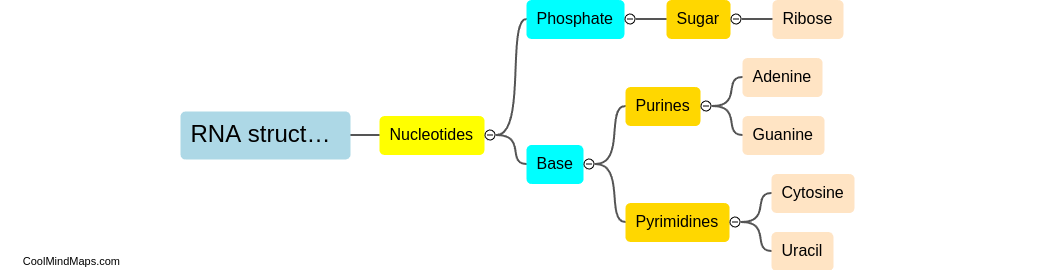
What is the structure of RNA?
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a single-stranded nucleic acid that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and gene expression. The structure of RNA is similar to DNA, with the main differences being that RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose sugar and uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) as one of its nitrogenous bases. RNA is made up of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U), and these bases are linked together by phosphate groups to form a single strand. RNA can form various secondary structures, including hairpin loops, stem-loop structures, and pseudoknots, which play important roles in its function and regulation.
This mind map was published on 29 April 2024 and has been viewed 102 times.