How do hallucinogens alter brain activity?
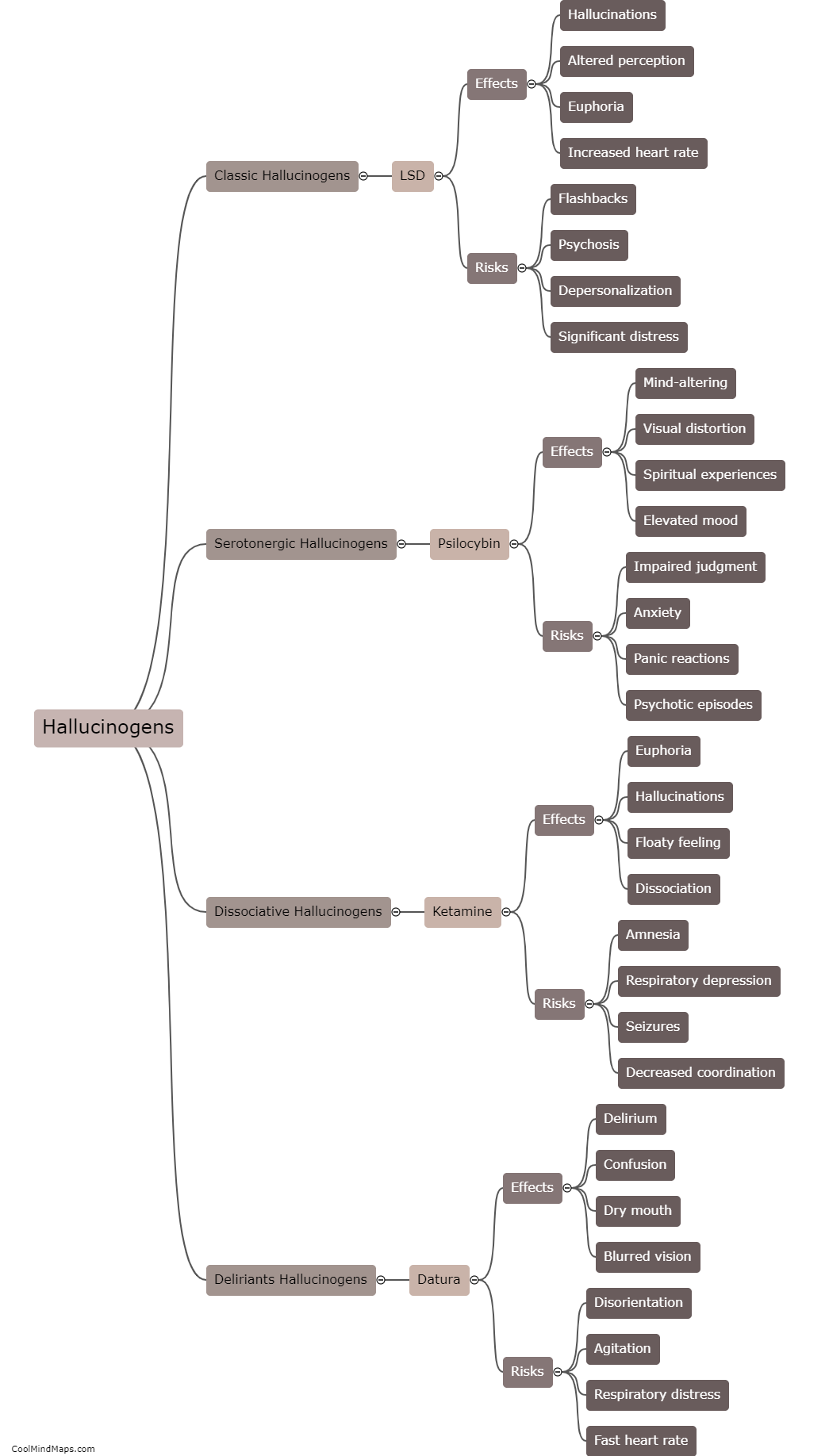
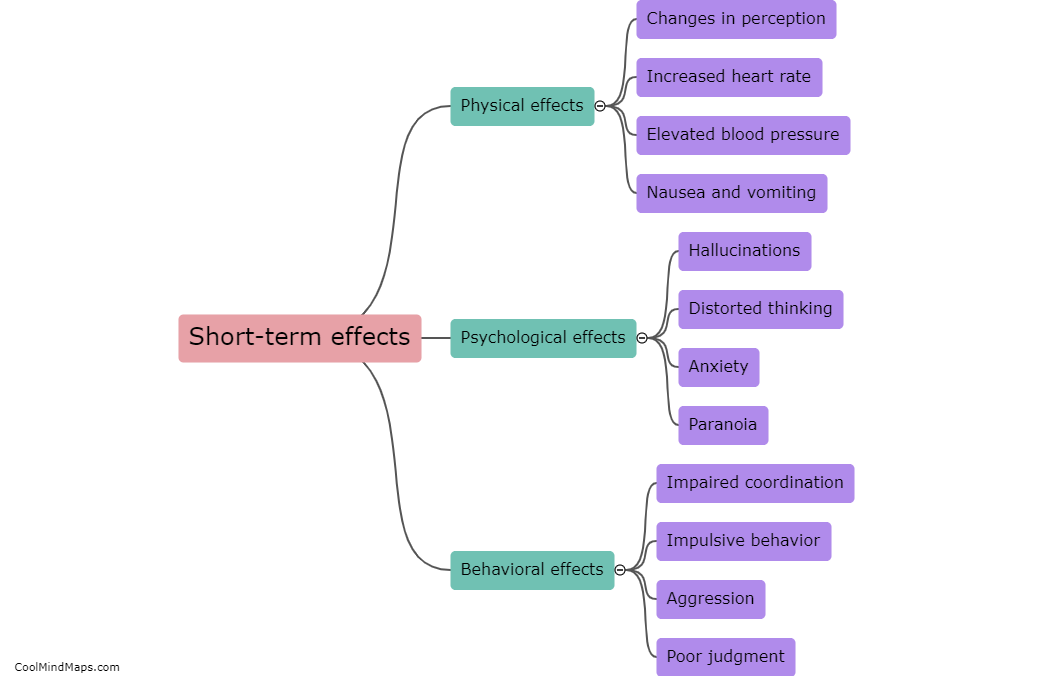
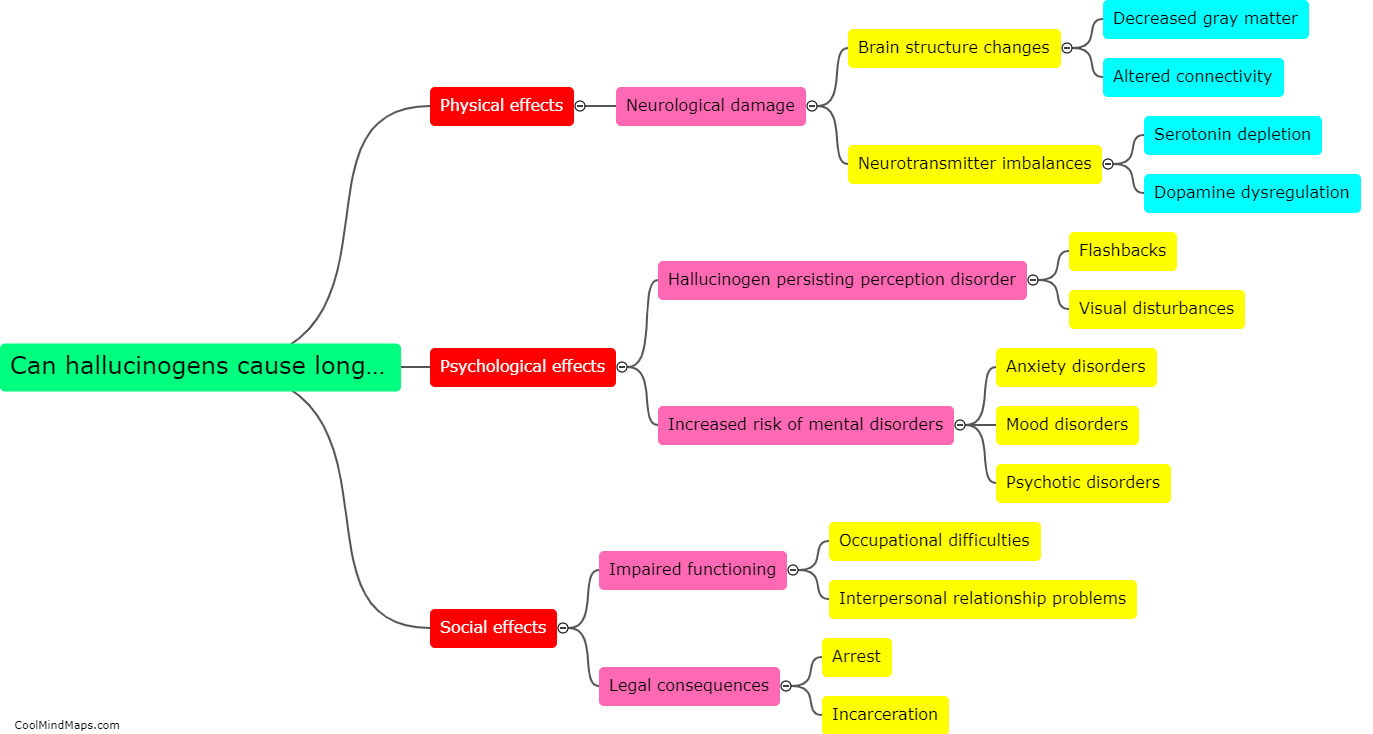
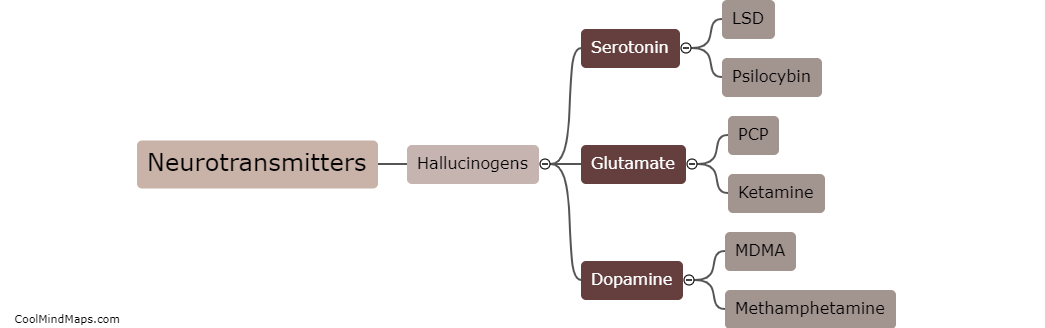
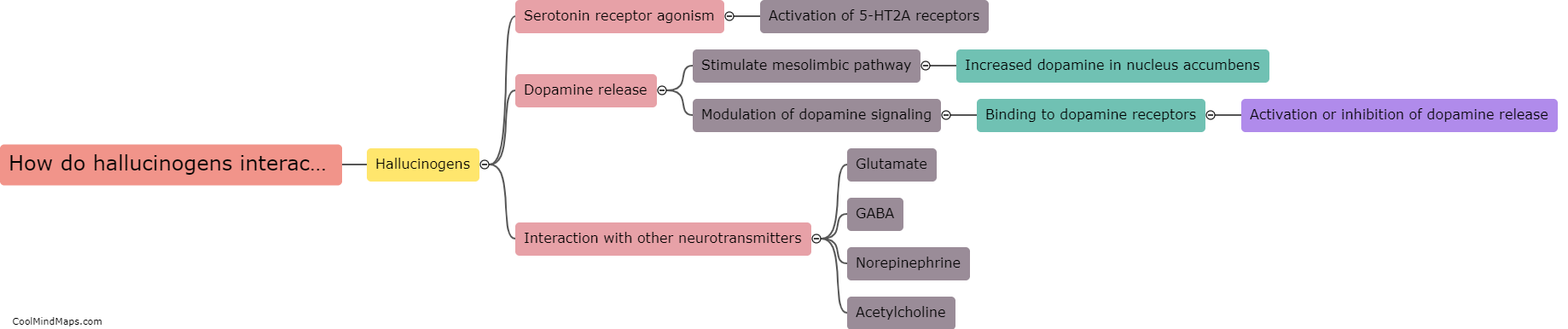
Hallucinogens, such as LSD, psilocybin (magic mushrooms), and DMT, interact with the brain's neurotransmitter systems to induce altered states of consciousness. These substances primarily target the serotonin 2A receptor, which modulates the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and glutamate. By binding to these receptors, hallucinogens disrupt normal neural communication, leading to an influx of sensory information and profound perceptual changes. This can result in the distortion of sensory experiences, such as seeing vibrant colors or hearing sounds that are not present. Additionally, hallucinogens may also increase connectivity between brain regions that typically do not communicate, leading to a breakdown in the brain's functional organization. These alterations in brain activity contribute to the hallucinogenic effects of these substances and can lead to various subjective experiences and profound changes in perception and consciousness.

This mind map was published on 5 December 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.