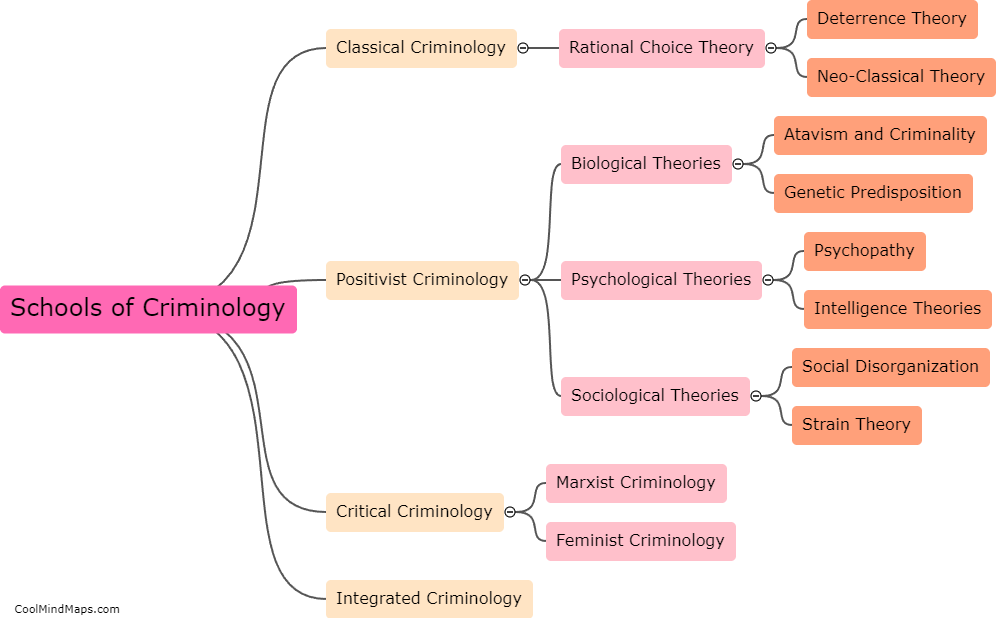
What are the main criminological schools?
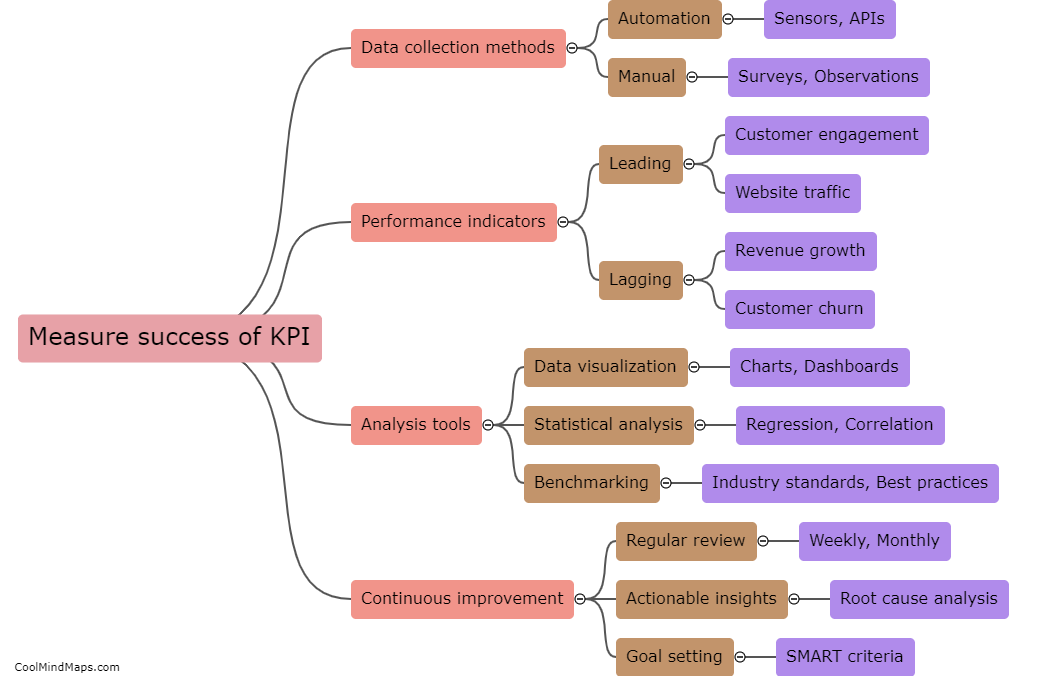
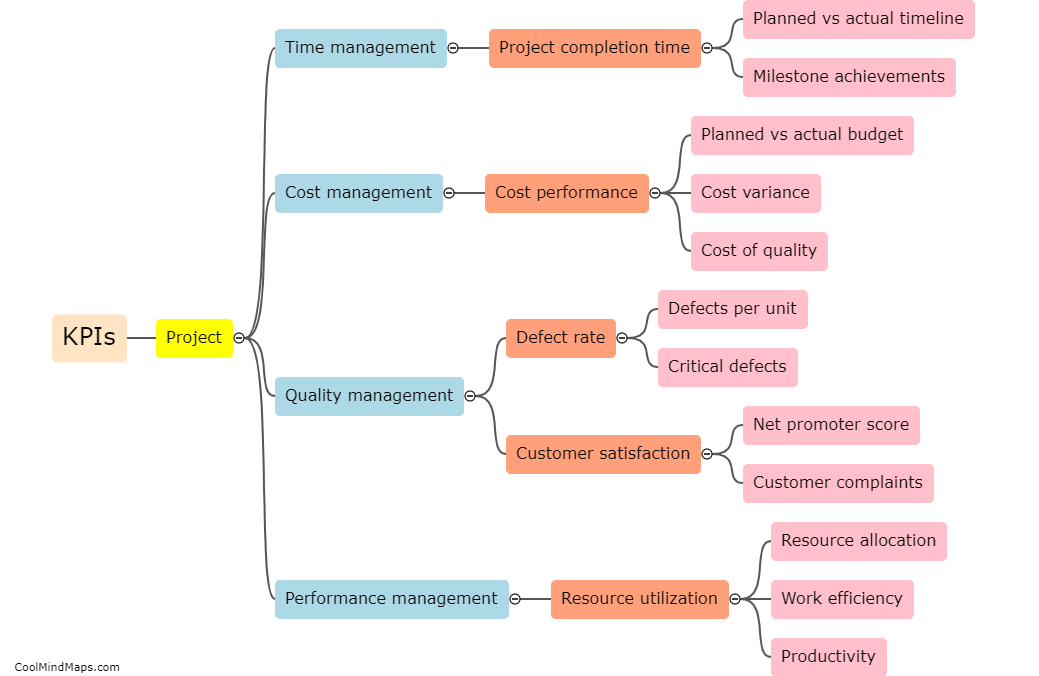
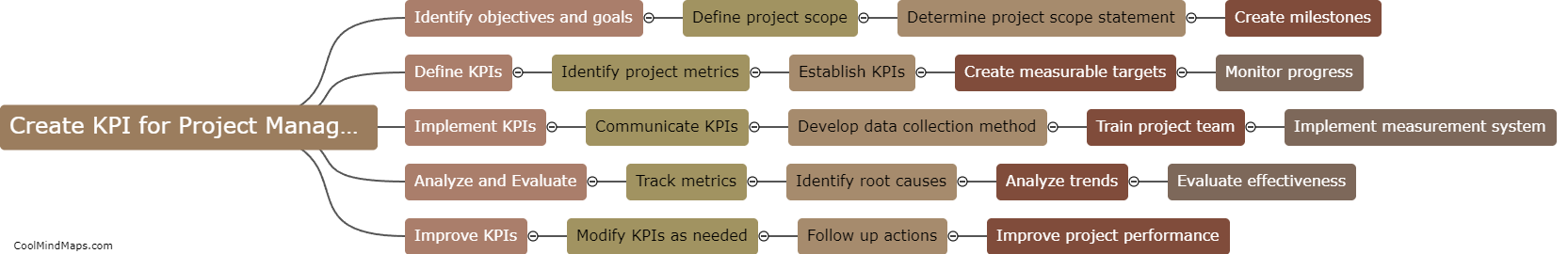
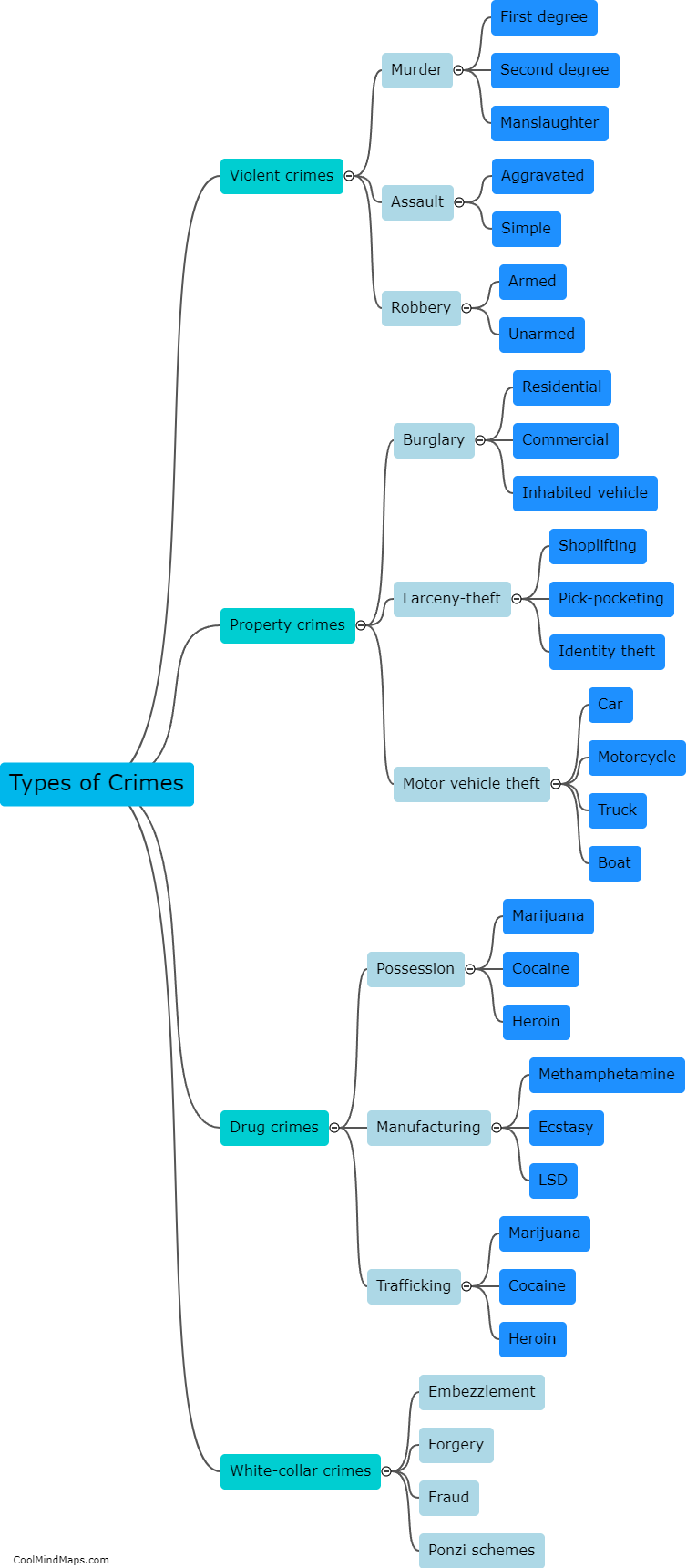
The main criminological schools refer to the different theoretical perspectives and approaches used to explain why people engage in criminal behavior. These schools include classical, positivist, strain, social learning, control, labeling, and critical