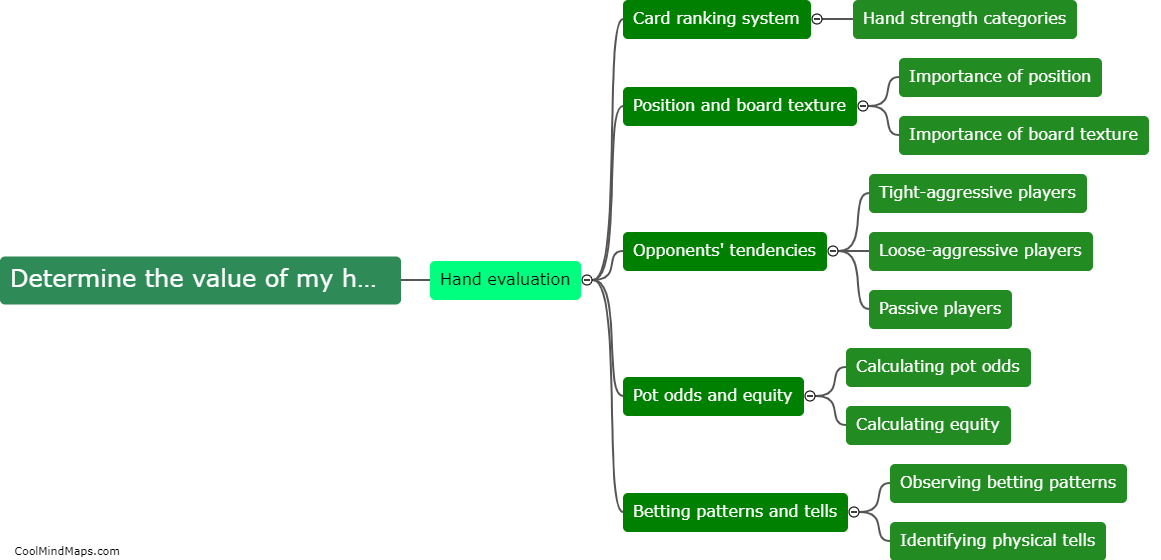
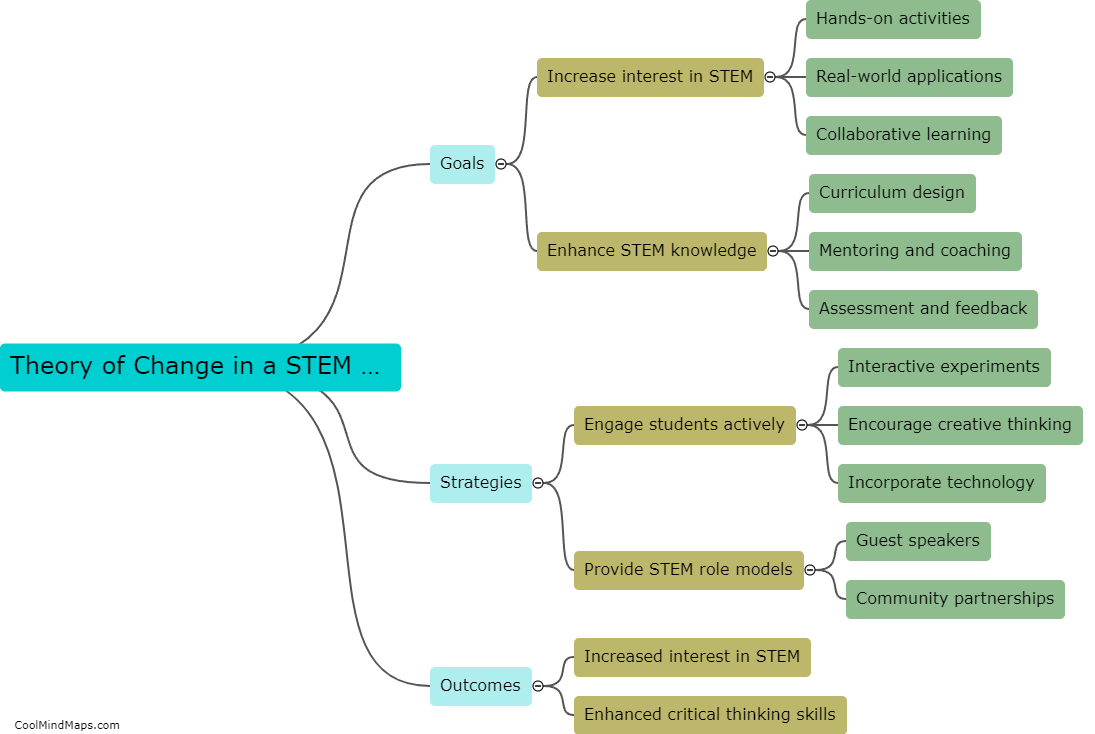
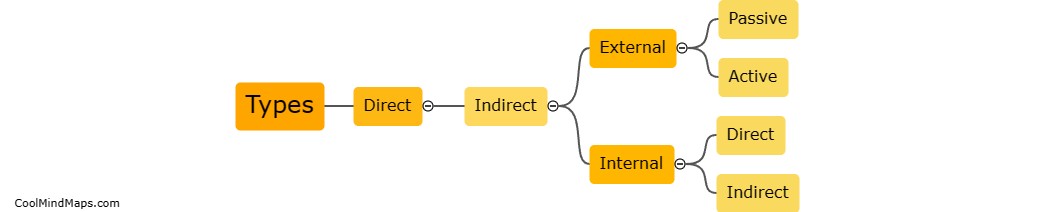
