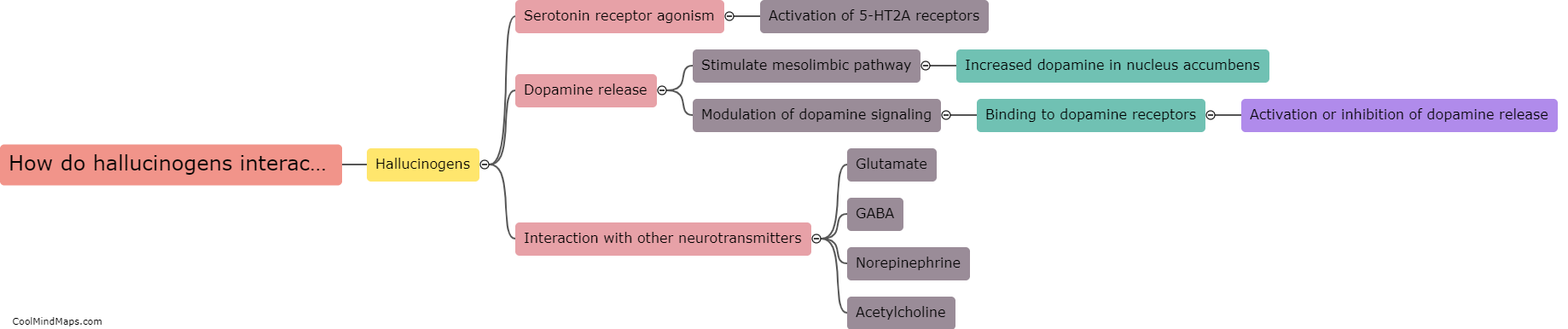
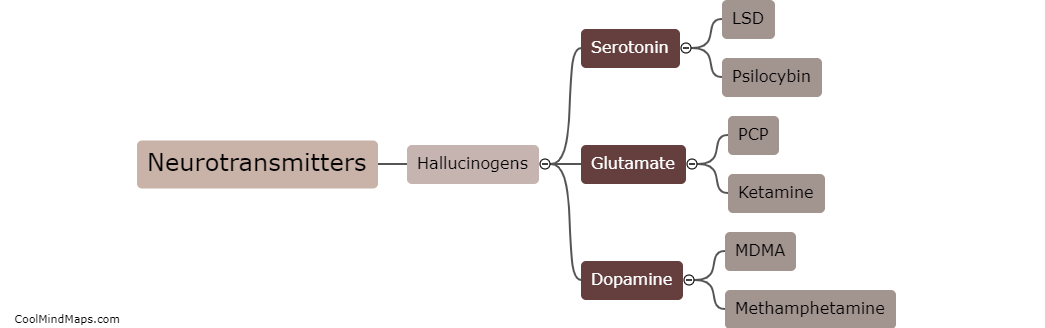
What neurotransmitters are affected by hallucinogens?
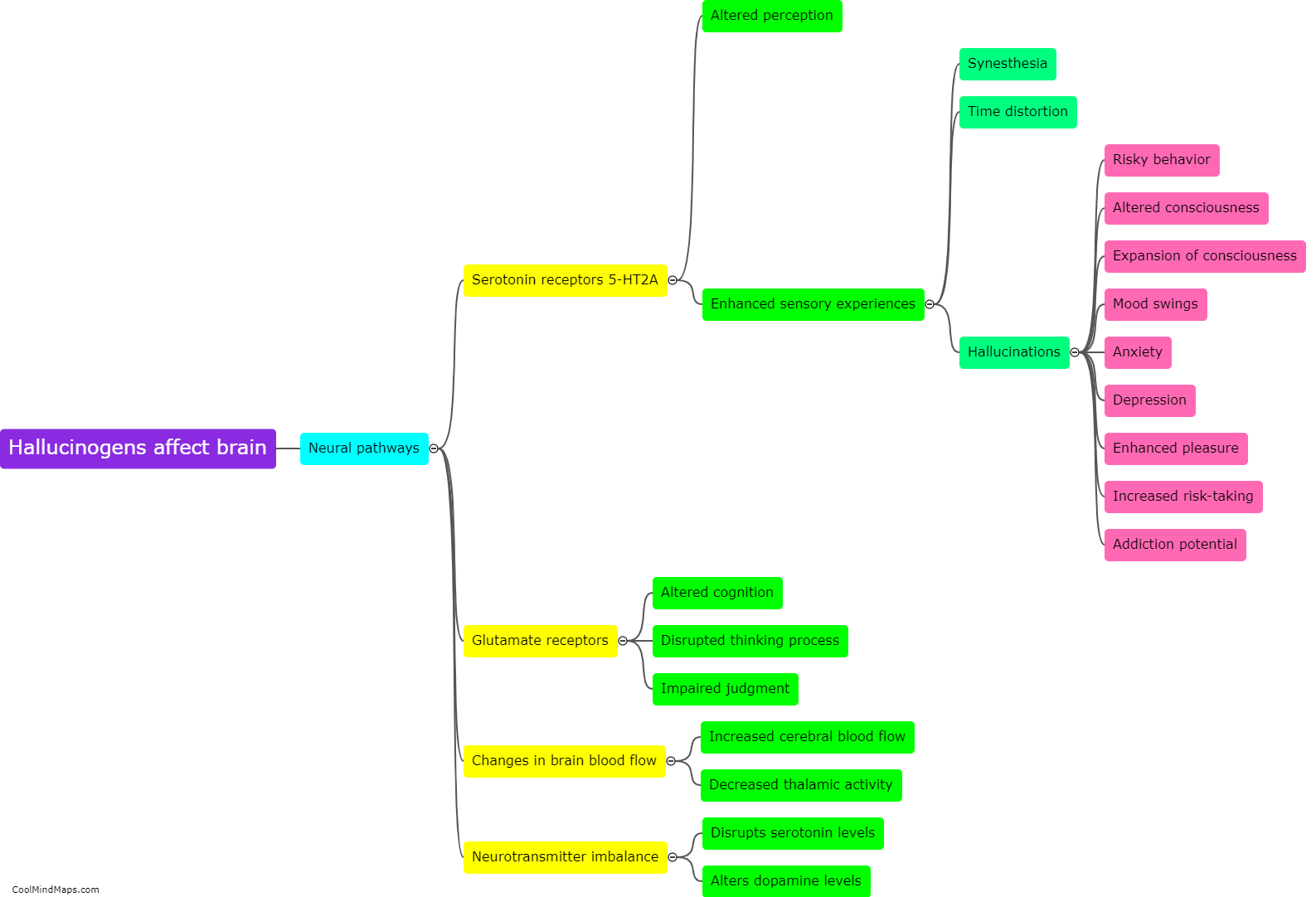
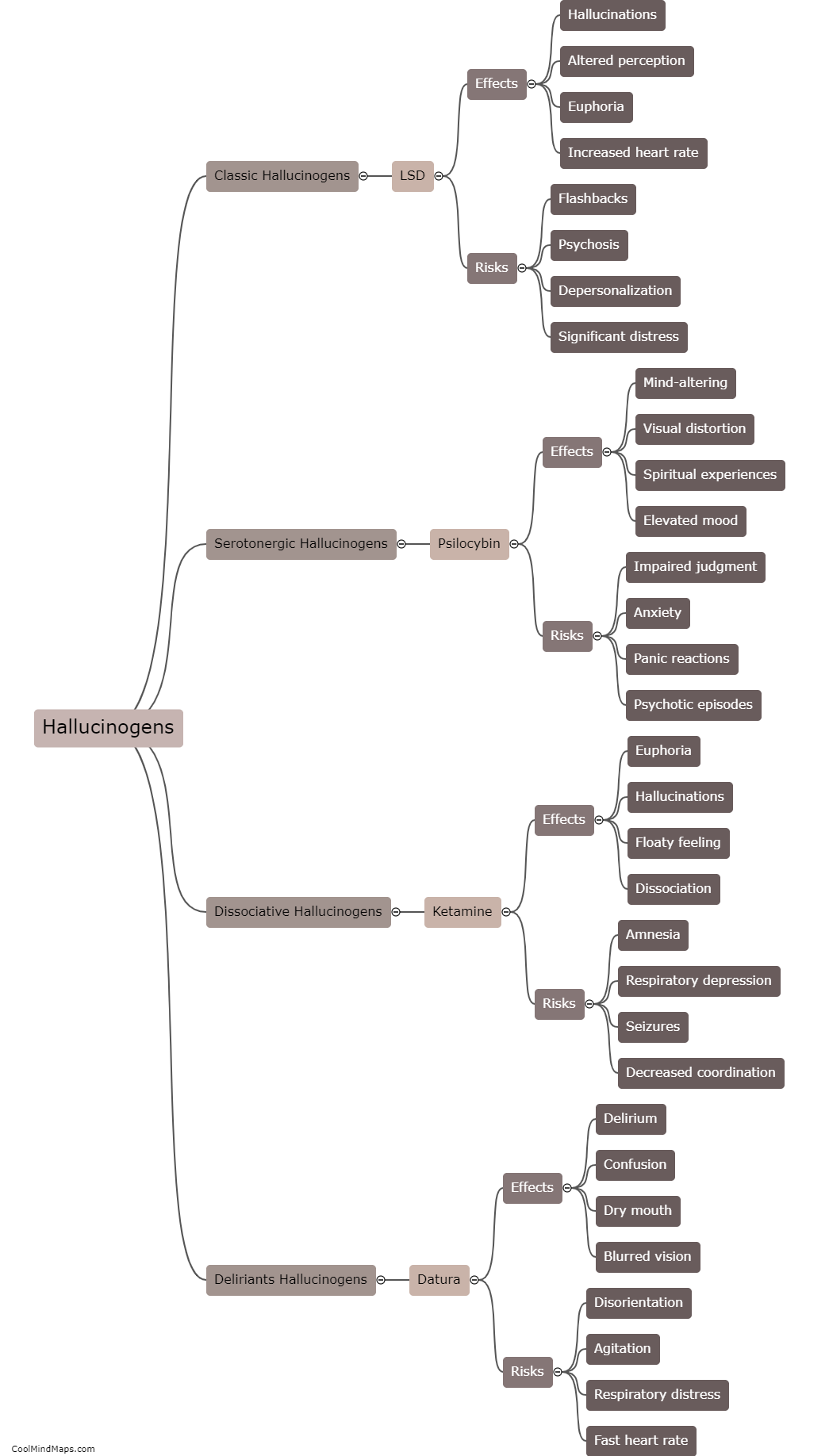
Hallucinogens are substances that can profoundly alter perception, cognition, and mood. These substances primarily target the serotonin system in the brain, affecting various neurotransmitters involved in transmitting signals between nerve cells. The most prominent neurotransmitter affected by hallucinogens is serotonin itself. Hallucinogenic drugs, such as LSD and psilocybin, bind to serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor subtype, leading to an increase in serotonin transmission. This excessive stimulation of serotonin receptors is believed to produce the characteristic hallucinogenic effects. Additionally, hallucinogens can also impact other neurotransmitters, including dopamine and glutamate, which further contribute to their psychedelic properties. The complex interaction of hallucinogens with multiple neurotransmitter systems ultimately results in the unique and often profound subjective experiences associated with these substances.
This mind map was published on 5 December 2023 and has been viewed 89 times.