criminology. Classical criminology emphasizes the importance of free will and rational decision-making in criminal behavior, while positivist criminology focuses on understanding the biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to criminal behavior. Strain theory argues that crime results from a lack of access to legitimate means of achieving societal goals, and social learning theory underscores the importance of socialization experiences in shaping criminal behavior. Control theory posits that crime is the result of weakened social bonds, while labeling theory contends that criminal behavior arises from societal reactions to the person, rather than the behavior itself. Finally, critical criminology challenges the assumptions underlying the other schools and critiques the broader social structures and institutions that perpetuate inequality and injustice.
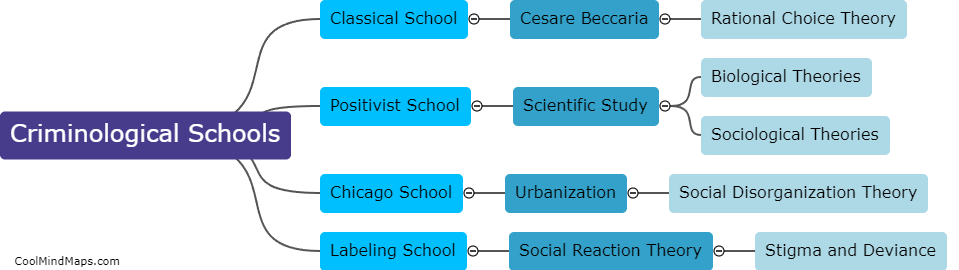
This mind map was published on 8 June 2023 and has been viewed 186 times.