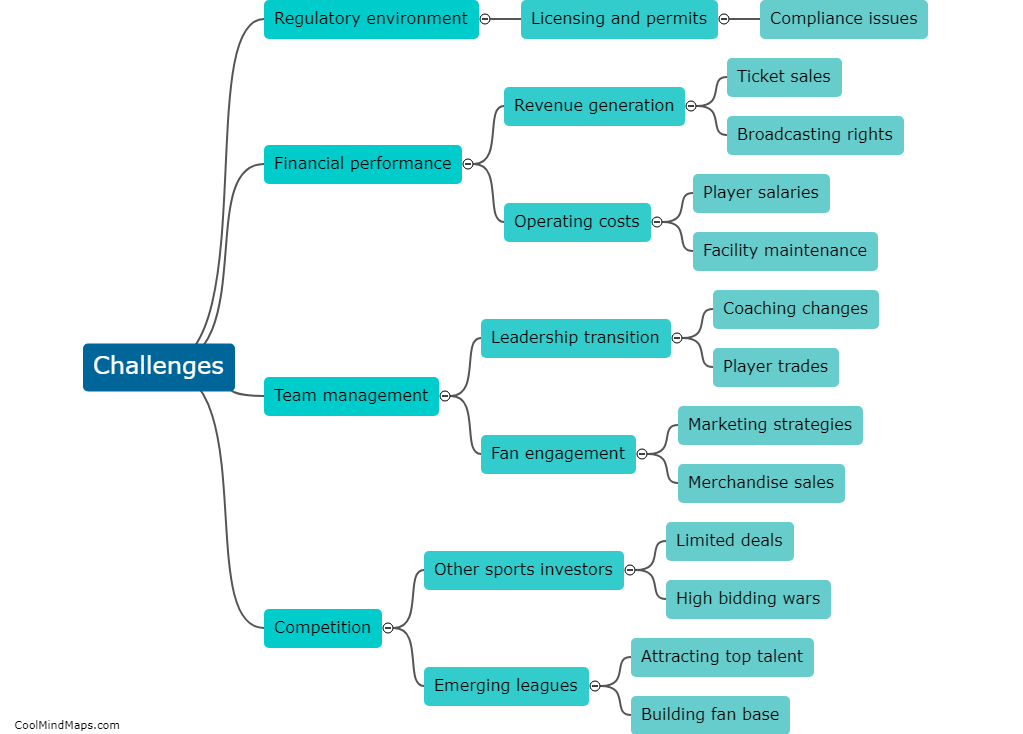
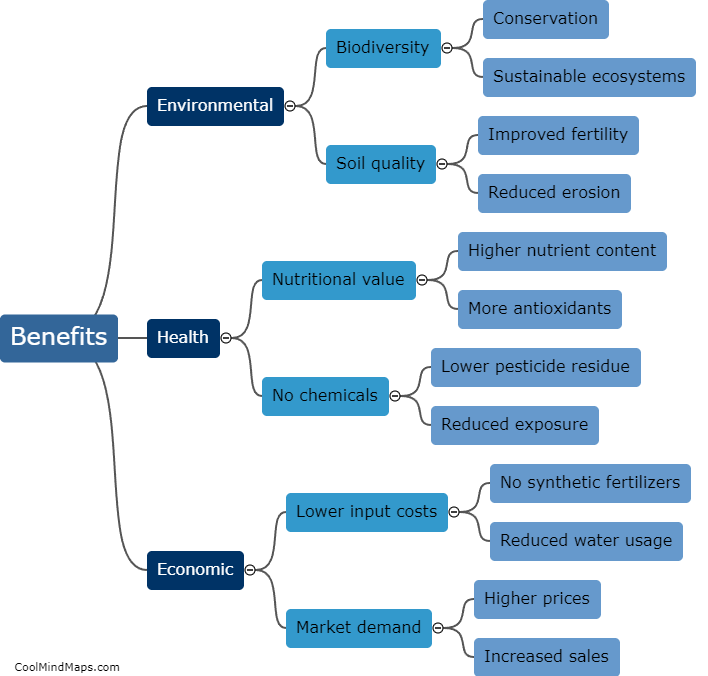
