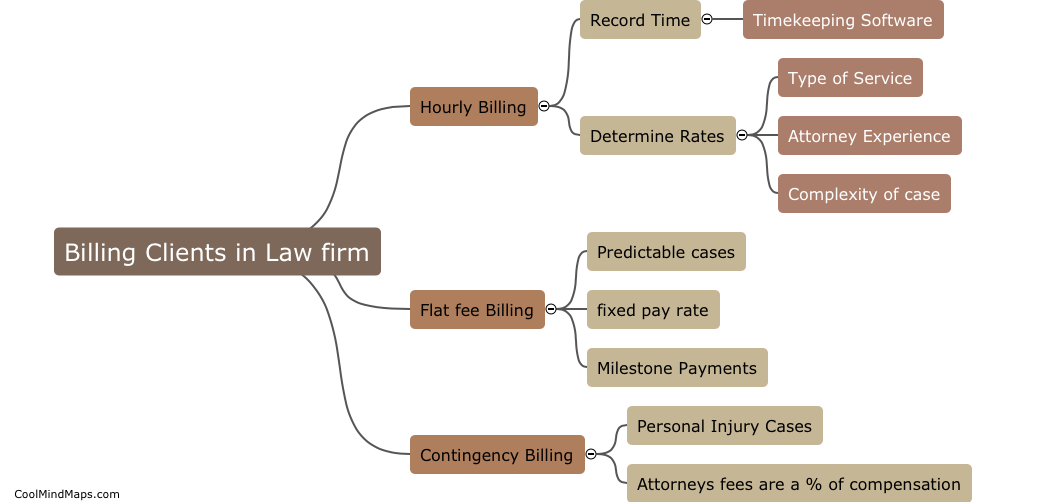
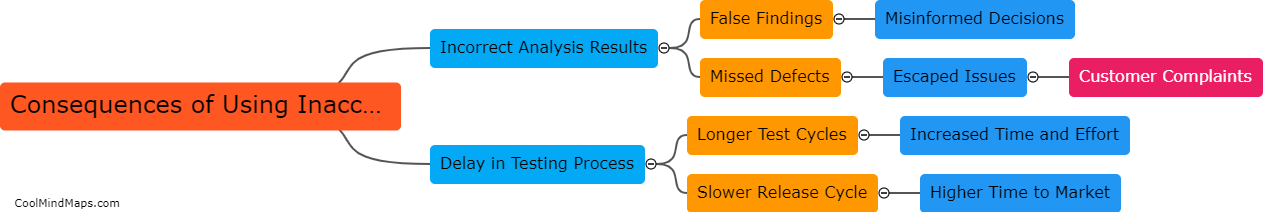
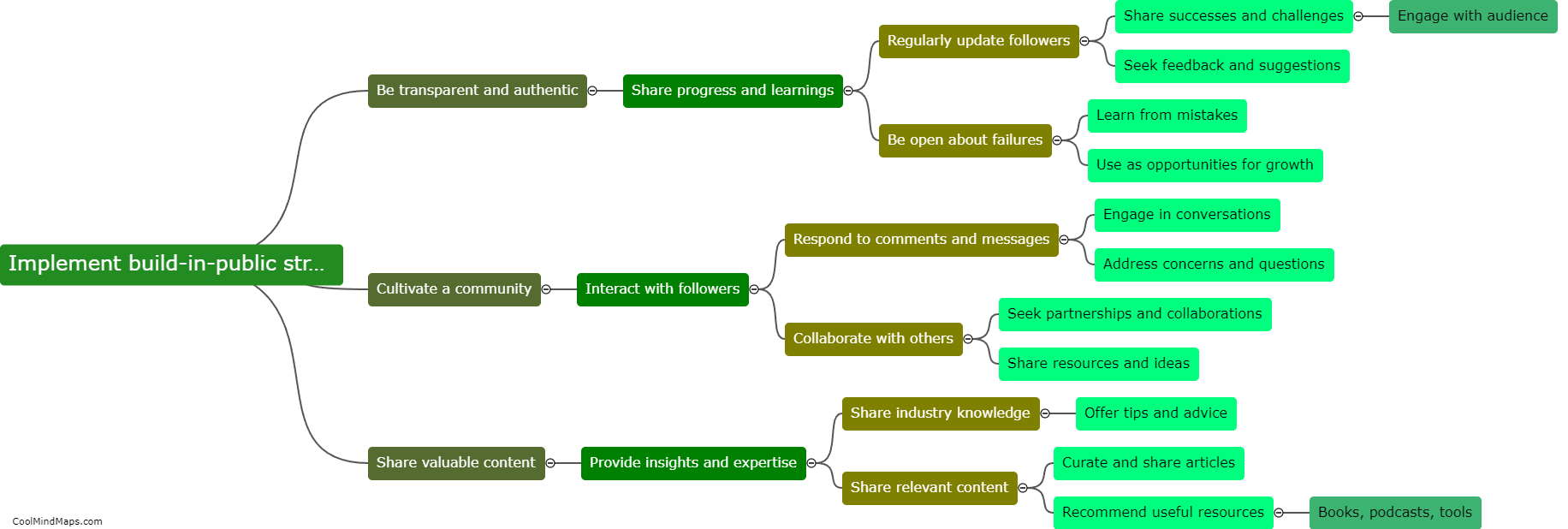
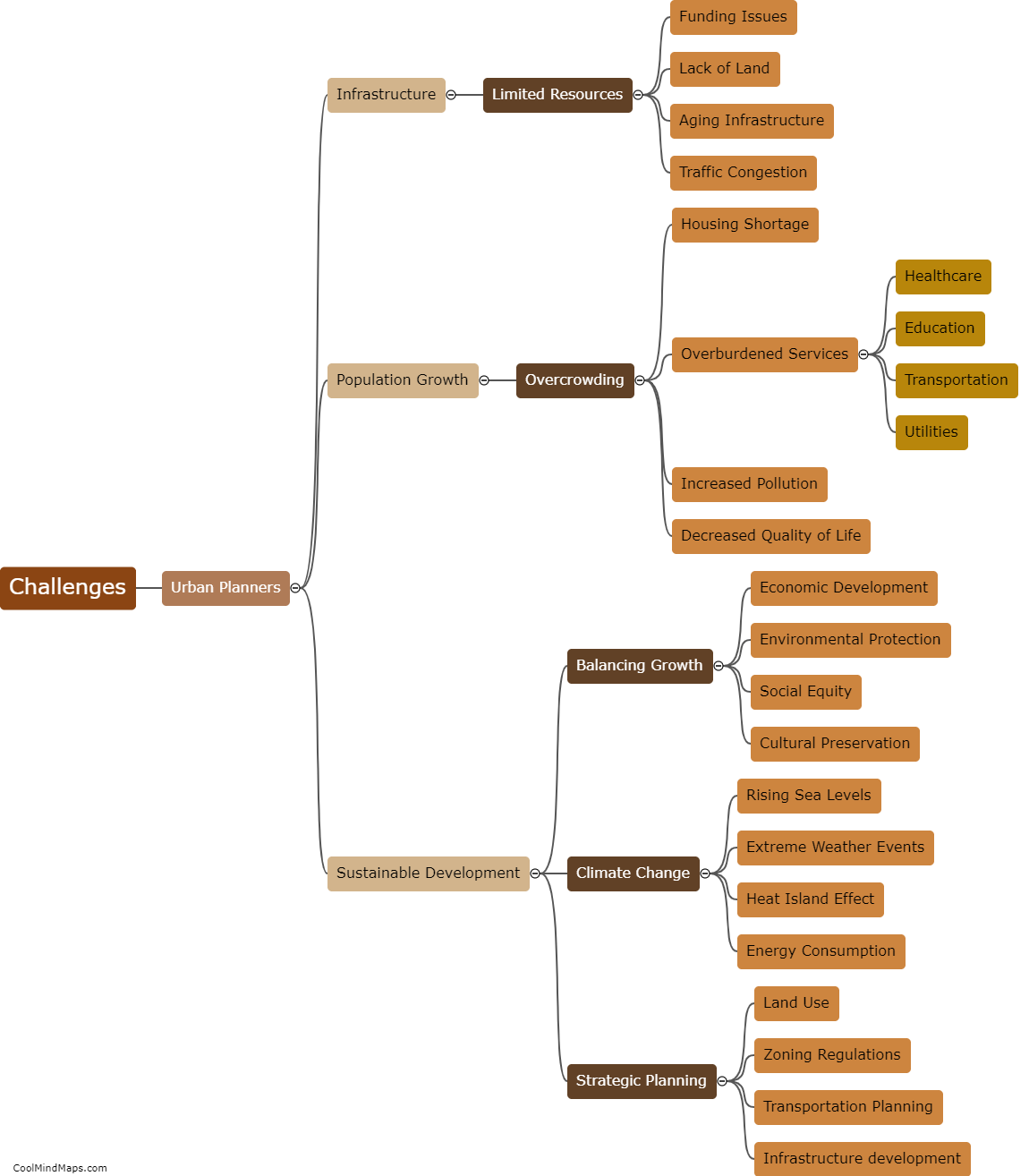
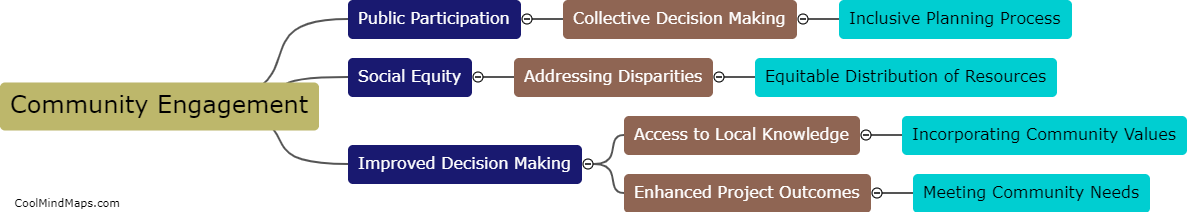
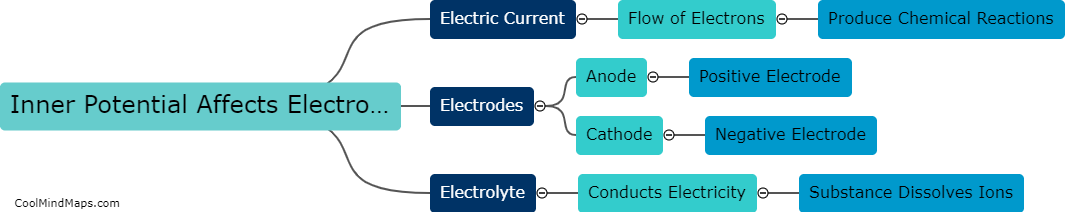
