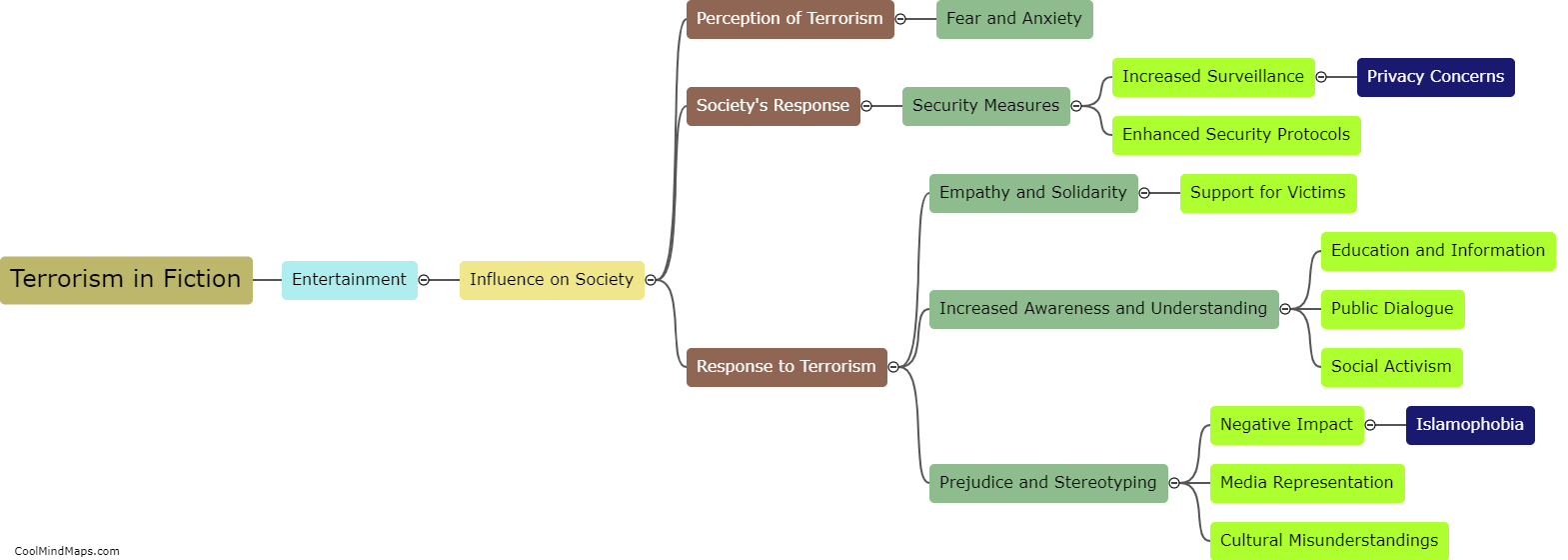
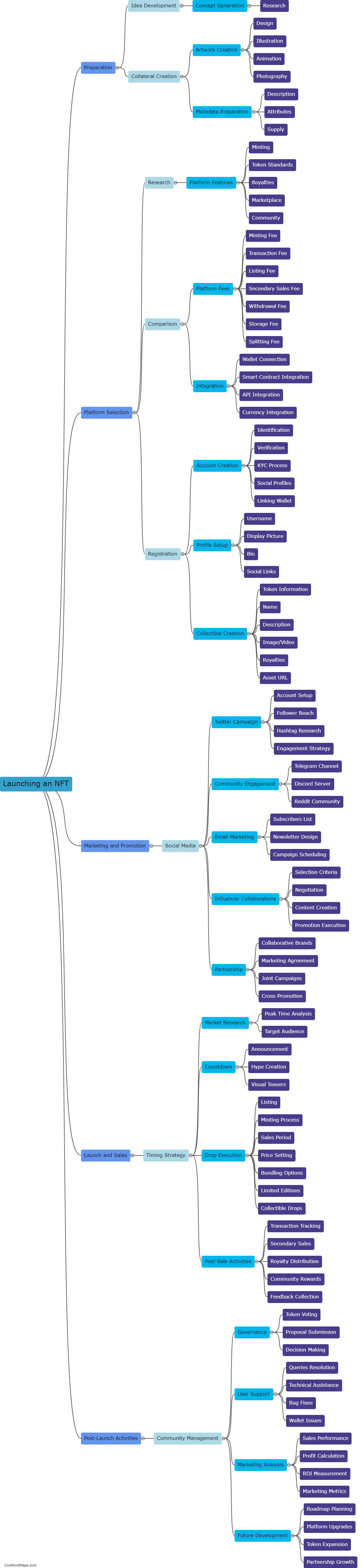
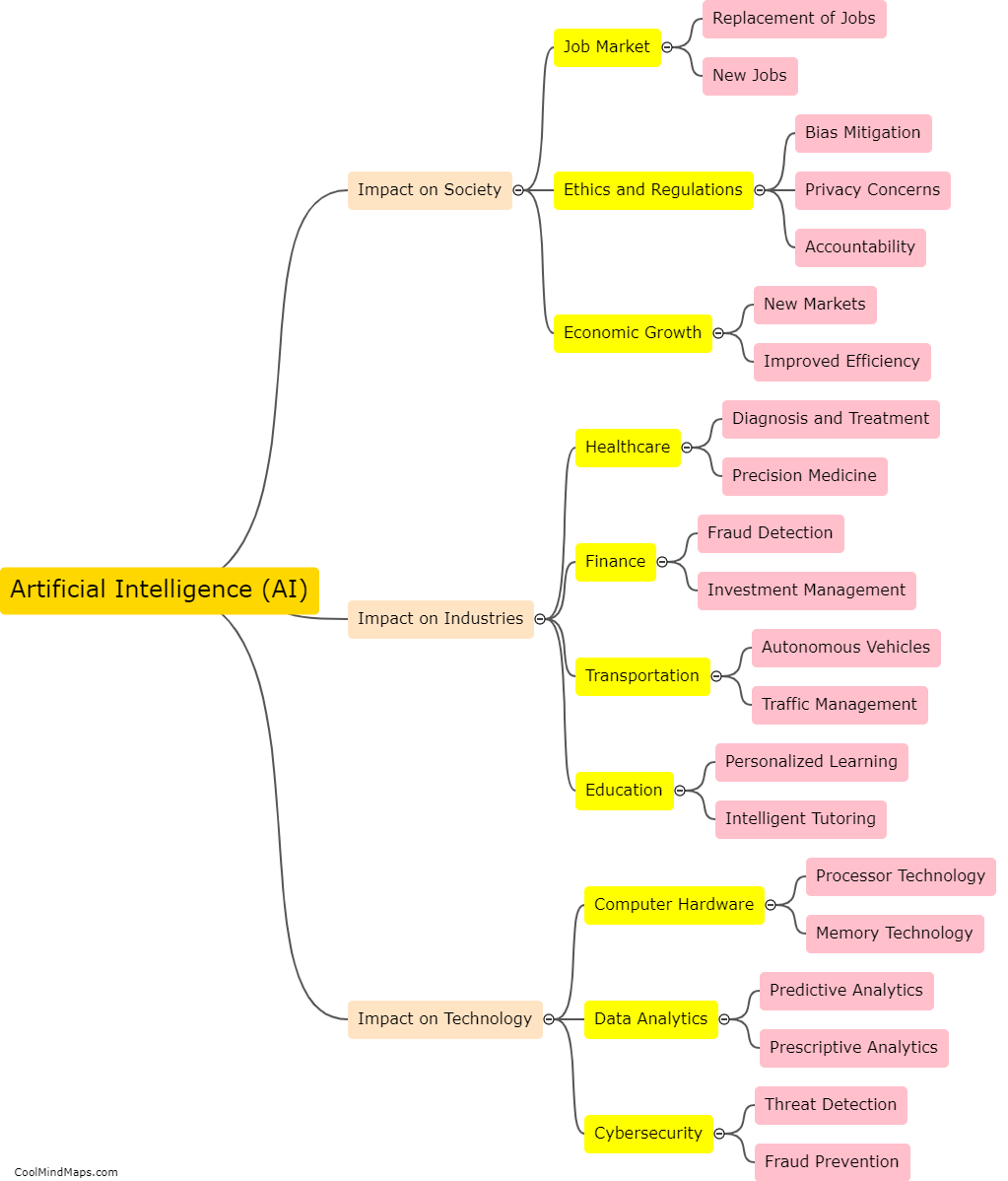
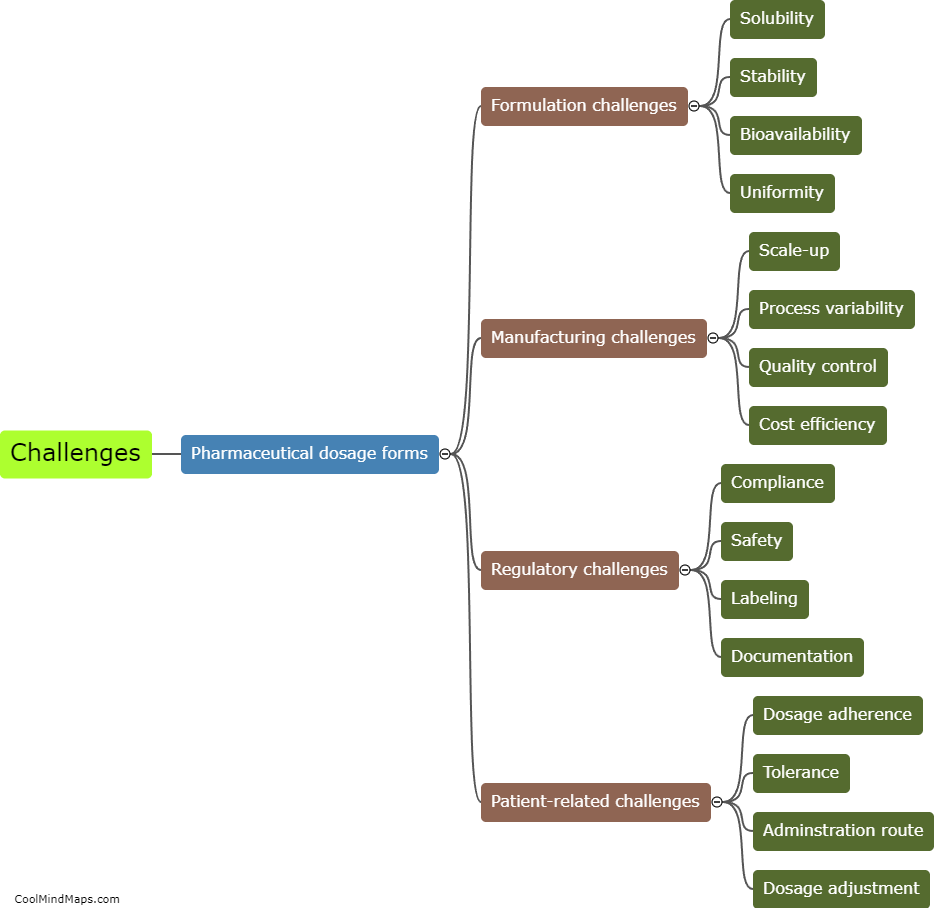
What are the similarities and differences in Locke and Hobbes' theories of human nature?
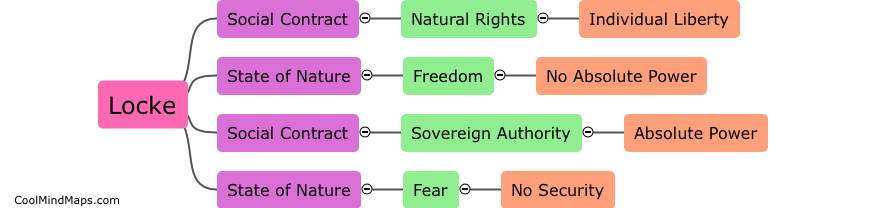
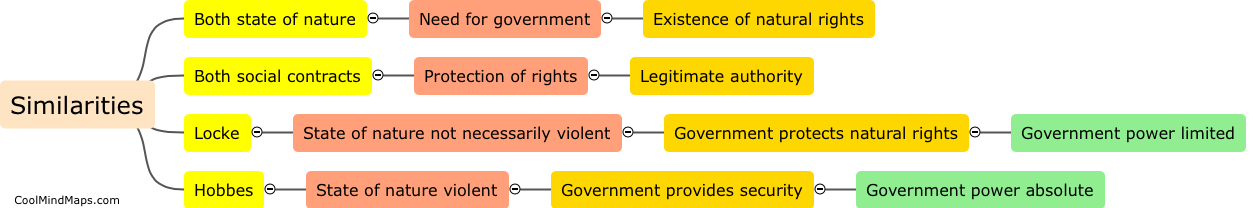
John Locke and Thomas Hobbes, two influential political philosophers of the 17th century, had contrasting views on human nature. Both philosophers recognized that humans possess certain rights and liberties, but their understanding and emphasis on these rights differ. Locke believed that humans are born with inherent natural rights including life, liberty, and property, and that the purpose of government is to protect these rights. In contrast, Hobbes viewed human nature as inherently selfish and driven by a desire for power and self-preservation. According to Hobbes, humans enter into a social contract to establish a strong government to maintain order and prevent chaos. While both Locke and Hobbes acknowledged the importance of government, their theories diverged in their understanding of human nature, with Locke emphasizing individual rights and liberties, and Hobbes emphasizing the need for a strong central authority to ensure peace and stability.
This mind map was published on 8 November 2023 and has been viewed 98 times.