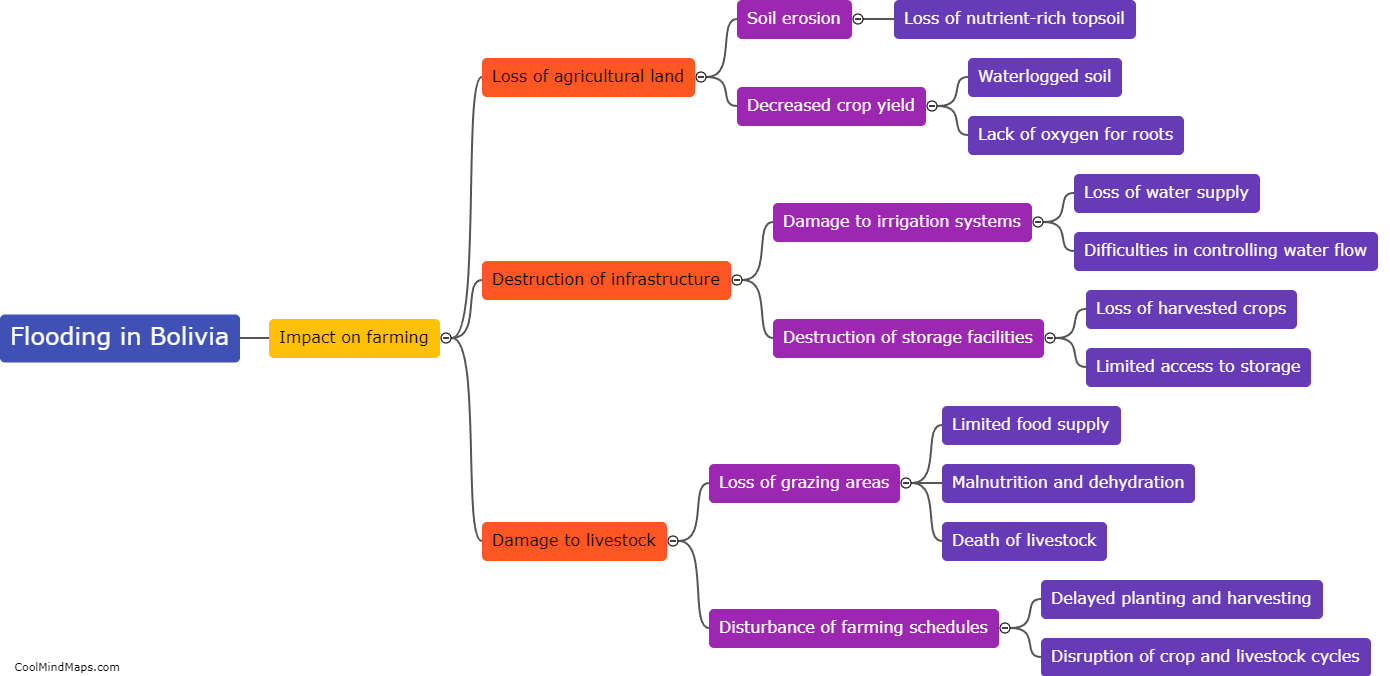
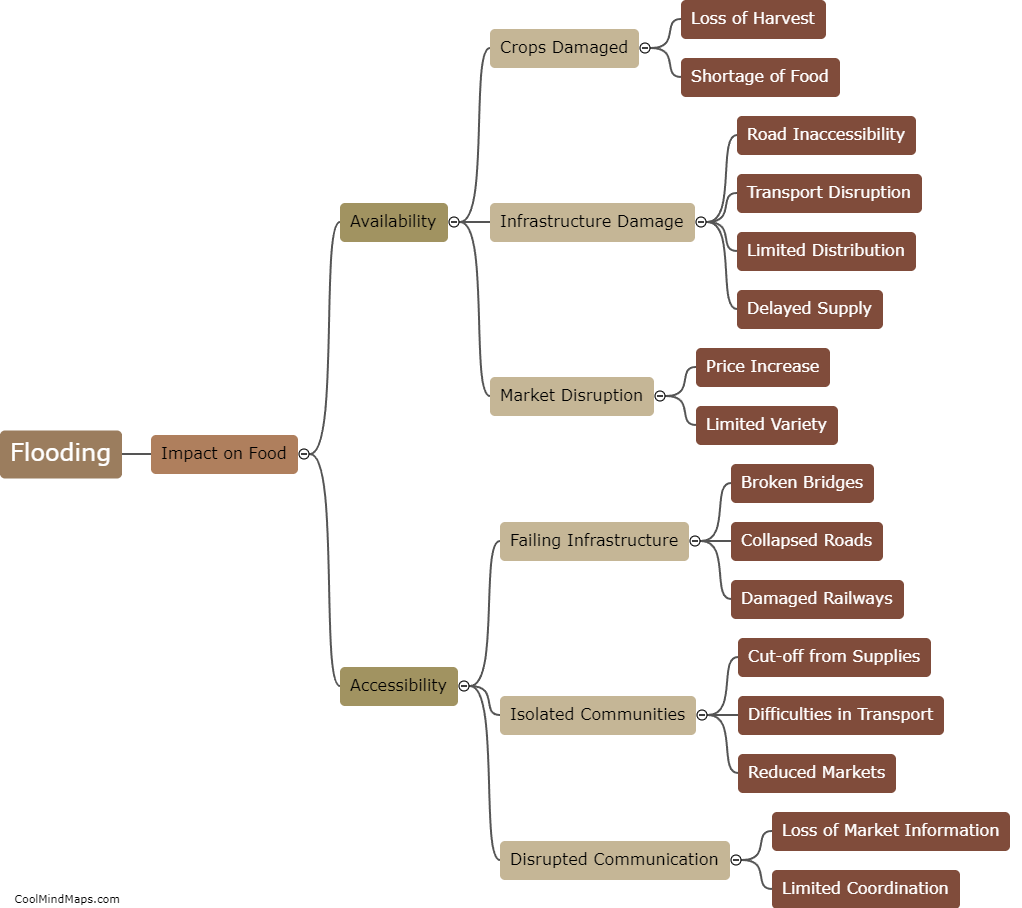
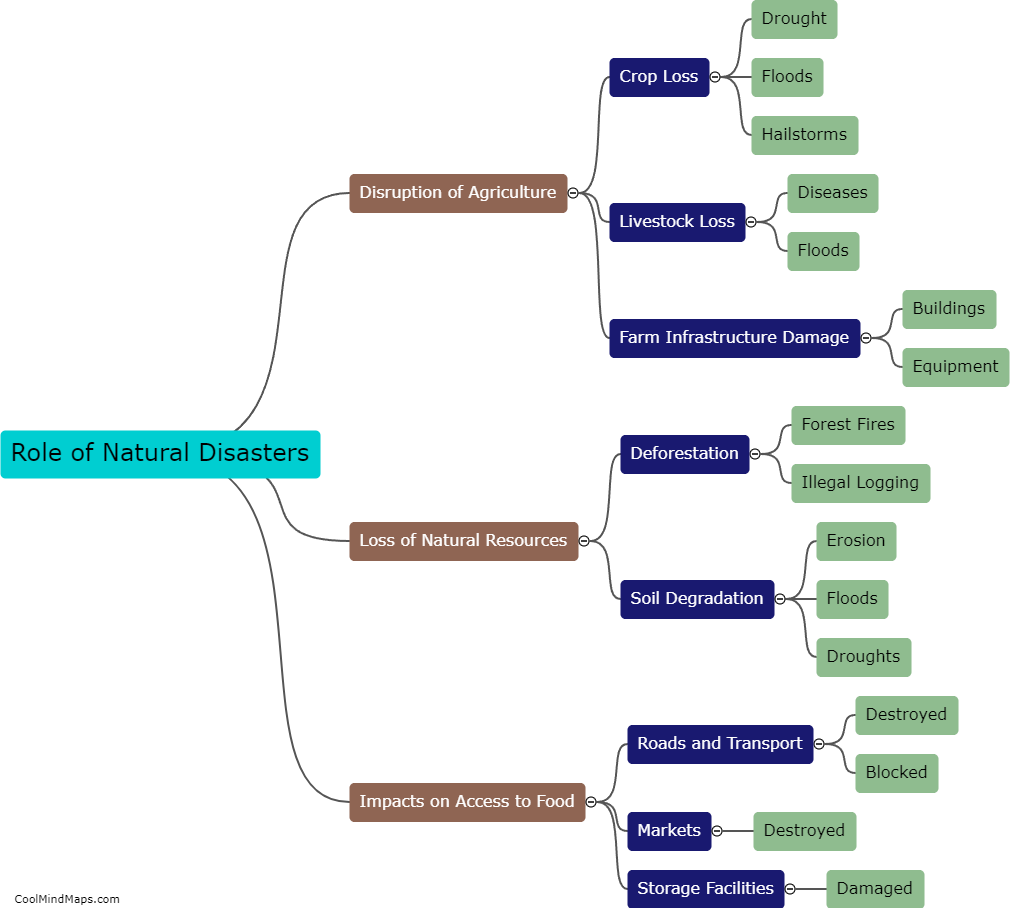
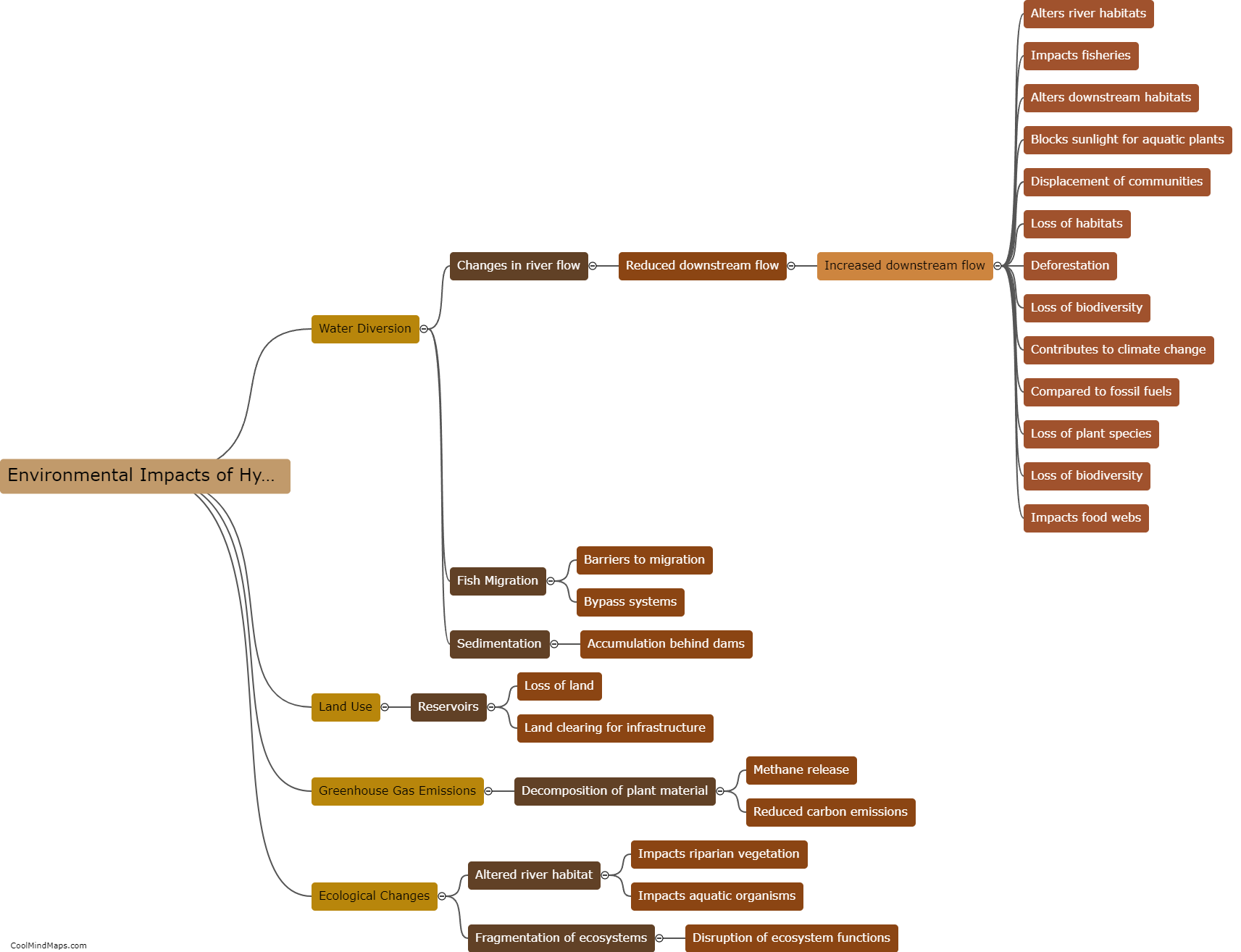
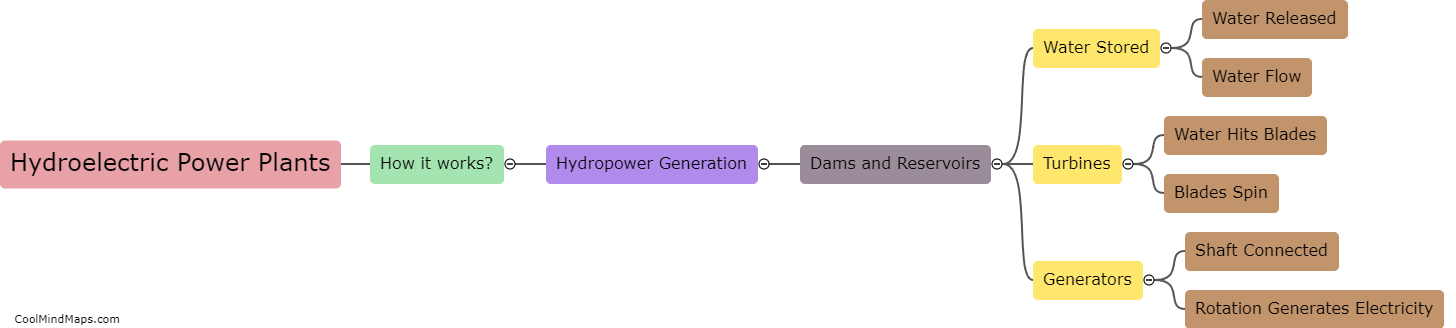
How do hydroelectric power plants work?
Hydroelectric power plants harness the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. The process begins by diverting a large amount of water from a river or dam using a dam or reservoir, creating a high water level or head. The stored water is then released, flowing through large pipes called penstocks, which channel the force of the water onto the turbines. The rotating turbines convert the kinetic energy of the flowing water into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is then further transformed into electrical energy by spinning electromagnets within a generator, creating an alternating current. This electrical current is transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries for consumption. Hydroelectric power plants are a sustainable and renewable energy source that operate with minimal greenhouse gas emissions and provide a reliable and clean source of electricity.
This mind map was published on 10 September 2023 and has been viewed 96 times.