How is money supply measured?
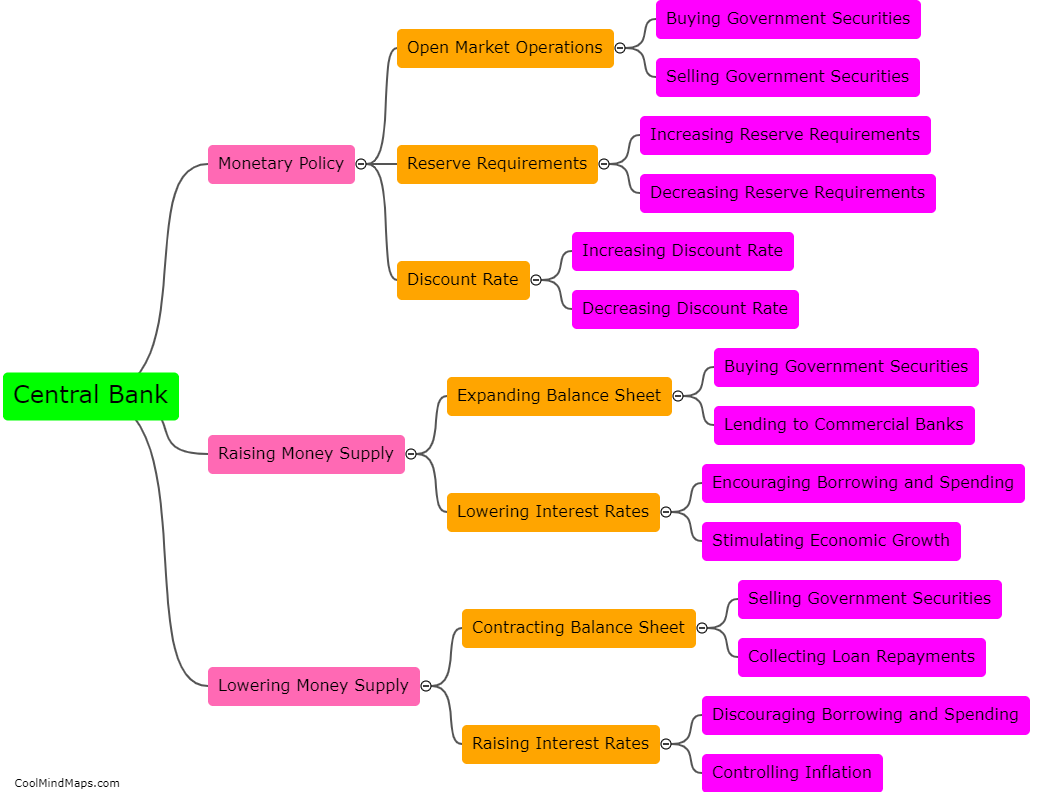
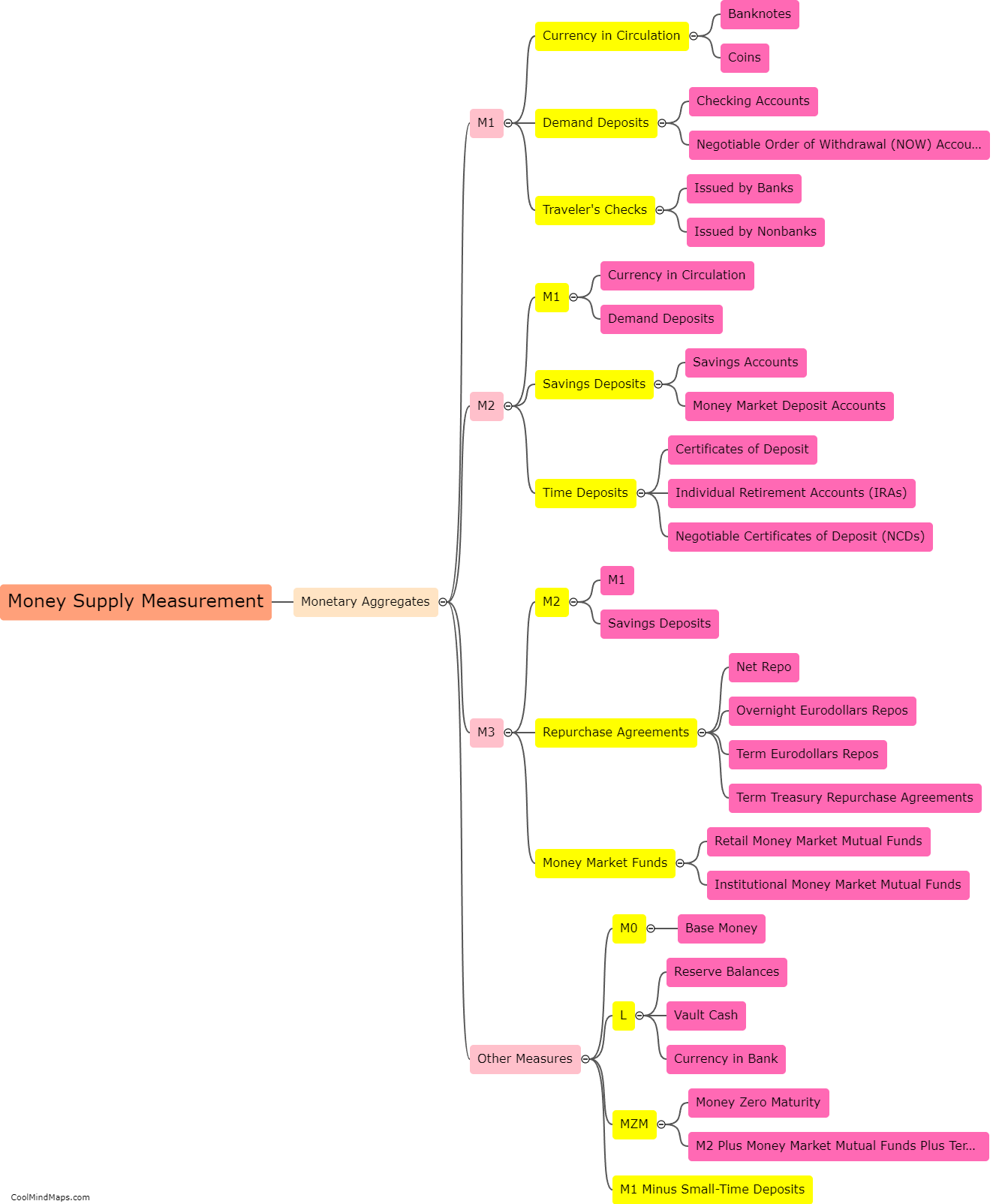
The measurement of money supply refers to the process of quantifying the total amount of money in circulation within an economy at a given time. Central banks and monetary authorities are responsible for tracking and monitoring the levels of money supply. They typically employ different monetary aggregates as indicators to measure the money supply. These aggregates encompass various forms of money, including physical currency, demand deposits, time deposits, and other liquid instruments that can be quickly converted into cash. The most common measures of money supply include M1, which represents the most liquid forms of money, and M2, which includes a broader range of financial assets. By monitoring and adjusting the money supply, central banks can influence economic growth, inflation, and monetary stability.
This mind map was published on 19 September 2023 and has been viewed 102 times.