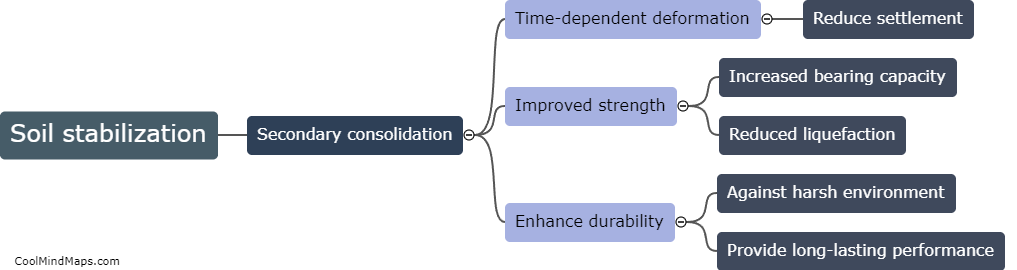
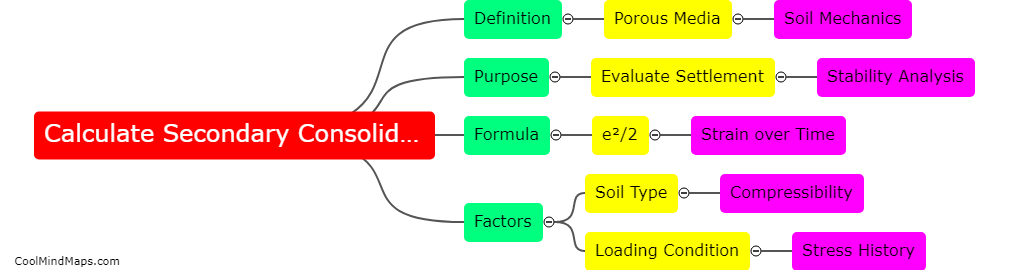
How to calculate secondary consolidation?
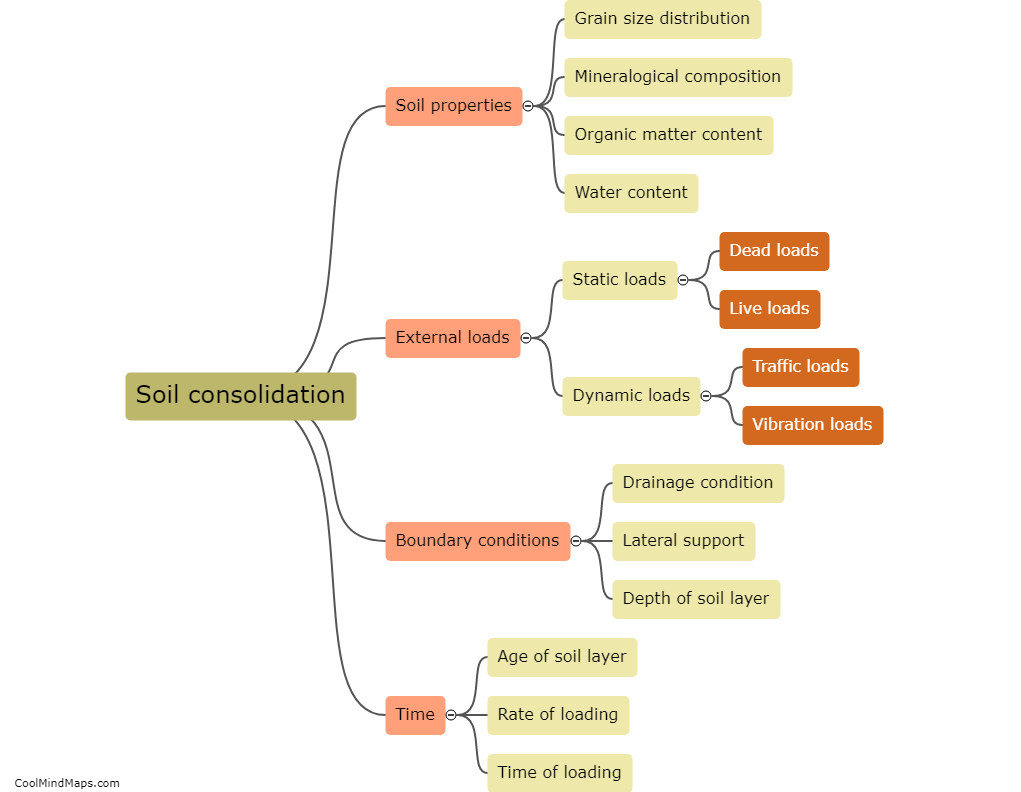
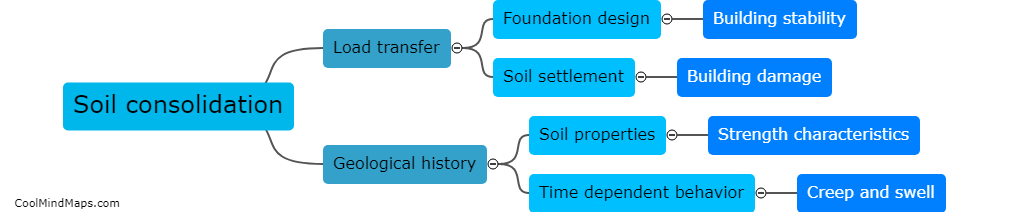
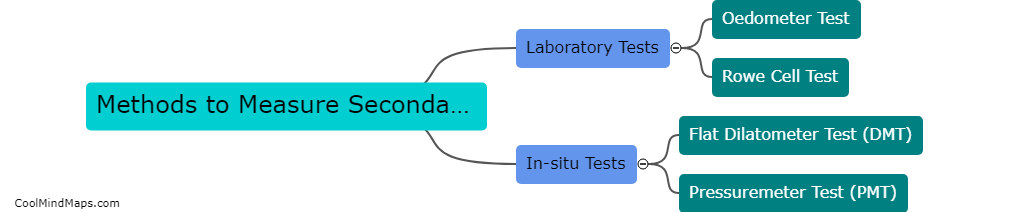
Secondary consolidation is a process of soil compression that occurs after the initial settlement of a structure or a load. To calculate the amount of secondary consolidation, you need to measure the rate at which the soil continues to compress over time. This can be done by conducting laboratory tests on soil samples and plotting the results on a graph over time. The rate of secondary consolidation can then be determined by measuring the slope of the graph. Other factors that need to be considered when calculating secondary consolidation include the thickness and properties of the soil layers, the magnitude and duration of the load, and the moisture content of the soil.
This mind map was published on 11 May 2023 and has been viewed 119 times.