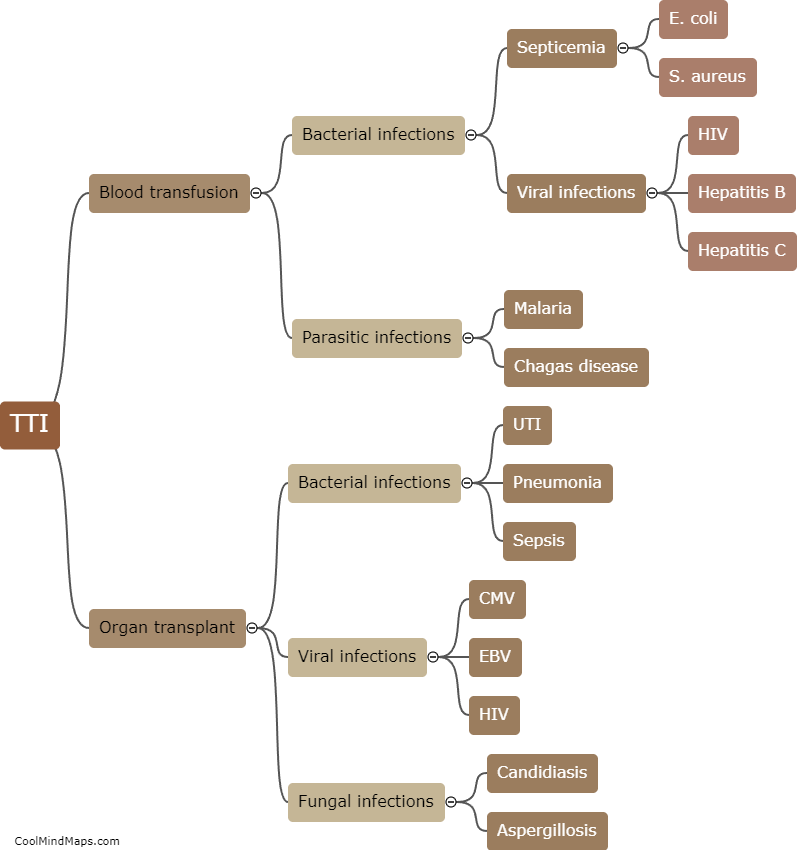
What is transfusion-transmitted infection?
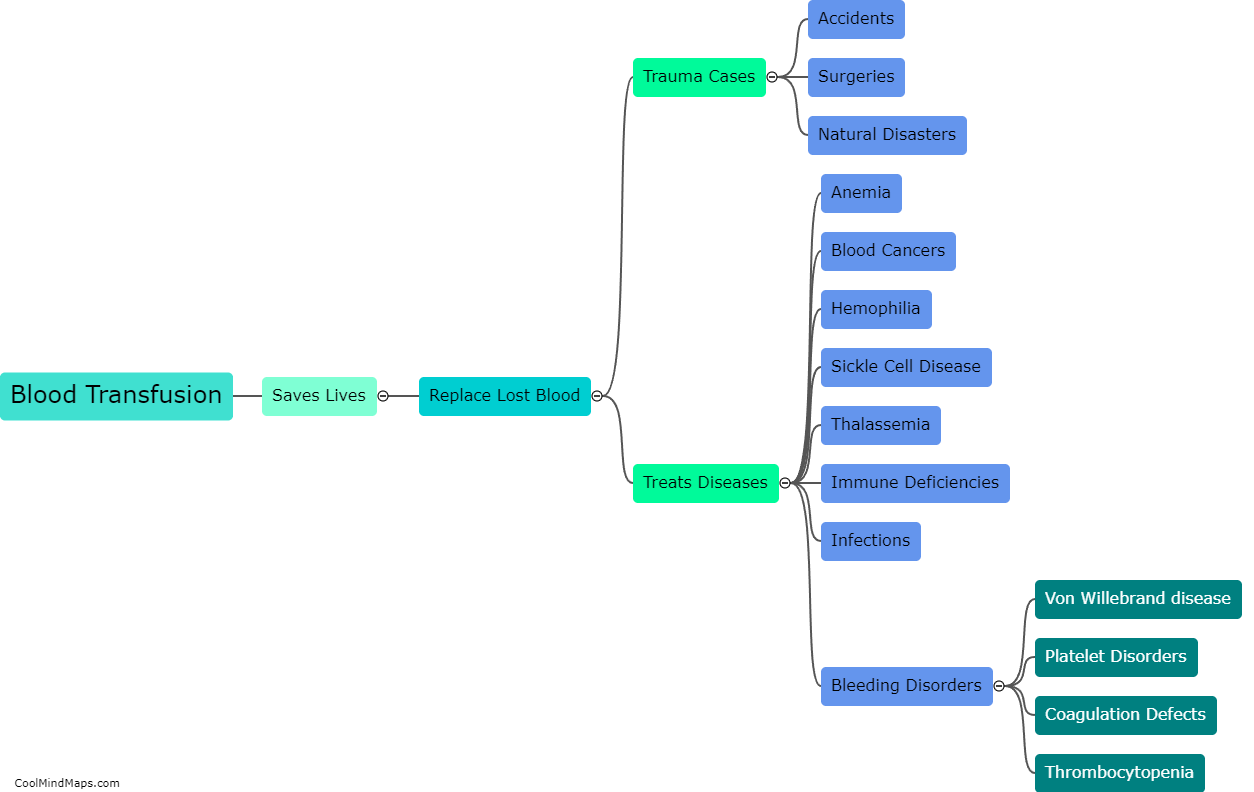
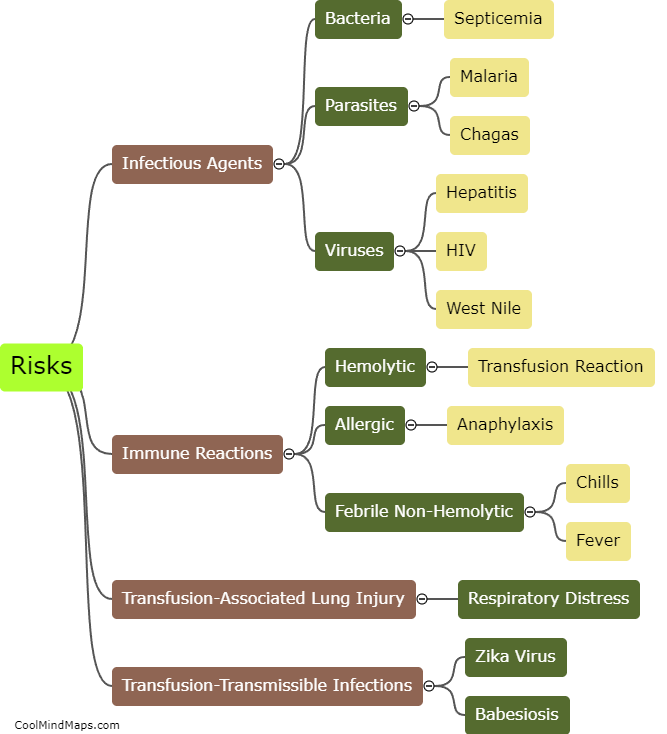
Transfusion-transmitted infection refers to the transmission of infectious agents such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites through blood transfusions. Transfusion-transmitted infections can occur when the blood of a donor, who may be asymptomatic or undiagnosed with an infection, is transfused into a recipient. The most common transfusion-transmitted infections include hepatitis B and C, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and West Nile virus. The risk of transfusion-transmitted infection can be reduced by careful screening of donors and the use of advanced testing methods to detect infectious agents in donated blood.
This mind map was published on 25 June 2023 and has been viewed 102 times.