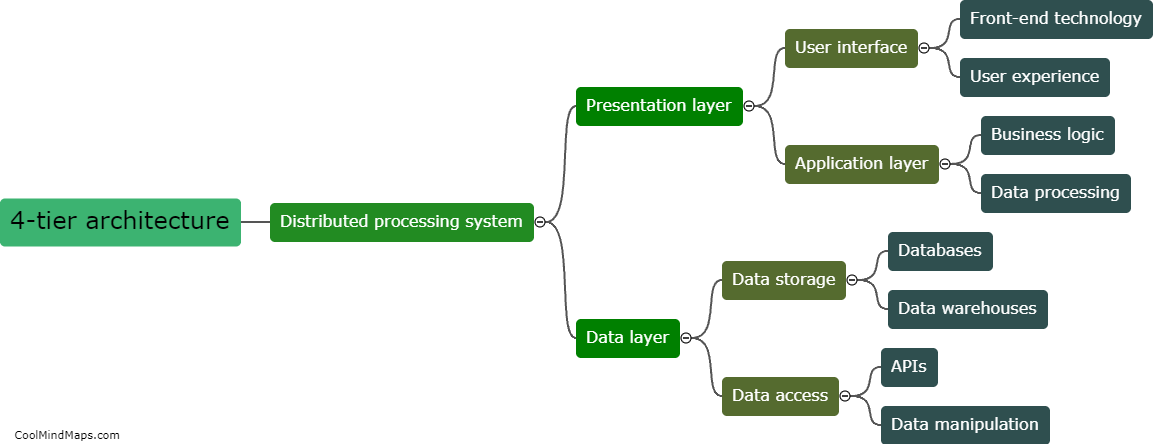
What are the different stages in the evolution of a star?
