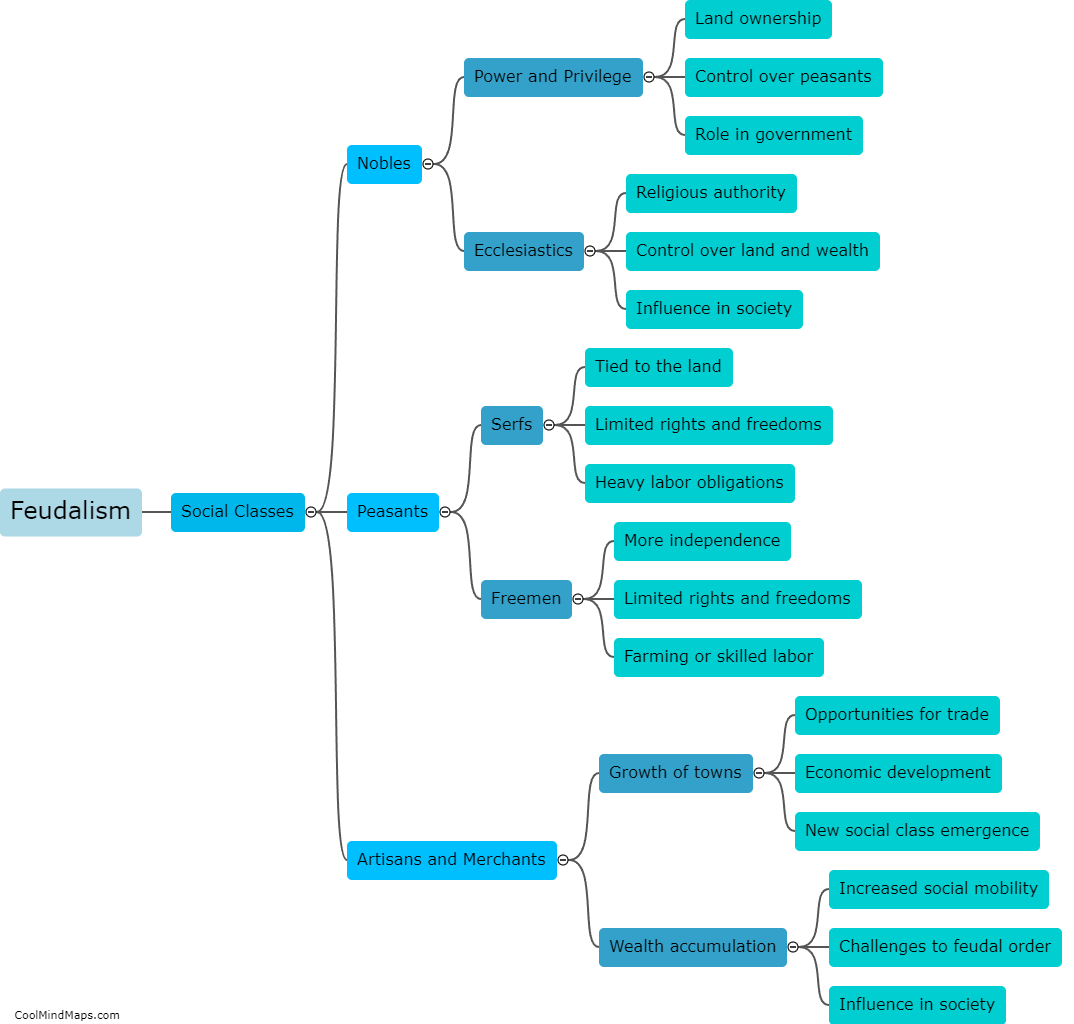
What are the key characteristics of feudalism?
Feudalism was a social, economic, and political system that dominated medieval Europe during the Middle Ages. Its key characteristics can be summarized as follows. Firstly, feudalism was based on a hierarchy of obligations and relationships between lords and vassals. Lords granted land, known as fiefs, to vassals in exchange for loyalty, military service, and financial payments. This relationship formed the basis of the feudal contract. Secondly, feudalism was decentralized with power and authority being dispersed among numerous lords who held control over their territories. This resulted in a fragmented political structure, making the central authority weak and ineffective. Thirdly, the economic system of feudalism was primarily agricultural. Serfs, who were legally tied to the land, worked for the lord in exchange for protection and a small piece of land to cultivate for themselves. Lastly, feudalism was a rigid social system where social mobility was limited. The society was divided into different classes, including the nobility, clergy, and peasantry, with individuals' social status being determined by birthright rather than individual merit. Overall, feudalism was characterized by its hierarchical structure, decentralized power, agrarian economy, and lack of social mobility.

This mind map was published on 1 August 2023 and has been viewed 115 times.