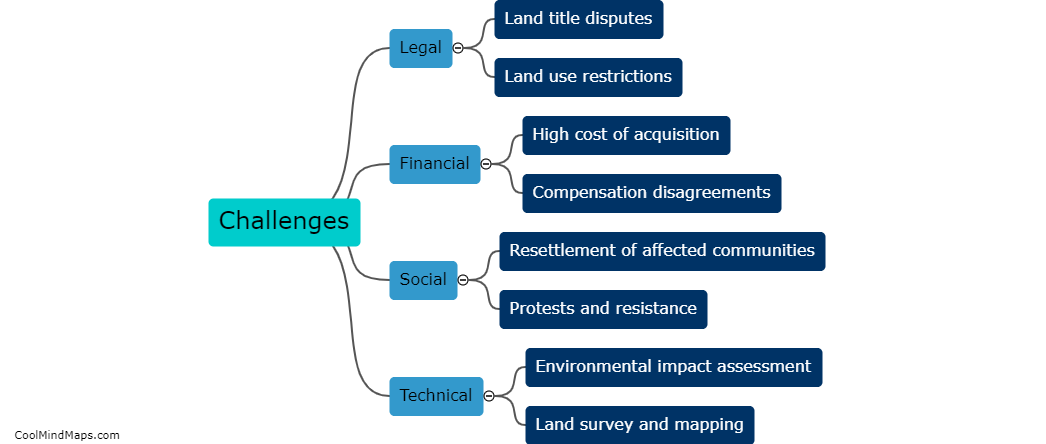
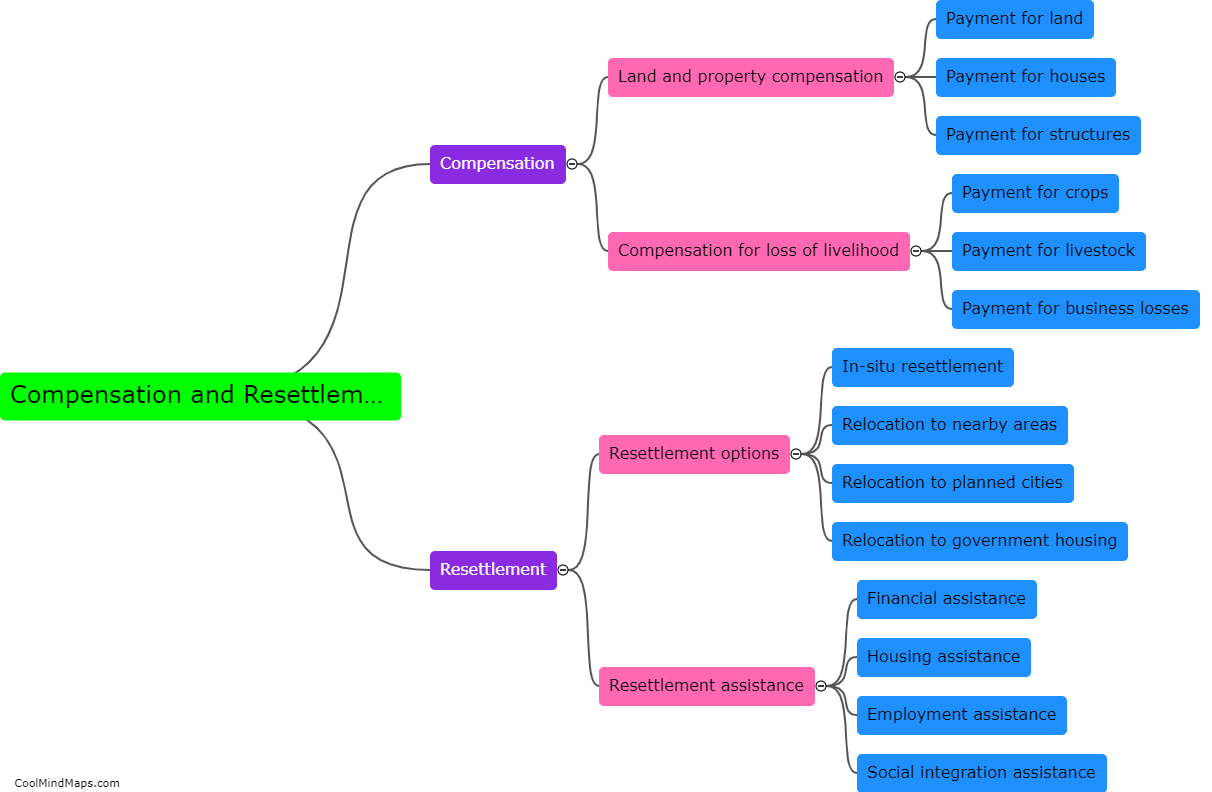
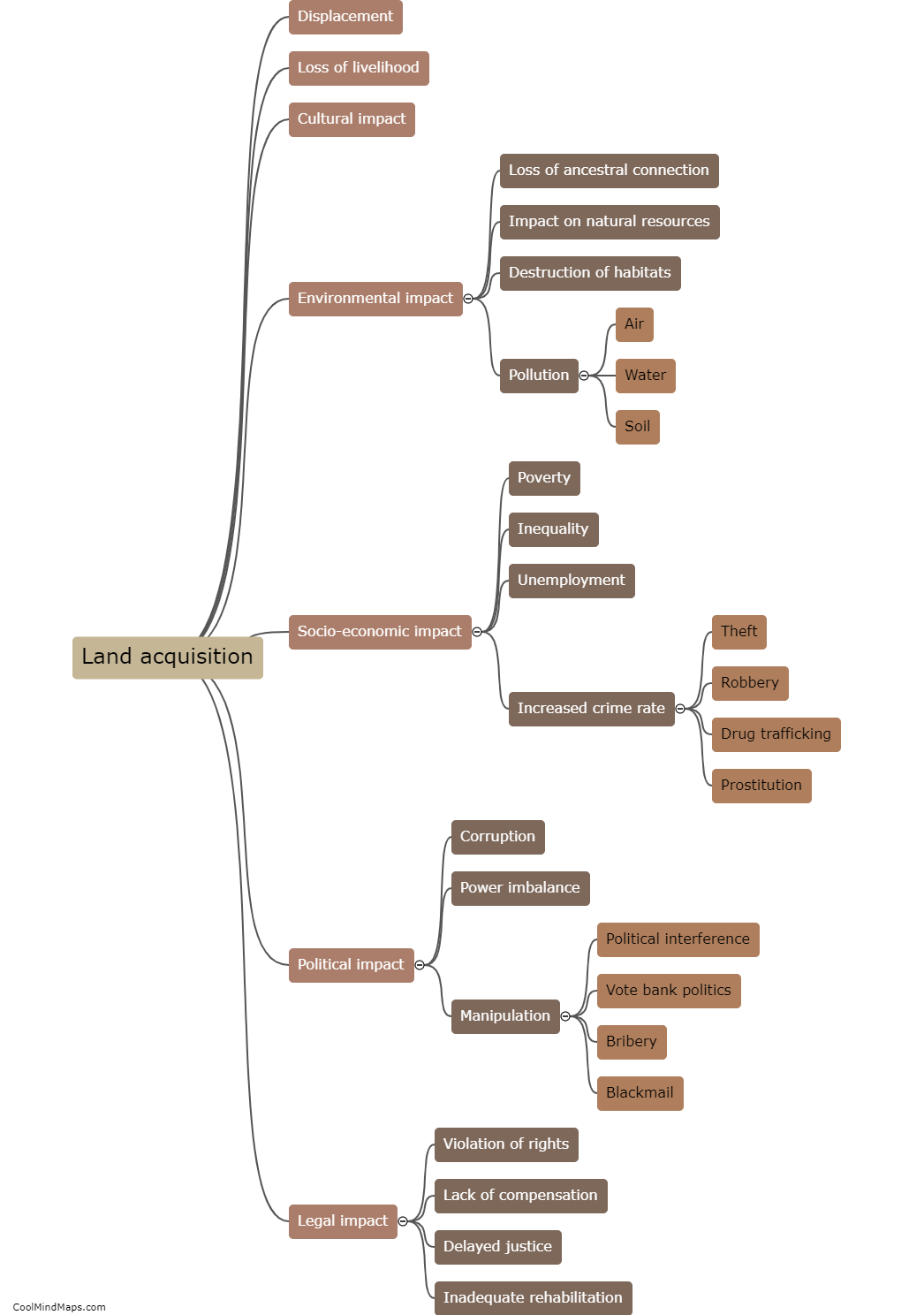
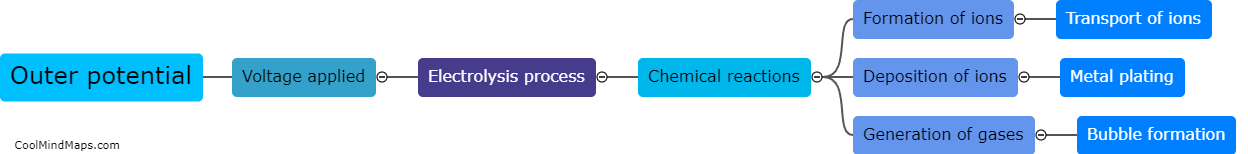
How does outer potential affect electrolysis?
The outer potential, also known as the applied voltage or electric potential difference, plays a crucial role in electrolysis. Electrolysis is a process that involves the decomposition of a compound into its constituent ions through the use of an electric current. The outer potential is responsible for driving this current through the electrolyte solution. It determines the rate at which the electrolysis reaction occurs by controlling the flow of electrons to the electrode surfaces. A higher outer potential will result in a more significant electron flow, leading to a faster electrolysis reaction. On the other hand, a lower outer potential will slow down the reaction. Thus, the outer potential directly influences the efficiency and speed of electrolysis processes.
This mind map was published on 27 November 2023 and has been viewed 103 times.