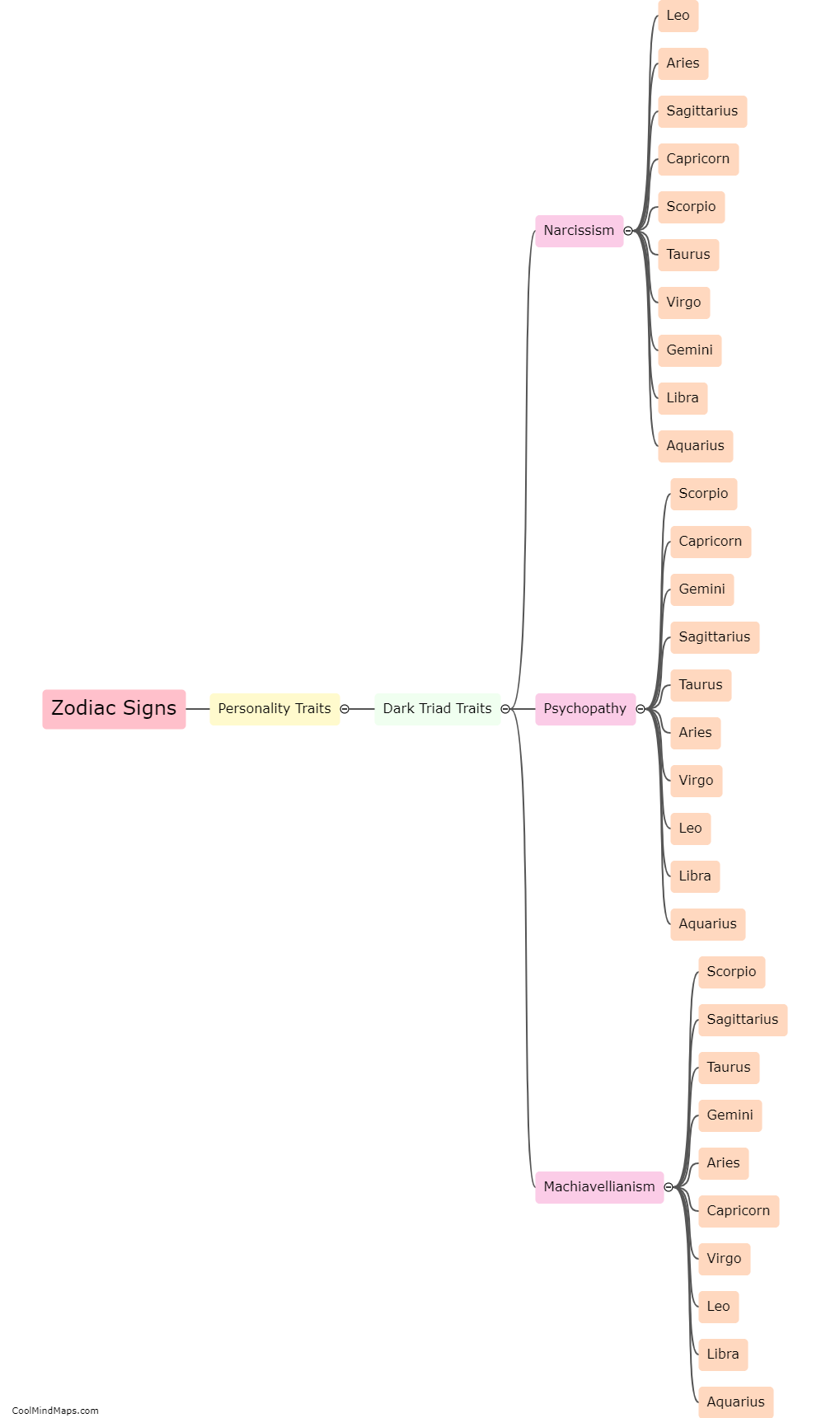
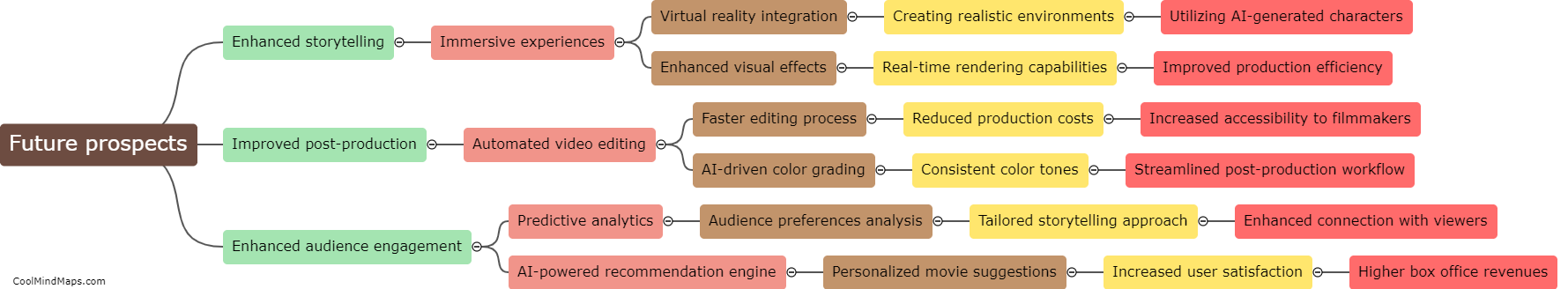
