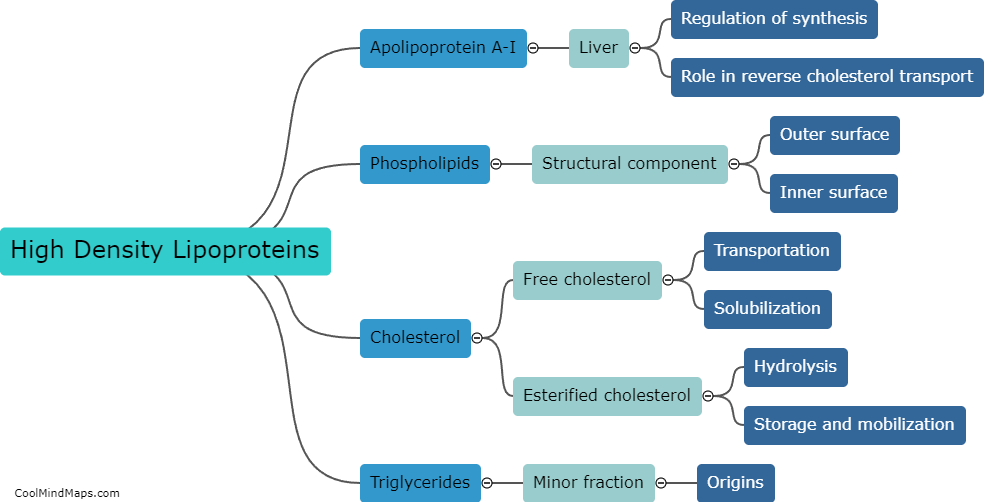
What are the components of HDL?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is often referred to as the "good cholesterol" because it helps remove excess low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" from the bloodstream. HDL is made up of several components. The core of HDL contains cholesterol and triglycerides, which are essential for transporting fats throughout the body. Surrounding the core are proteins called apolipoproteins, which help stabilize and transport HDL. These apolipoproteins also interact with various enzymes, such as lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) and cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP), which further modify and metabolize cholesterol within HDL. Overall, the combination of cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoproteins, and enzymes form the vital components of HDL responsible for its role in maintaining cardiovascular health.
This mind map was published on 7 January 2024 and has been viewed 76 times.