How site-directed mutagenesis methods work?
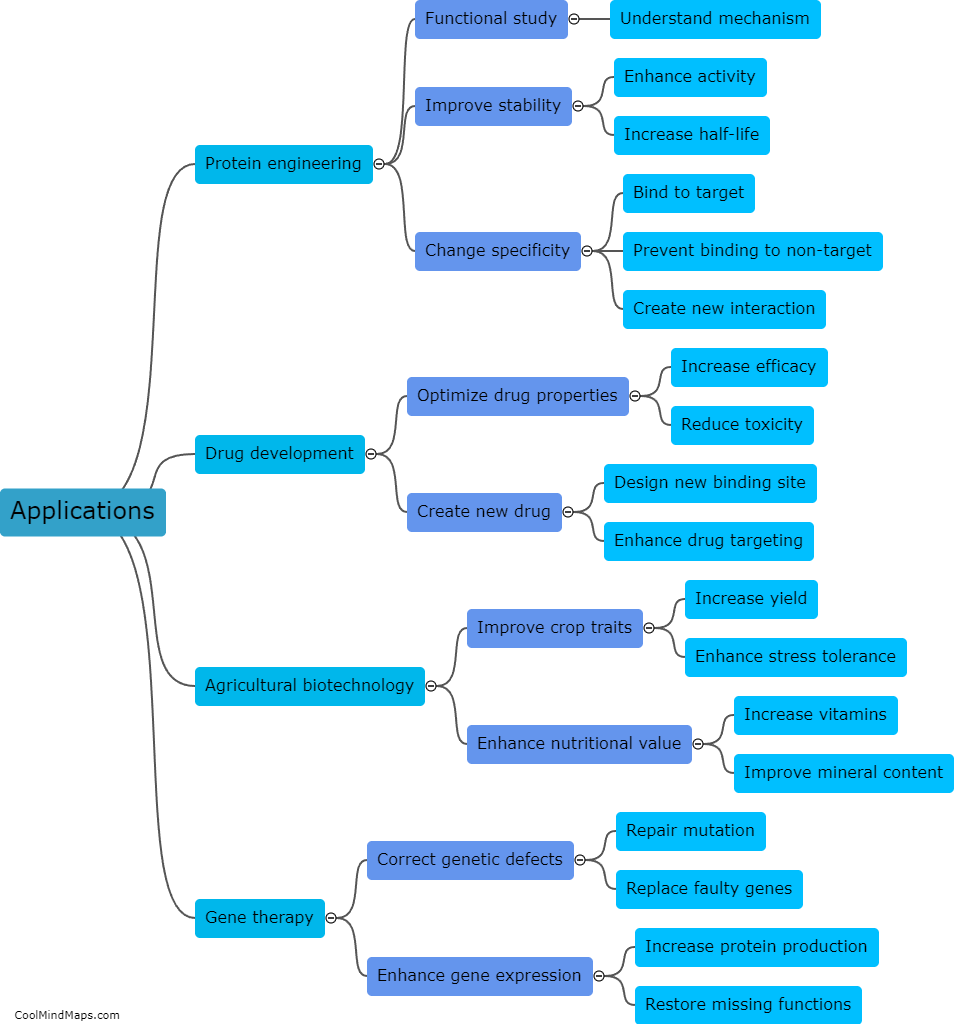
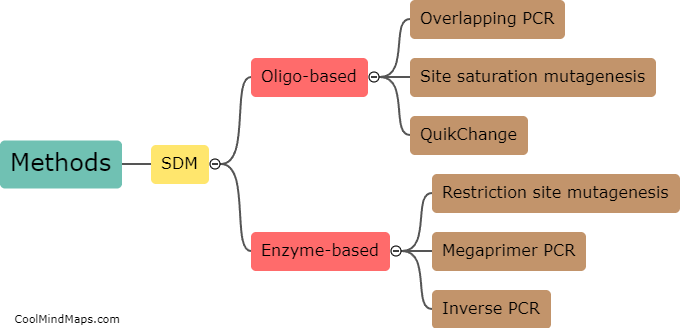
Site-directed mutagenesis methods are widely used in molecular biology research to introduce specific changes in a DNA sequence. These methods involve creating mutations in a target gene at desired locations, allowing scientists to investigate the functional consequences of specific alterations. The most common approach involves designing and synthesizing primers that carry the desired mutation(s) and then using these primers in a PCR reaction with the original DNA template. The resulting mutated DNA can then be inserted into a vector and expressed in a host organism. Other methods, such as oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis or CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing, provide alternative ways to introduce site-specific mutations. Ultimately, site-directed mutagenesis methods enable researchers to probe the structure-function relationship of proteins and understand the molecular basis of various biological processes.

This mind map was published on 19 November 2023 and has been viewed 108 times.