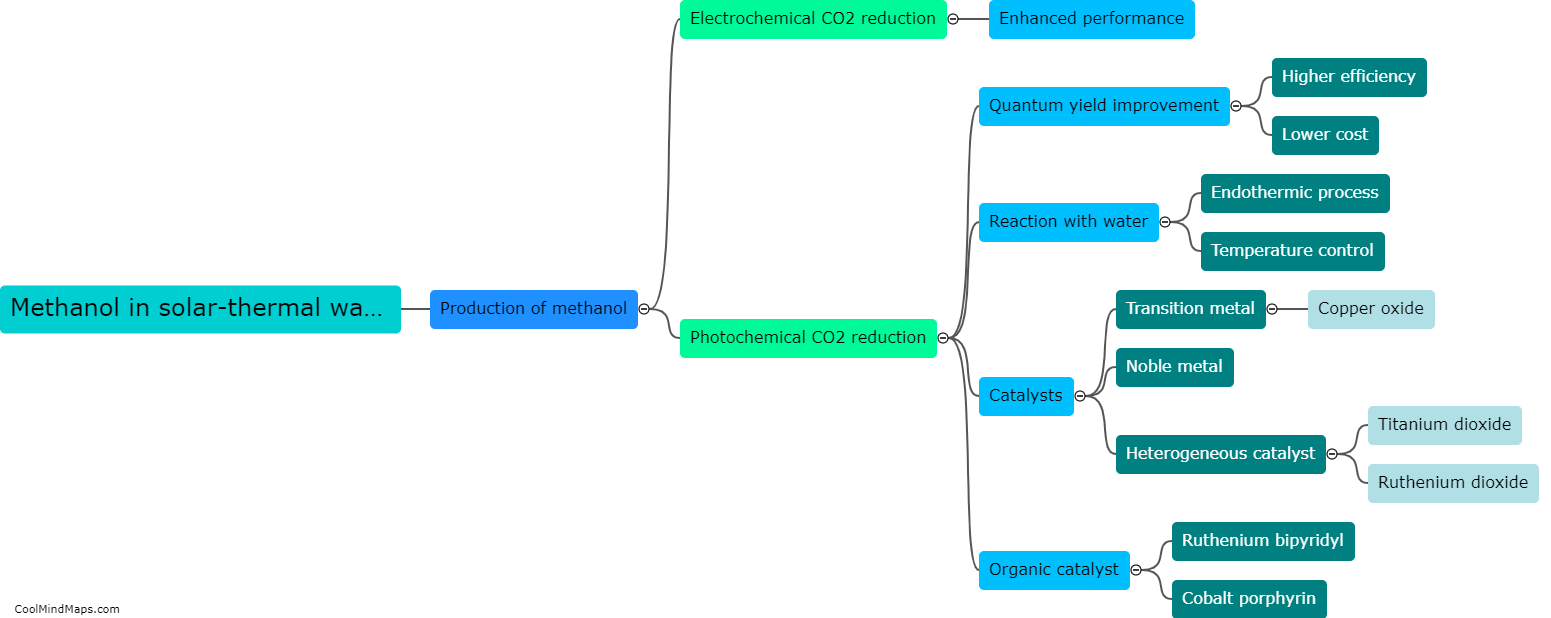
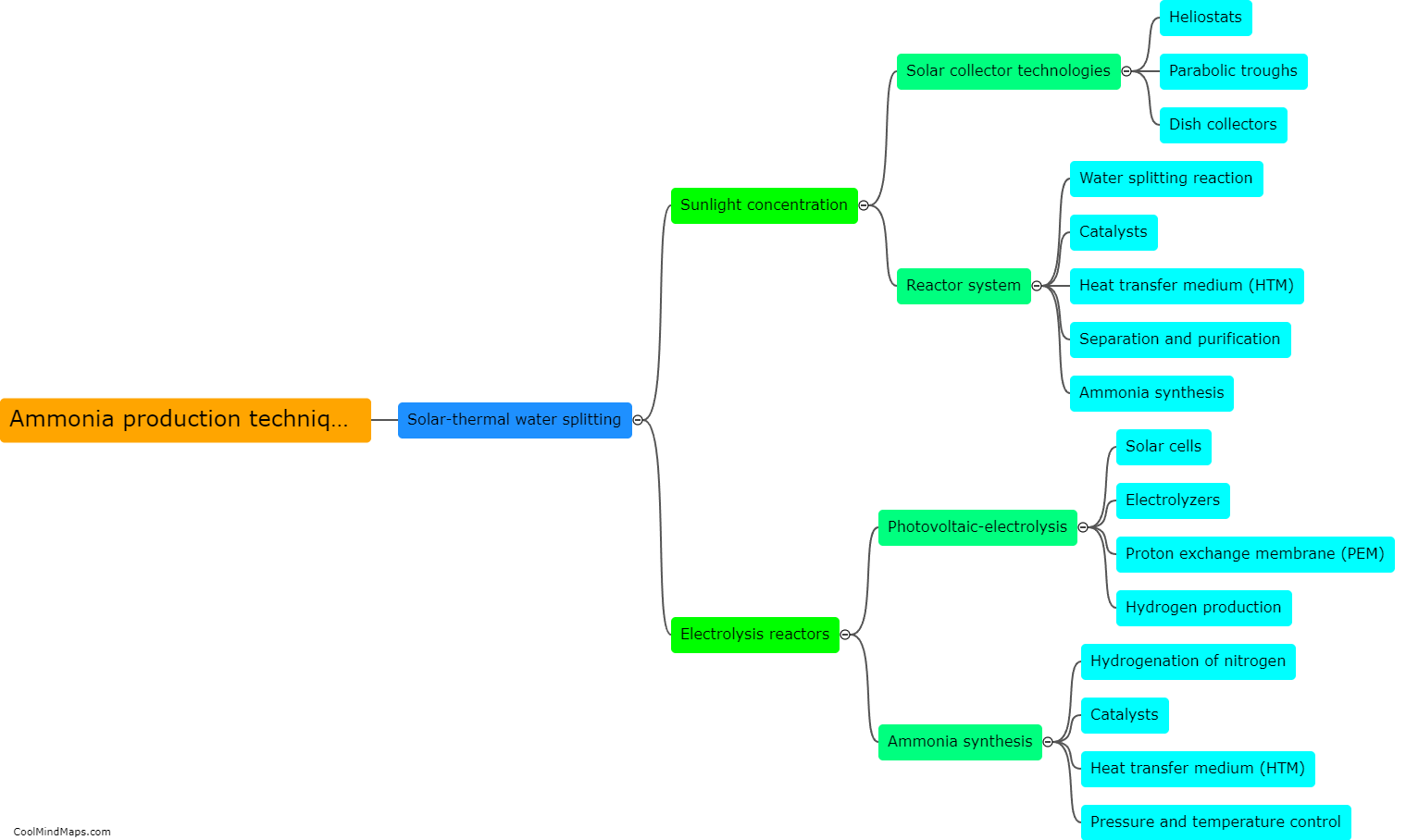
How is ammonia produced through solar-thermal water splitting?
