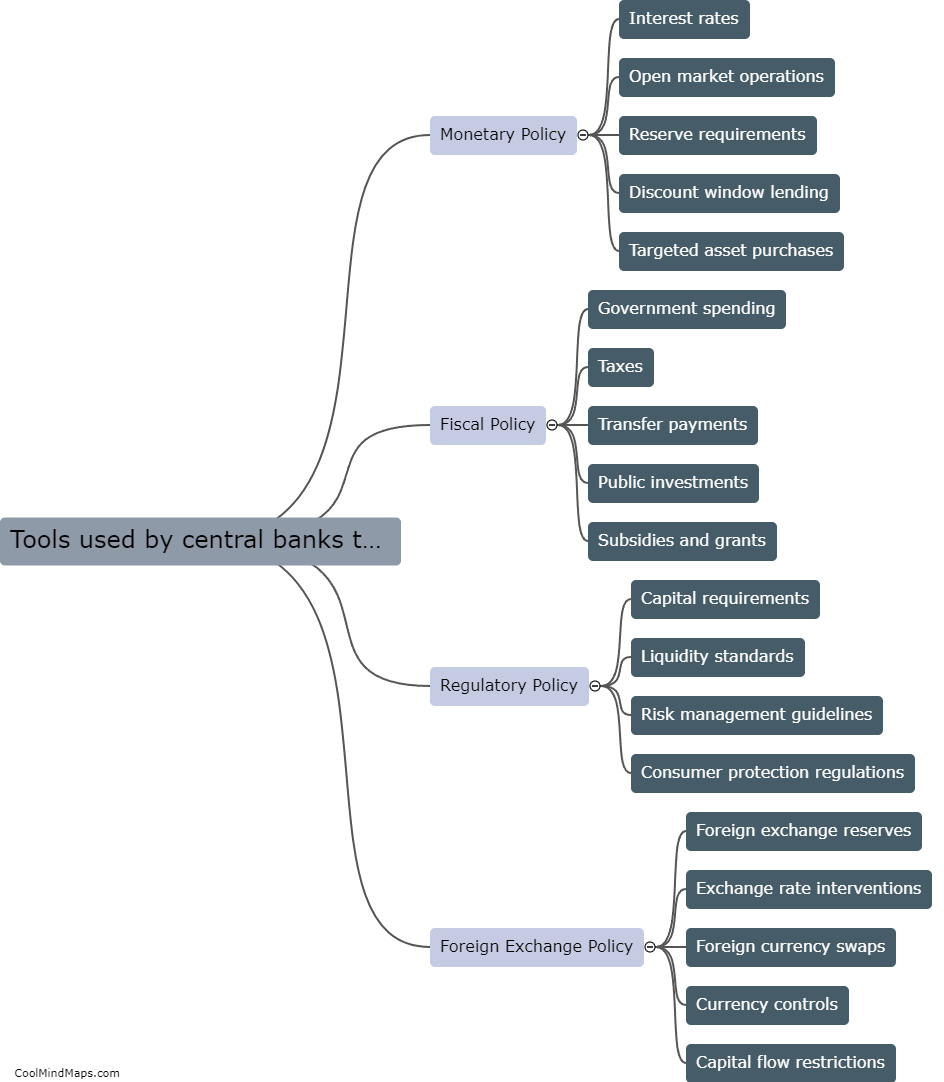
What is inflation?
