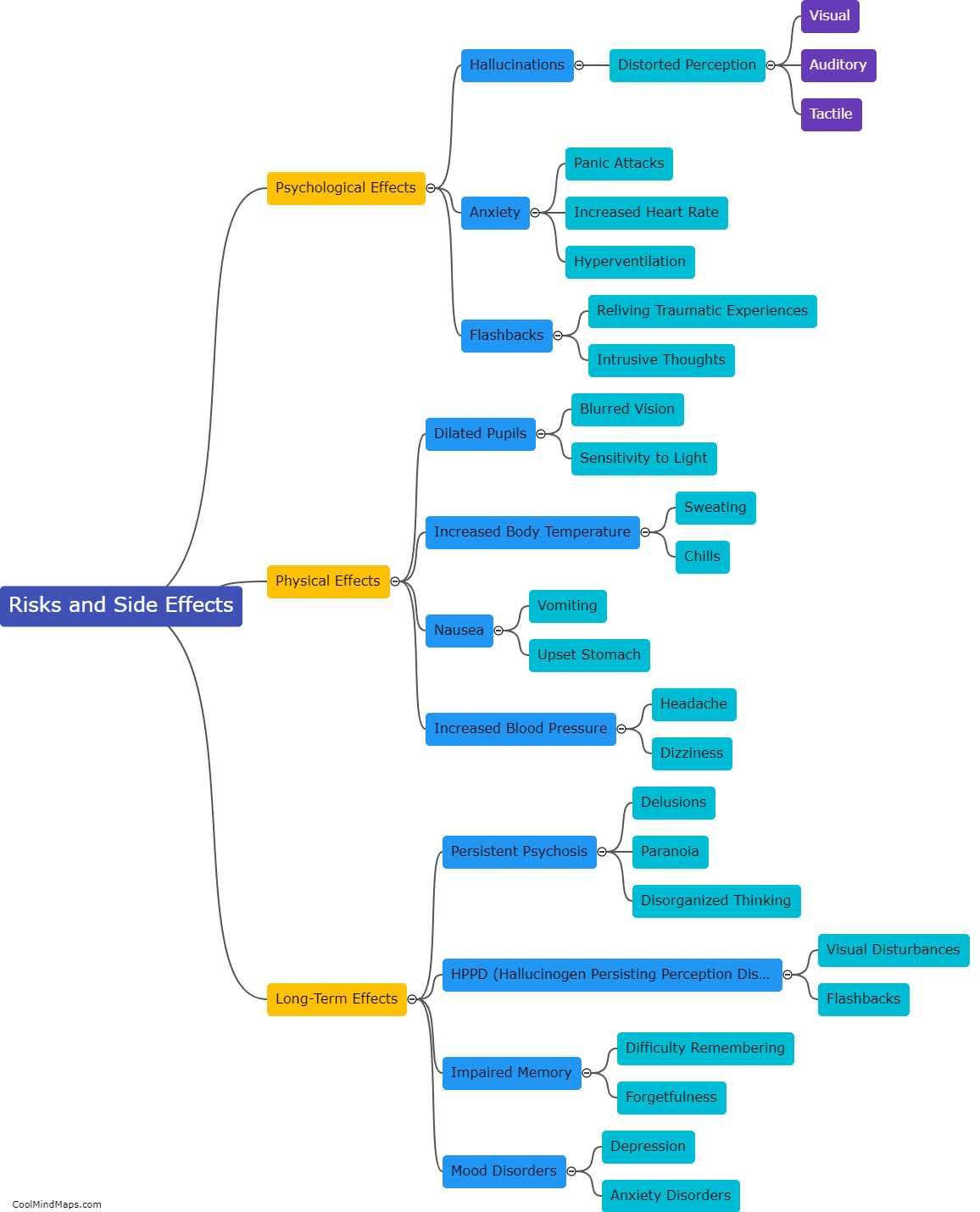
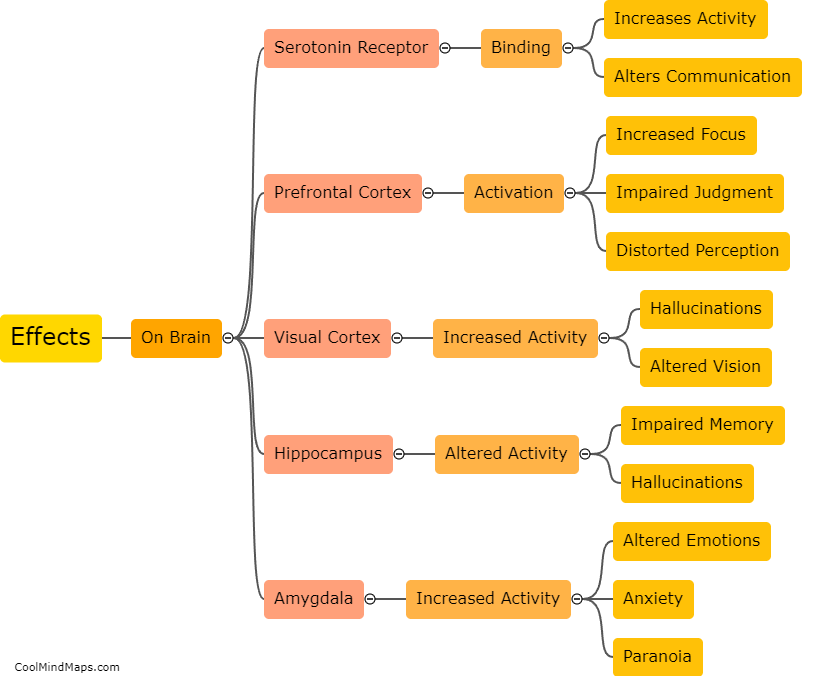
What are the effects of LSD on the brain?
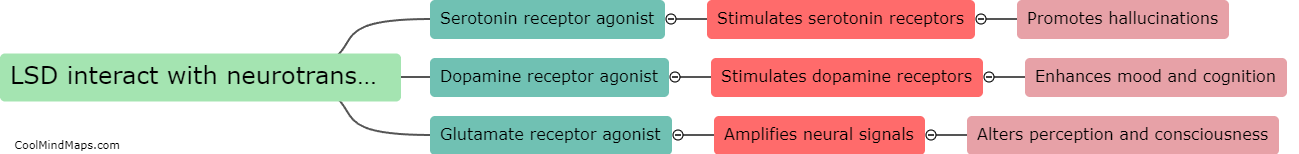
LSD, also known as acid, is a powerful hallucinogenic drug that can profoundly alter perception, mood, and cognition. When consumed, LSD binds to serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptors, leading to a cascade of effects. The primary effect of LSD on the brain involves the disruption of normal communication between different regions, causing a heightened level of connectivity. This increased connectivity can give rise to distorted sensory perceptions, intense visual hallucinations, and altered states of consciousness. Additionally, the drug affects the release of various neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which can impact mood, emotions, and cognitive processes. It is important to note that research on the exact mechanisms and long-term effects of LSD on the brain is limited, making it crucial for further scientific exploration to fully understand the complexities of LSD's impact.
This mind map was published on 19 December 2023 and has been viewed 75 times.