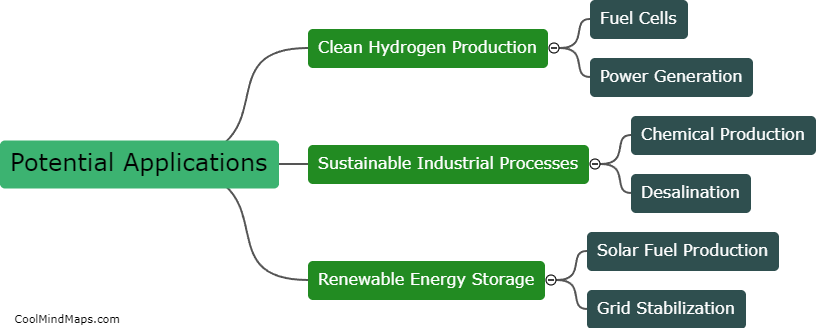
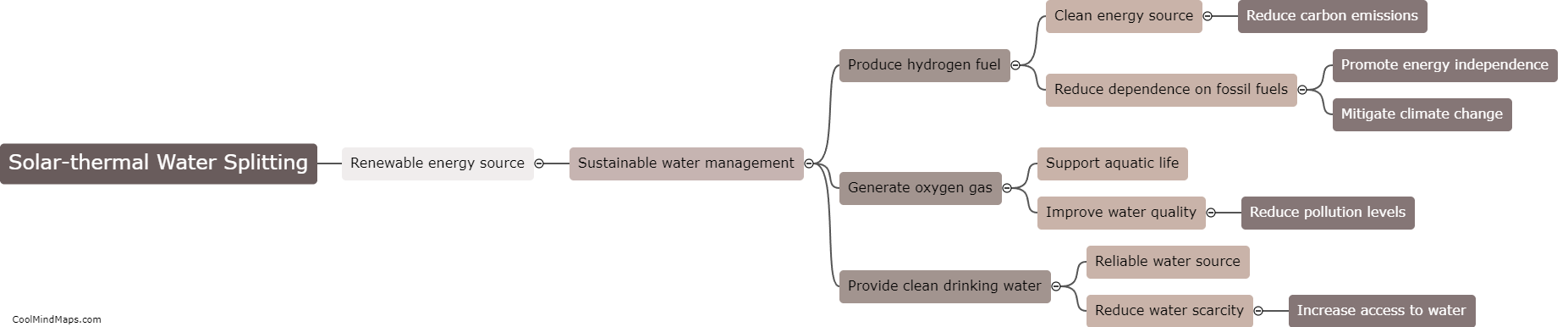
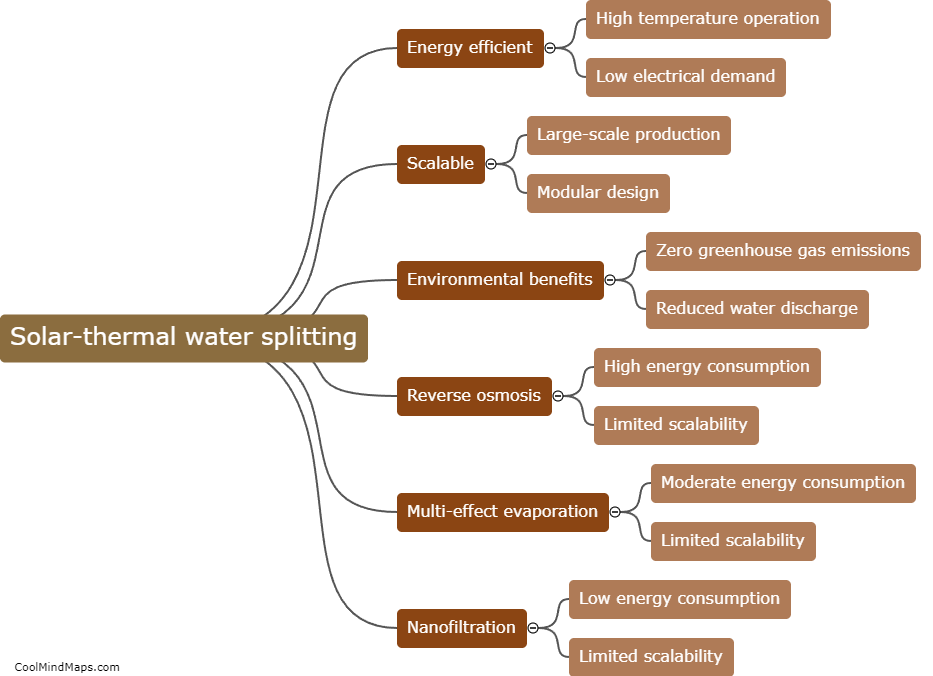
Ammonia can be produced through solar-thermal water splitting using a two-step process known as the Haber-Bosch reaction. First, solar energy is used to heat water and split it into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through a process called thermal water splitting. This is achieved by utilizing solar-thermal concentrators to focus sunlight onto a solar receiver, which transfers the heat to a catalyst material. The catalyst promotes the dissociation of water molecules into their respective elements. In the second step, the produced hydrogen gas is combined with nitrogen gas (N2) extracted from the atmosphere, using renewable electricity, in a reactor to form ammonia (NH3) through the Haber-Bosch process. The solar energy in this process replaces the traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly method of ammonia production.
This mind map was published on 26 October 2023 and has been viewed 89 times.