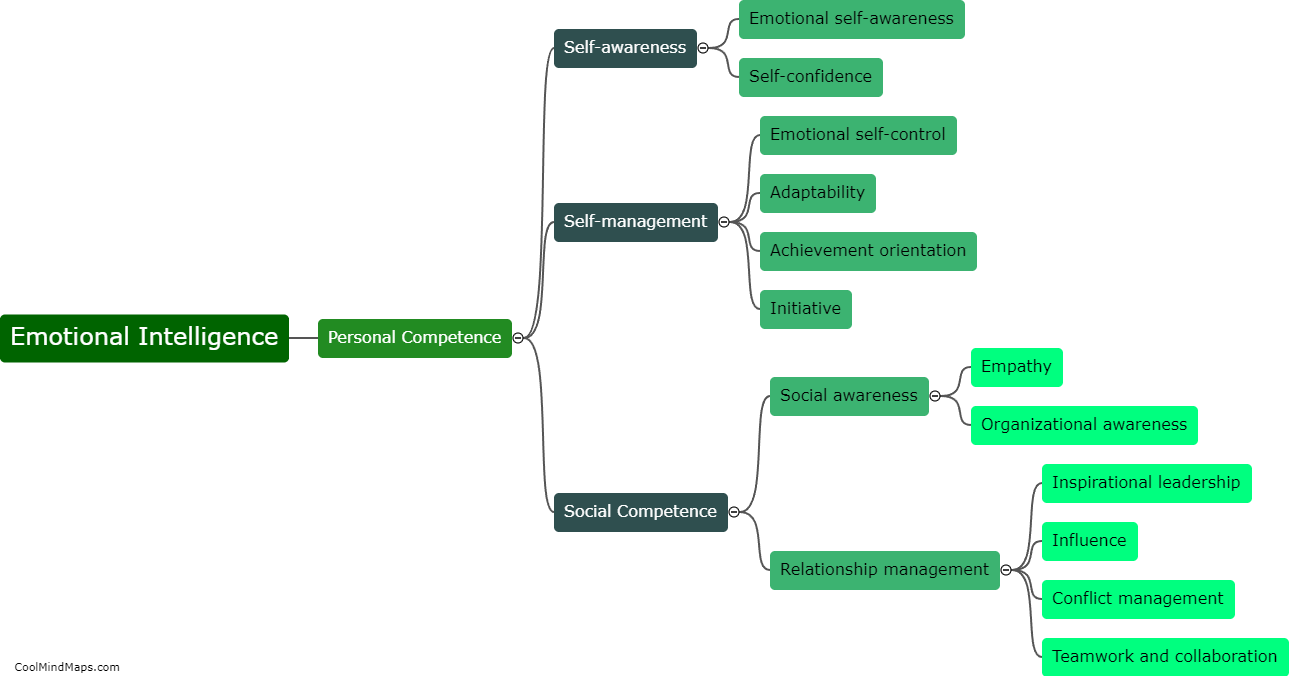
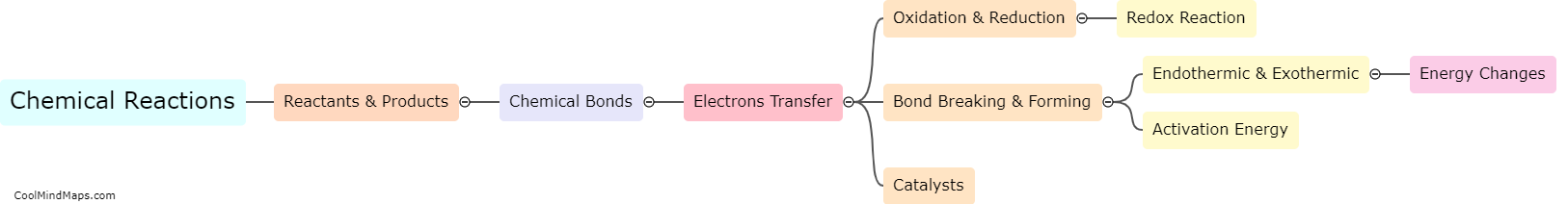
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
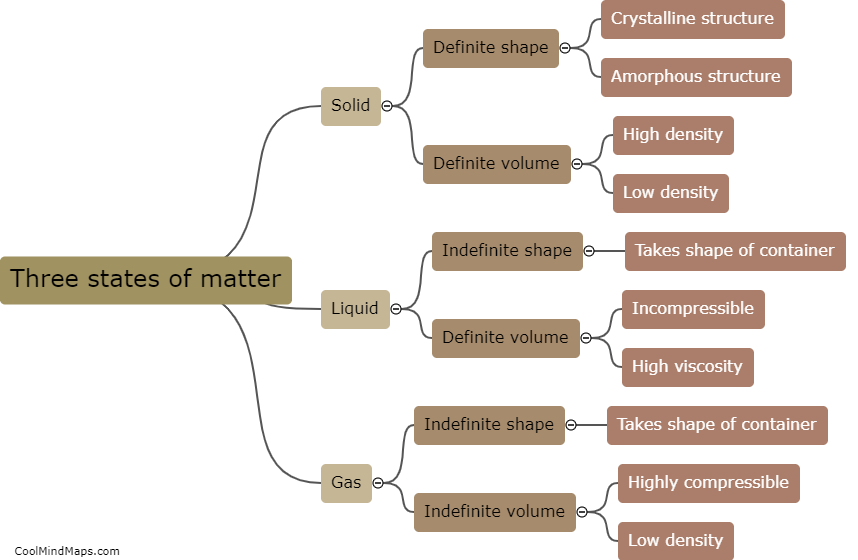
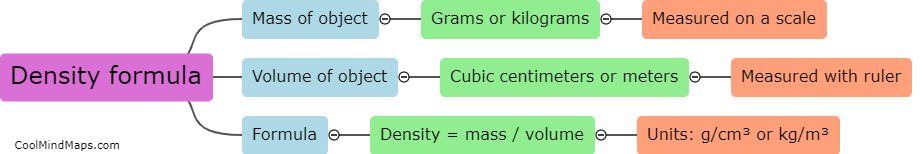
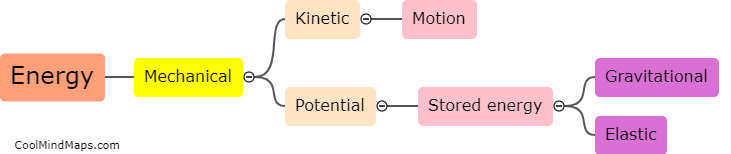
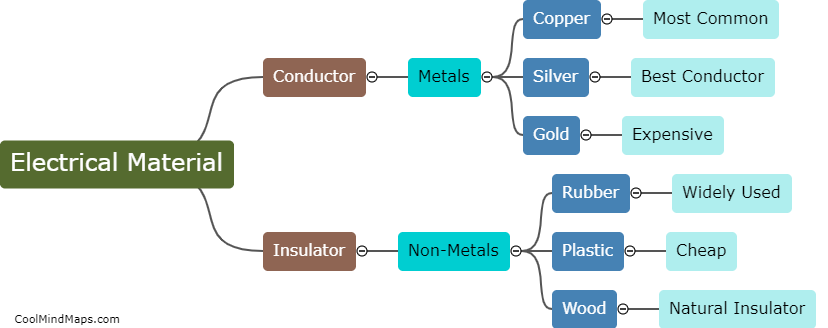
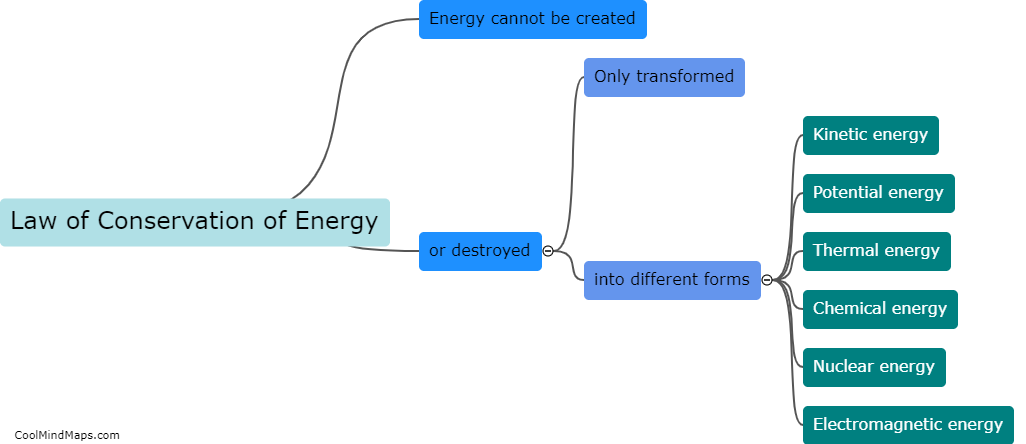
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant, though it may change forms. For example, when a ball is thrown into the air, it gains gravitational potential energy as it rises, but loses that same amount of energy as it falls back down. This law has important implications in our understanding of the physical world, and is used in everything from engineering to climate science.
This mind map was published on 18 April 2023 and has been viewed 96 times.