How does package management work in Linux?
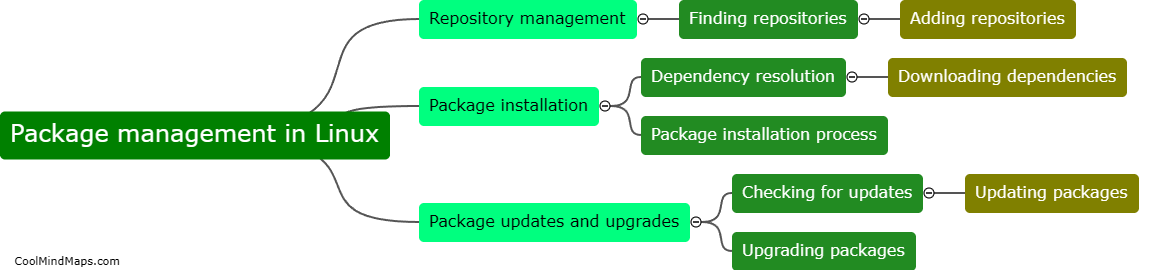
Package management in Linux refers to the process of installing, updating, configuring, and removing software packages on a Linux system. It involves the use of package managers, such as apt, yum, or pacman, which are tools that automate the process of managing software installations and dependencies. These package managers use repositories, which are collections of software packages and their metadata, to retrieve the necessary files and handle the installation process. Users can easily search for, select, and install packages using the package manager, ensuring that the software is correctly installed and any dependencies are met. Updates and upgrades can also be managed through the package manager, making it a convenient and efficient way to manage software on a Linux system.
This mind map was published on 29 July 2024 and has been viewed 53 times.