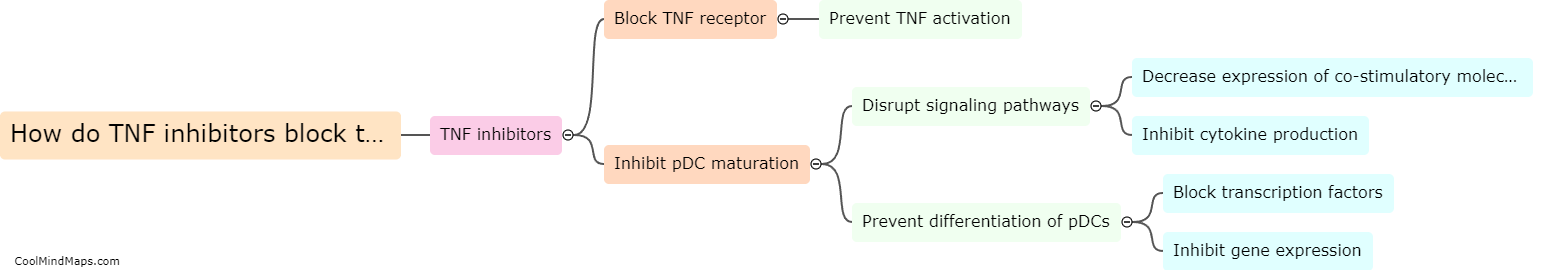
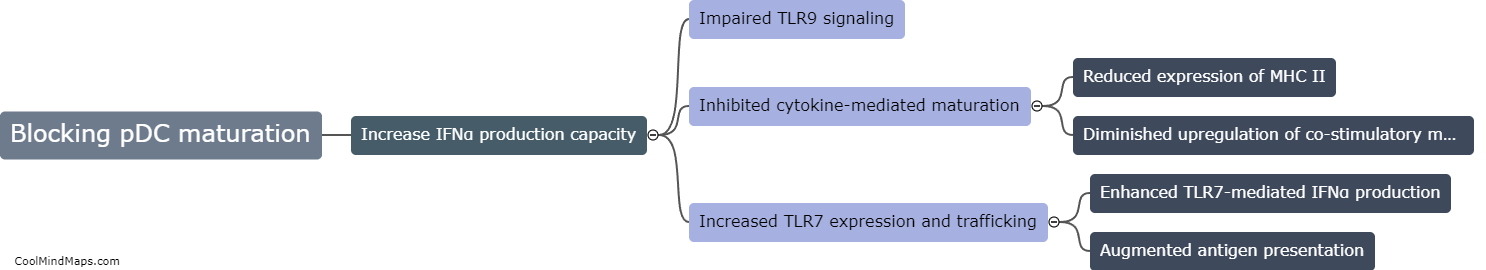
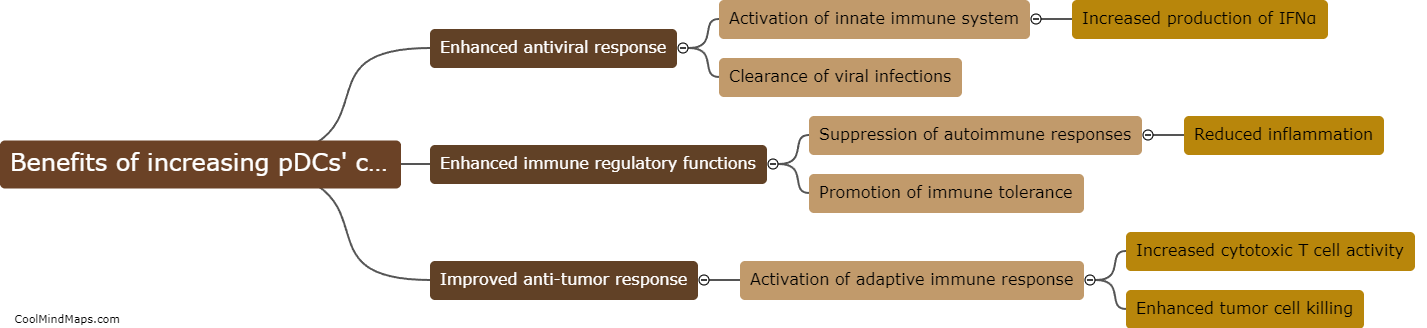
What is the mechanism behind the paradoxical psoriasis triggered by TNFi agents?
