How does Avogadro's Law relate to the volume and number of gas particles?
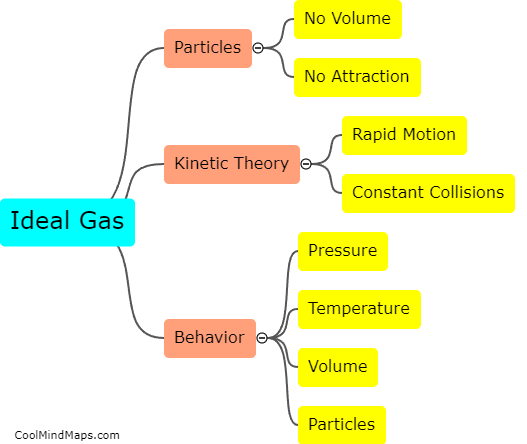
Avogadro's Law, also known as Avogadro's hypothesis, states that equal volumes of different gases at the same temperature and pressure contain an equal number of particles. This law, formulated by Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro in the 19th century, establishes a direct relationship between the volume of a gas and the number of gas particles. In other words, as the number of gas particles increases, the volume occupied by the gas also increases proportionally, assuming constant temperature and pressure. This means that when comparing two gases, the volume of each gas will be directly proportional to the number of particles it contains. Therefore, if the number of gas particles doubles, the volume of the gas will also double, and vice versa. Avogadro's Law forms a fundamental concept in understanding the behavior of gases and is crucial in various applications of gas chemistry.

This mind map was published on 30 October 2023 and has been viewed 130 times.