What was the Gregorian Reform?
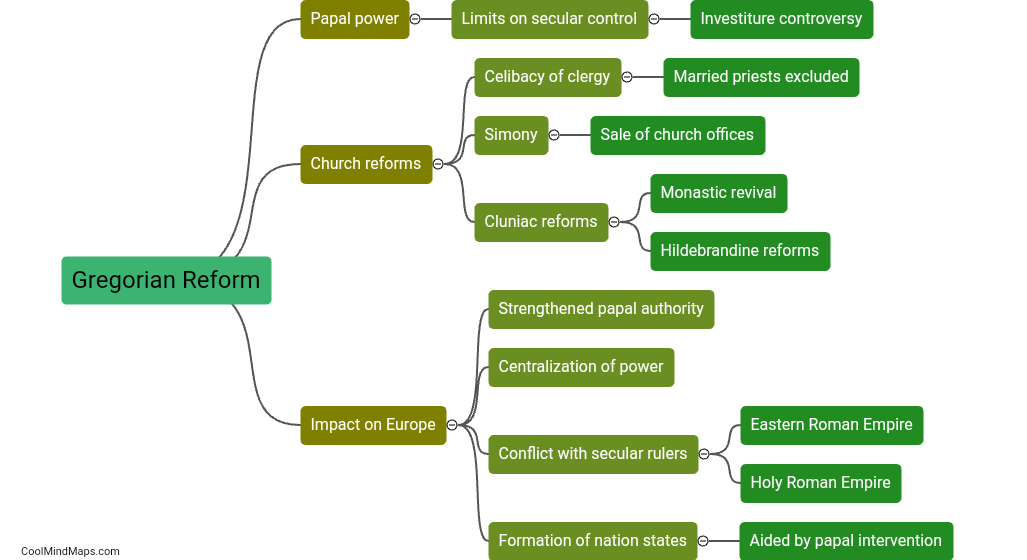
The Gregorian Reform refers to a series of initiatives launched by Pope Gregory VII in the late 11th century to cleanse and reform the Catholic Church. The primary aim of the reform was to assert papal authority, establish the independence of the Church from secular power, and tackle issues of corruption and immorality among the clergy. It sought to address simony (the buying and selling of ecclesiastical positions), lay investiture (the practice of secular rulers appointing bishops and abbots), and celibacy requirements for priests. The Gregorian Reform had significant political implications, as it challenged the authority of secular rulers and sparked conflicts between the papacy and various European monarchs. Despite facing opposition, the reform movement ultimately laid the groundwork for a more centralized and powerful papacy in the Middle Ages.
This mind map was published on 26 November 2023 and has been viewed 118 times.