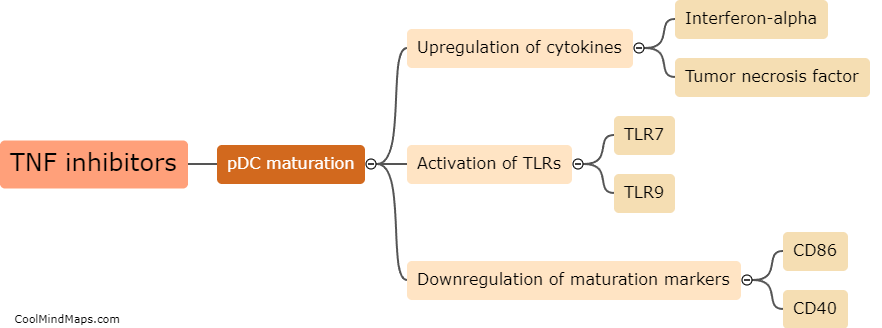
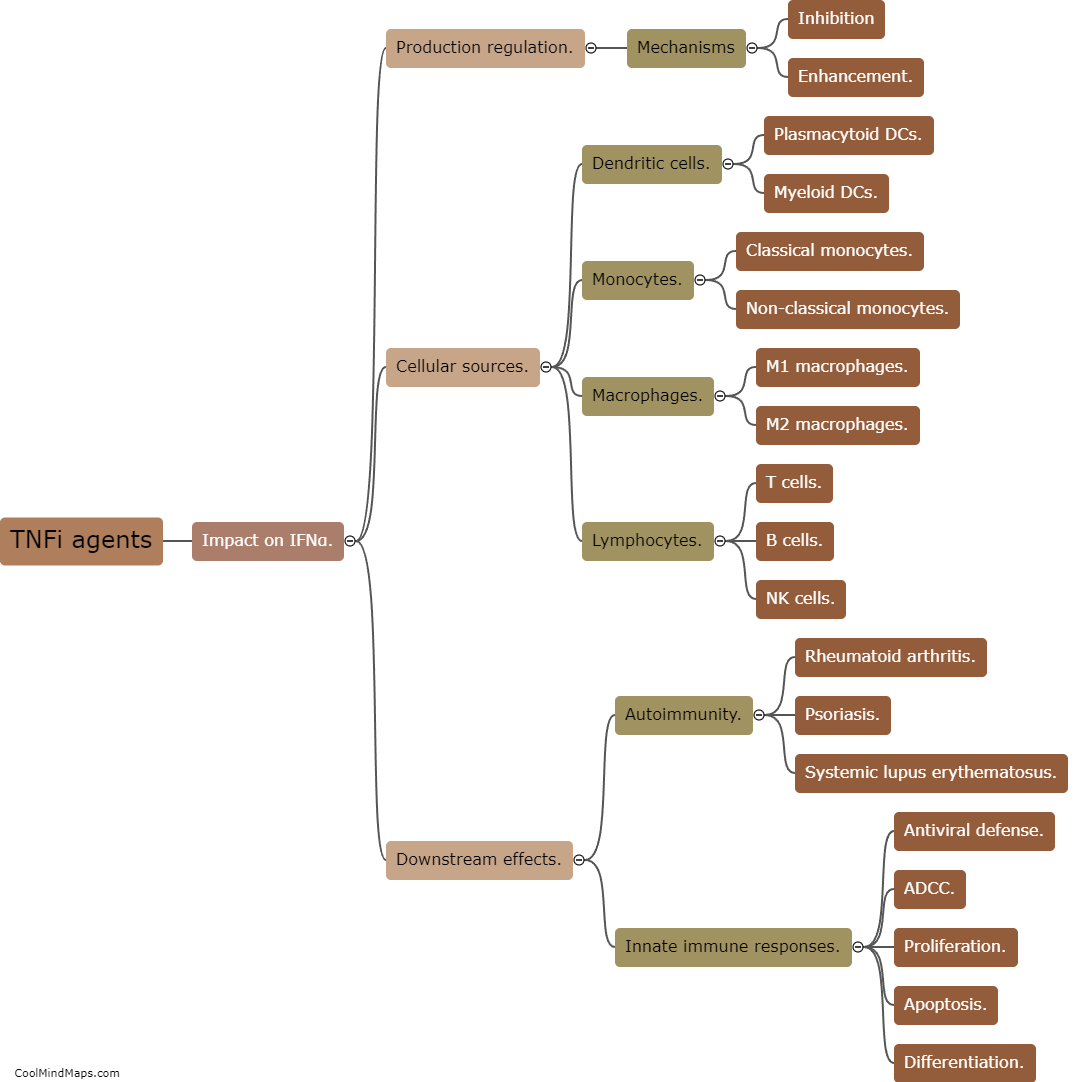
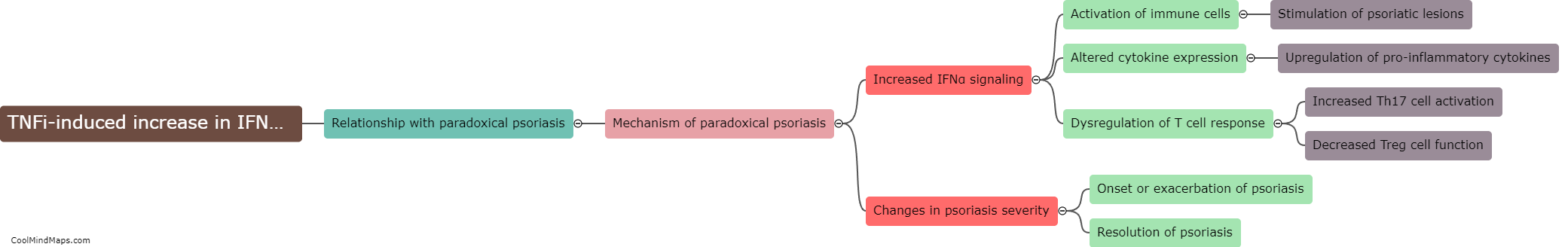
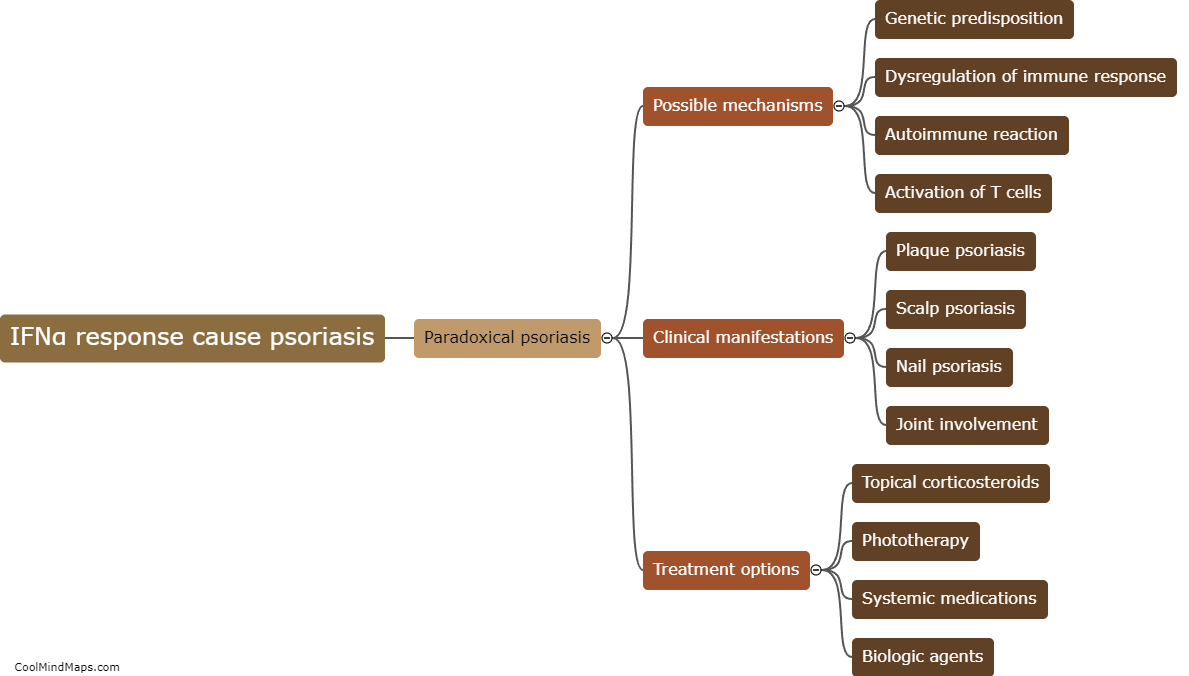
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and excessive skin cell growth. Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitors (TNFi) are a class of medications commonly used to treat psoriasis and other inflammatory conditions. Paradoxically, in some cases, TNFi agents can actually trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. The mechanism behind this paradoxical effect is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a complex interplay between the immune system, genetic factors, and the drug's impact on cytokines and other inflammatory pathways. TNFi agents block the action of TNF, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, which helps reduce inflammation in many diseases. However, in susceptible individuals, inhibiting TNF may lead to a dysregulation of other cytokines and immune responses, ultimately triggering or worsening psoriasis. Further research is needed to better elucidate the underlying mechanisms and develop strategies to prevent or manage this paradoxical response.

This mind map was published on 13 July 2023 and has been viewed 112 times.