What are the legal consequences for each degree of murder?
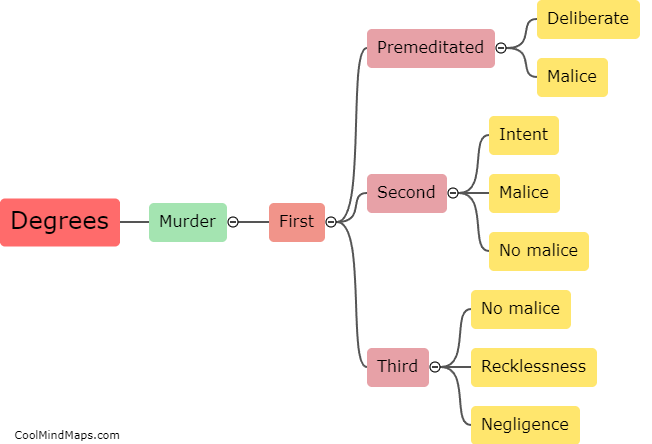
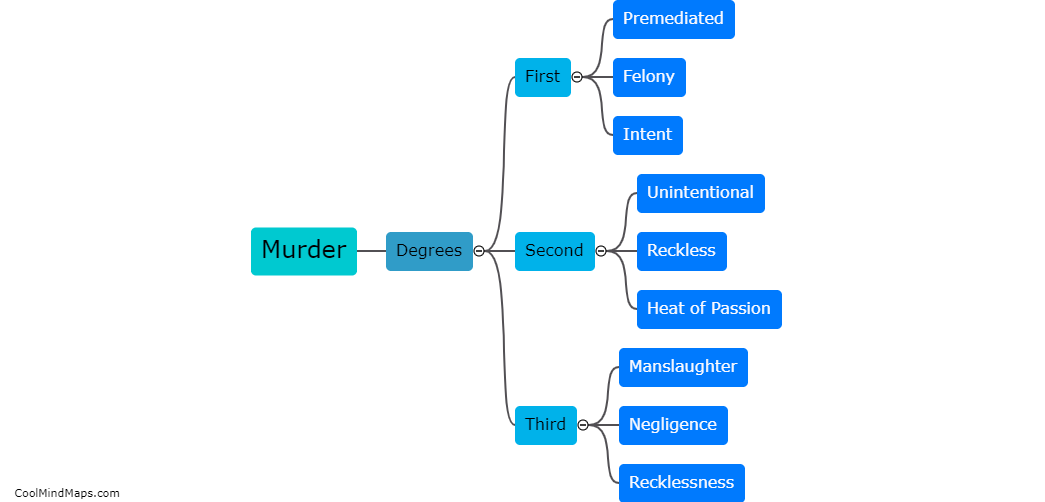
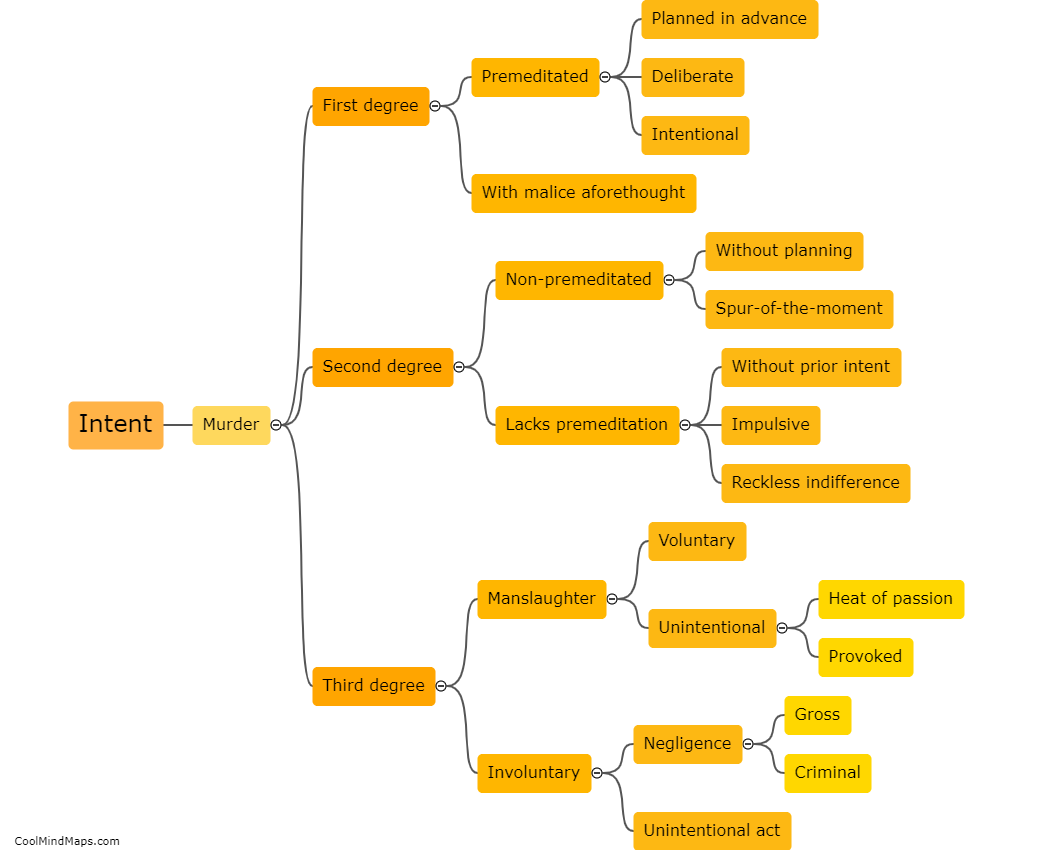
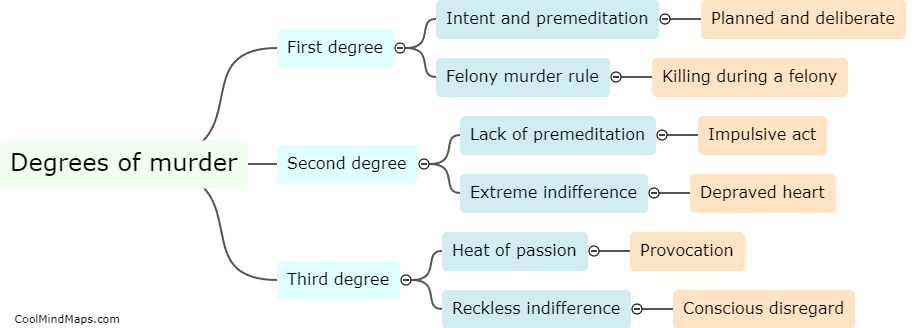
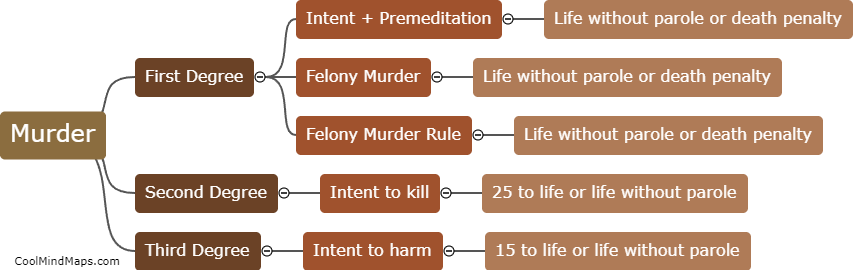
The legal consequences for each degree of murder vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances surrounding the crime. In general, first-degree murder is the most serious offense and typically involves premeditation and intent to cause the victim's death. Penalties for first-degree murder often include lengthy prison sentences, life imprisonment, or in some cases, the death penalty. Second-degree murder is generally defined as intentionally causing the death of another person without premeditation. The punishment for this offense is usually less severe than for first-degree murder but still carries substantial prison sentences. Manslaughter, a lesser offense, typically involves killing someone without malice aforethought, either as a result of recklessness or in the heat of passion. The consequences for manslaughter are generally less severe than for murder, but individuals may still face imprisonment or other criminal penalties. It is important to note that these consequences can vary significantly based on the jurisdiction and the specific laws in place.
This mind map was published on 19 December 2023 and has been viewed 126 times.