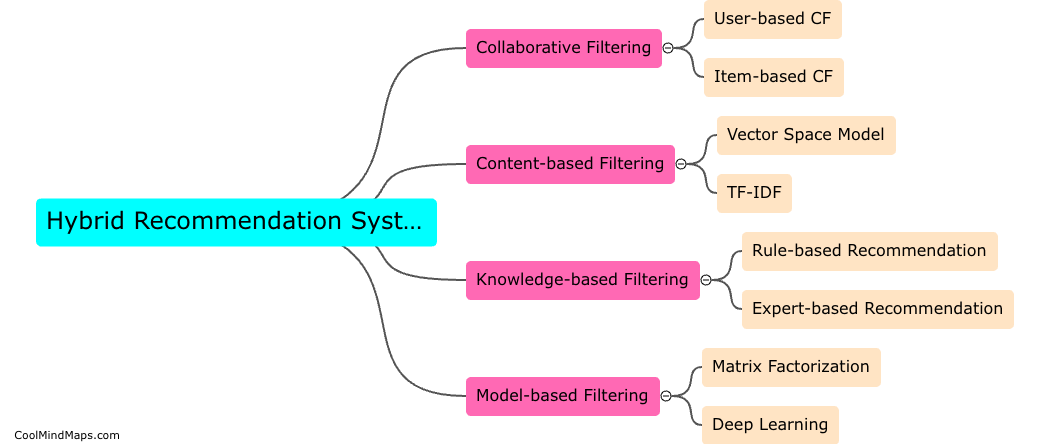
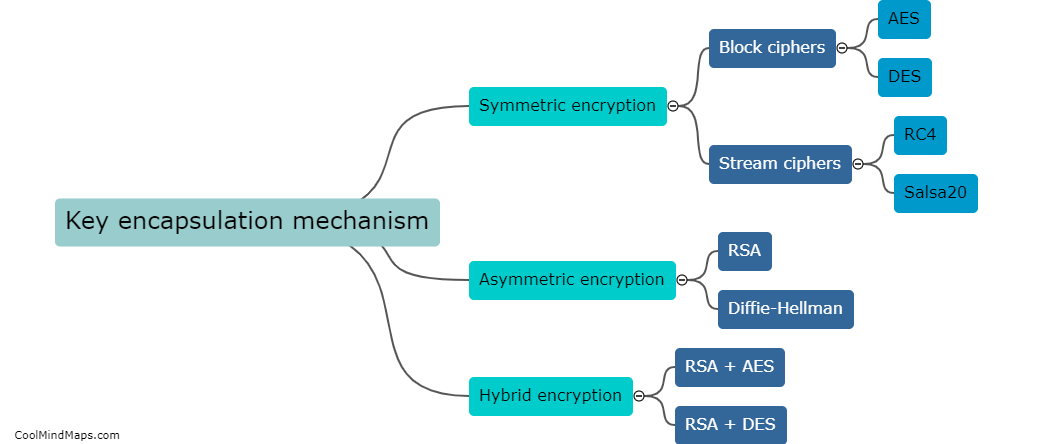
What is a key encapsulation mechanism?
A key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) is a cryptographic technique used to securely exchange and distribute encryption keys in a public-key encryption system. It involves encapsulating the session key used for encryption into a data structure called a "key encapsulation message." This message is then transmitted to the intended recipient, who possesses the corresponding private key to retrieve the encapsulated session key. The KEM ensures that only the authorized recipient can extract the session key, thereby ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the key exchange process. KEM is widely employed in various applications such as secure communication protocols, digital signatures, and secure key distribution.
This mind map was published on 4 February 2024 and has been viewed 143 times.