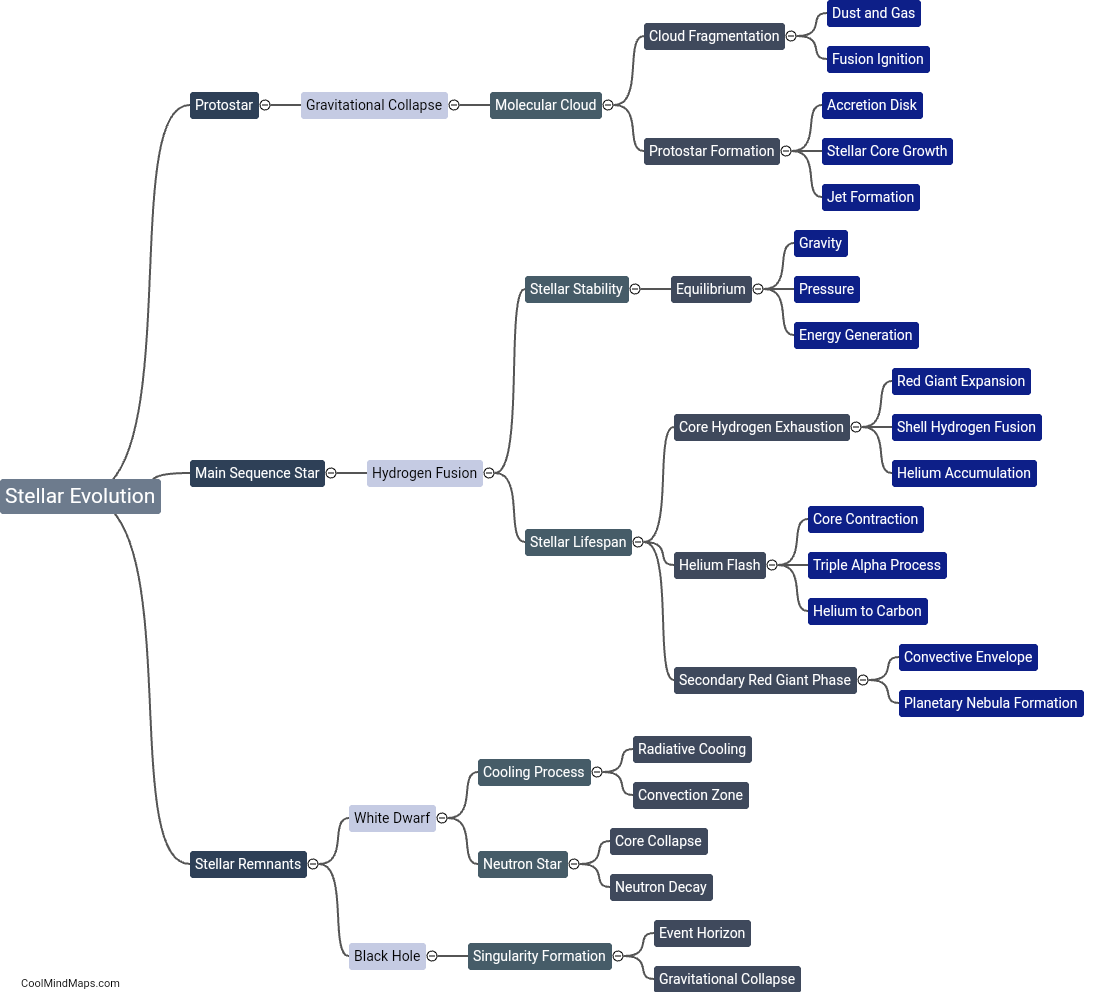
The evolution of a star can be divided into several stages, each characterized by distinct processes and changes. The first stage is the formation of a protostar, where a dense cloud of gas and dust collapses under its gravity, leading to the birth of a new star. As the protostar continues to contract, it enters the main sequence stage, where nuclear fusion in its core begins, primarily converting hydrogen into helium. This stage can last for millions or billions of years, depending on the mass of the star. After exhausting its core hydrogen fuel, a star enters the red giant phase, where it swells in size, becoming larger and redder. This phase ends when the star expels its outer layers, creating a planetary nebula and leaving behind a dense core called a white dwarf. For more massive stars, a supernova explosion occurs, leading to the formation of either a neutron star or a black hole. Each stage in the evolution of a star contributes to the rich and complex life cycle of these celestial objects.
This mind map was published on 23 January 2024 and has been viewed 86 times.