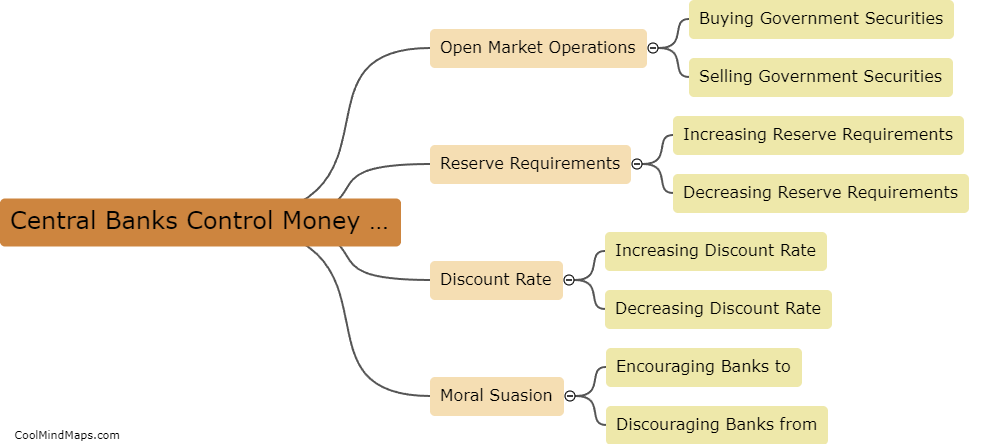
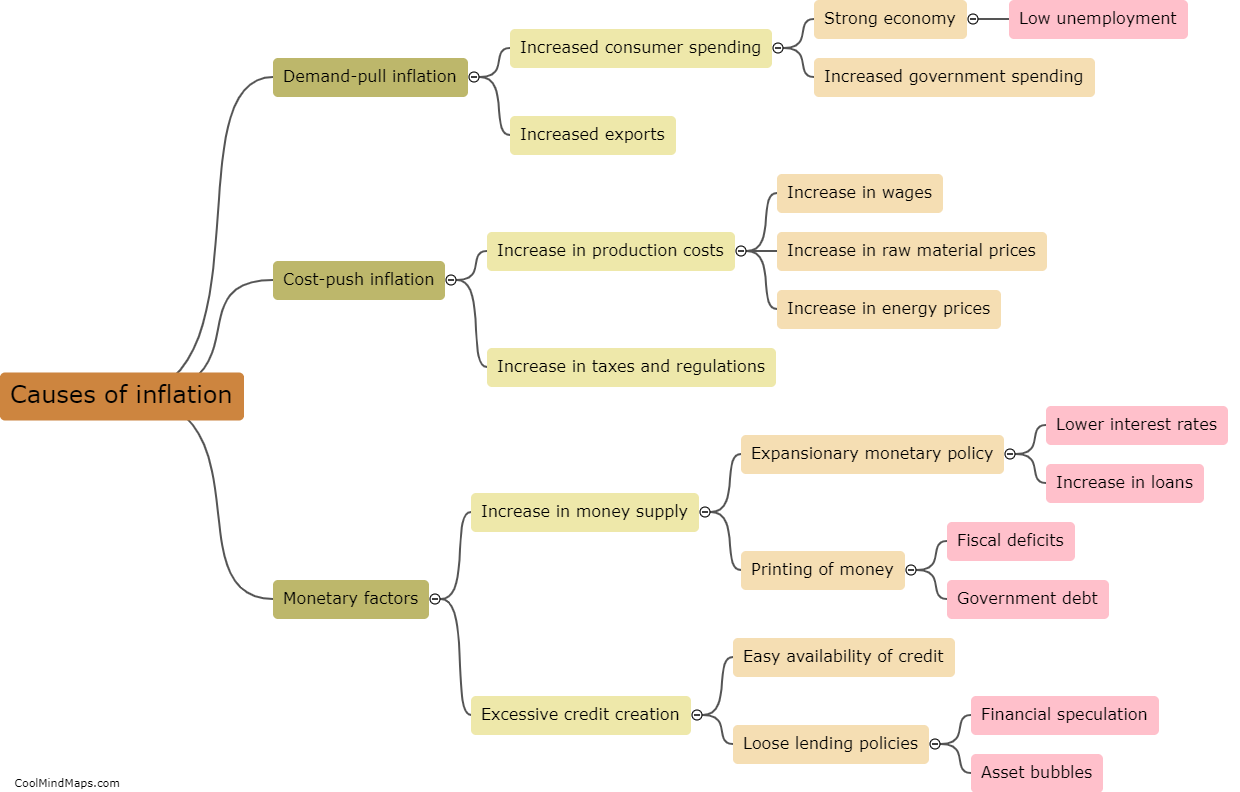
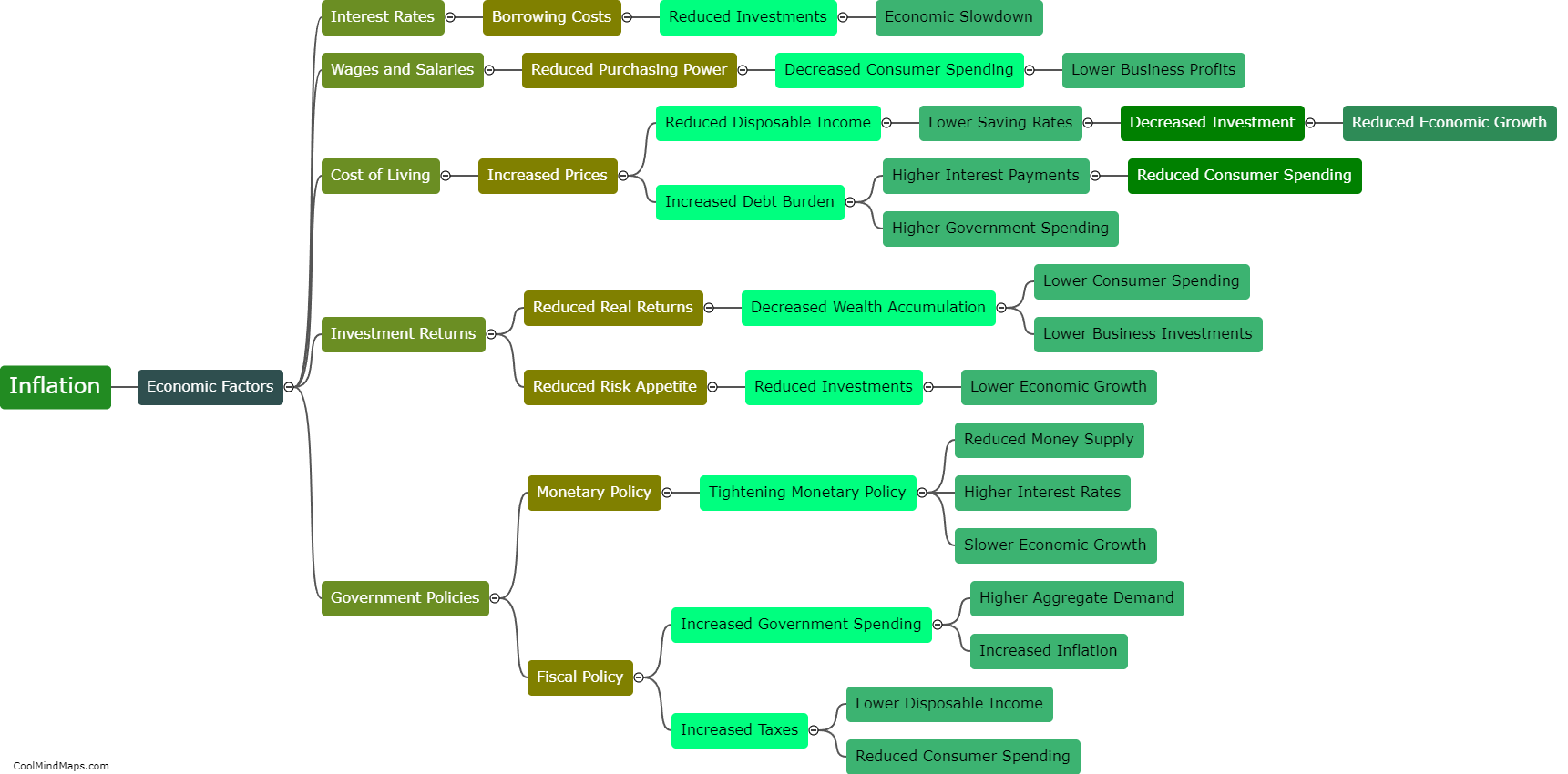
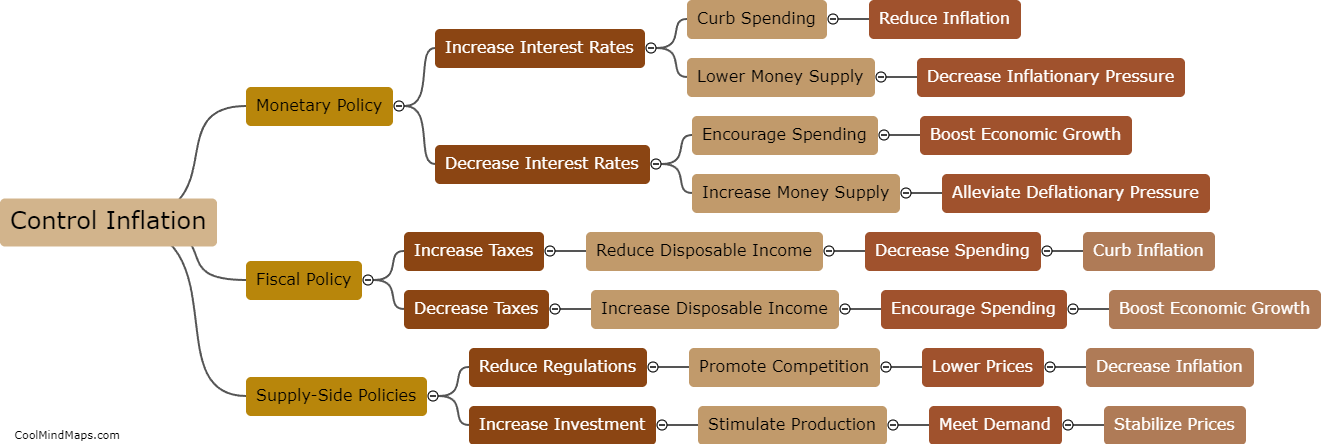
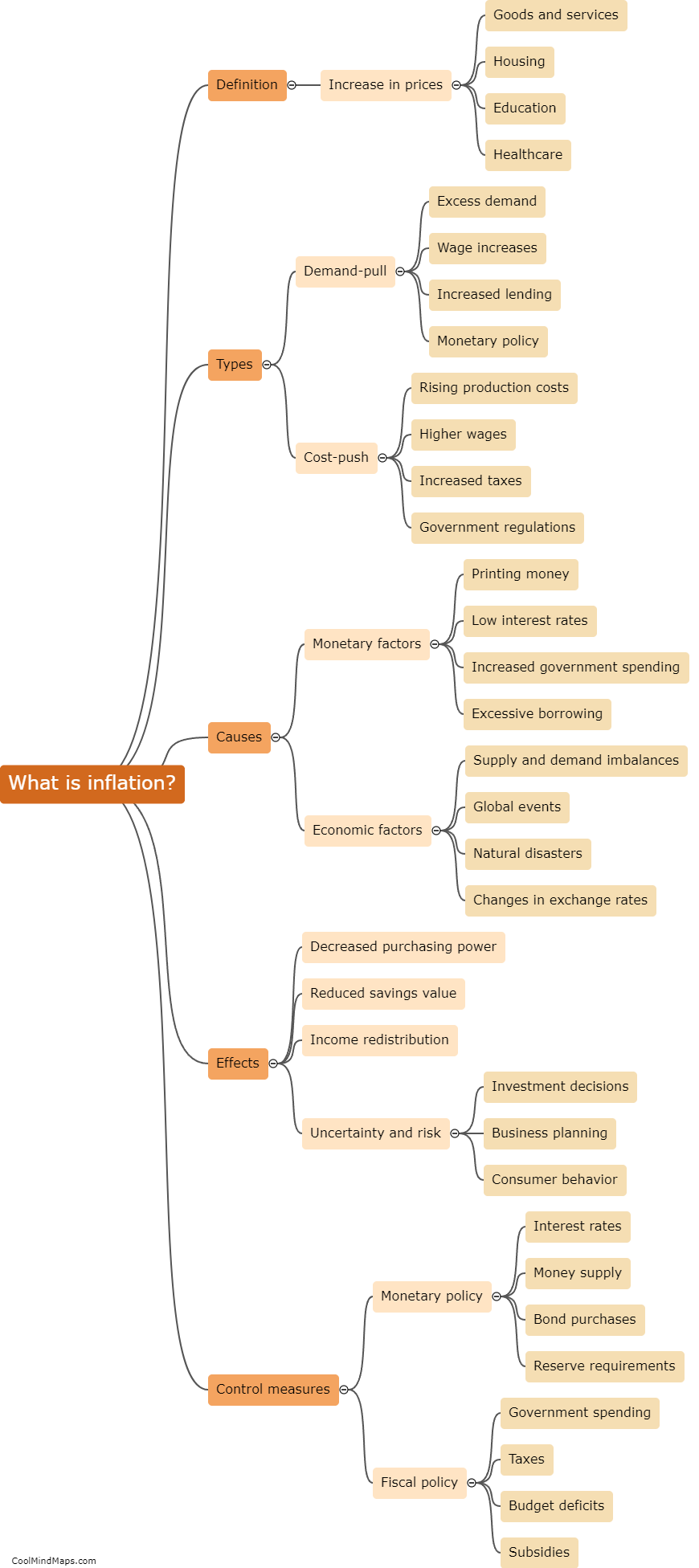
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general level of prices over a period of time. When inflation occurs, the purchasing power of money decreases, as each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. It is caused by a variety of factors, such as excessive growth in the money supply, rising costs of production, or increased demand for goods and services. The consequences of inflation can be both negative and positive. While a mild and controlled level of inflation can stimulate economic growth and encourage spending, high and unpredictable inflation rates can erode people's savings, disrupt the economy, and cause uncertainty and instability in financial markets. Central banks and governments often strive to maintain a stable and moderate inflation rate to foster economic stability and certainty.
This mind map was published on 19 September 2023 and has been viewed 119 times.