How can nanobots be controlled and monitored?
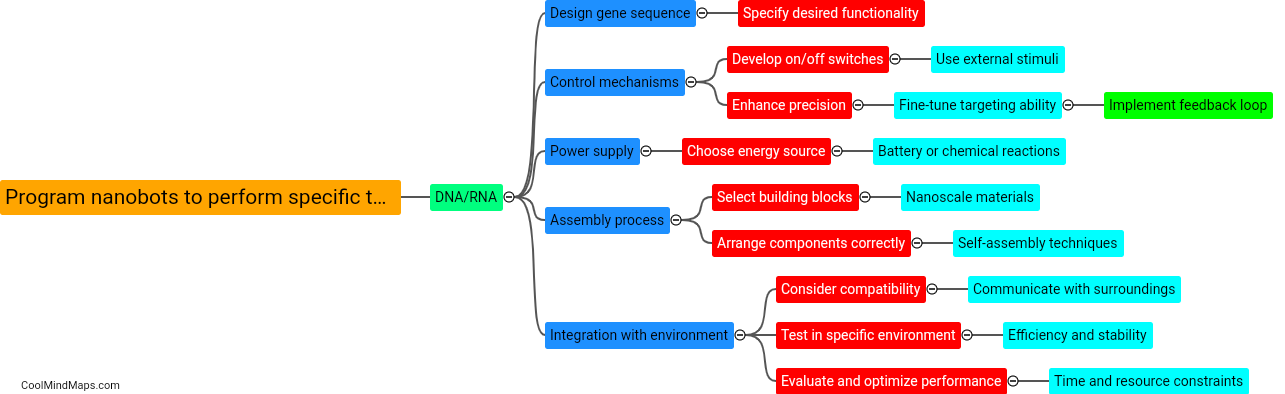
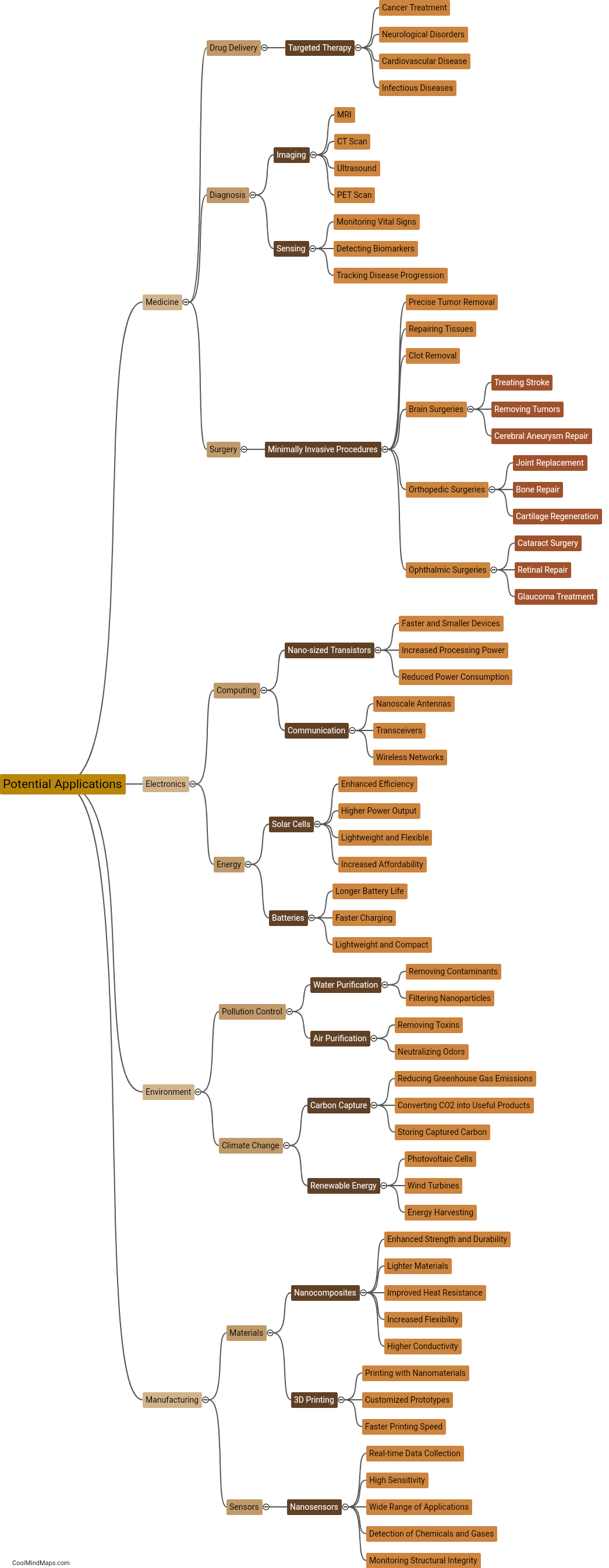
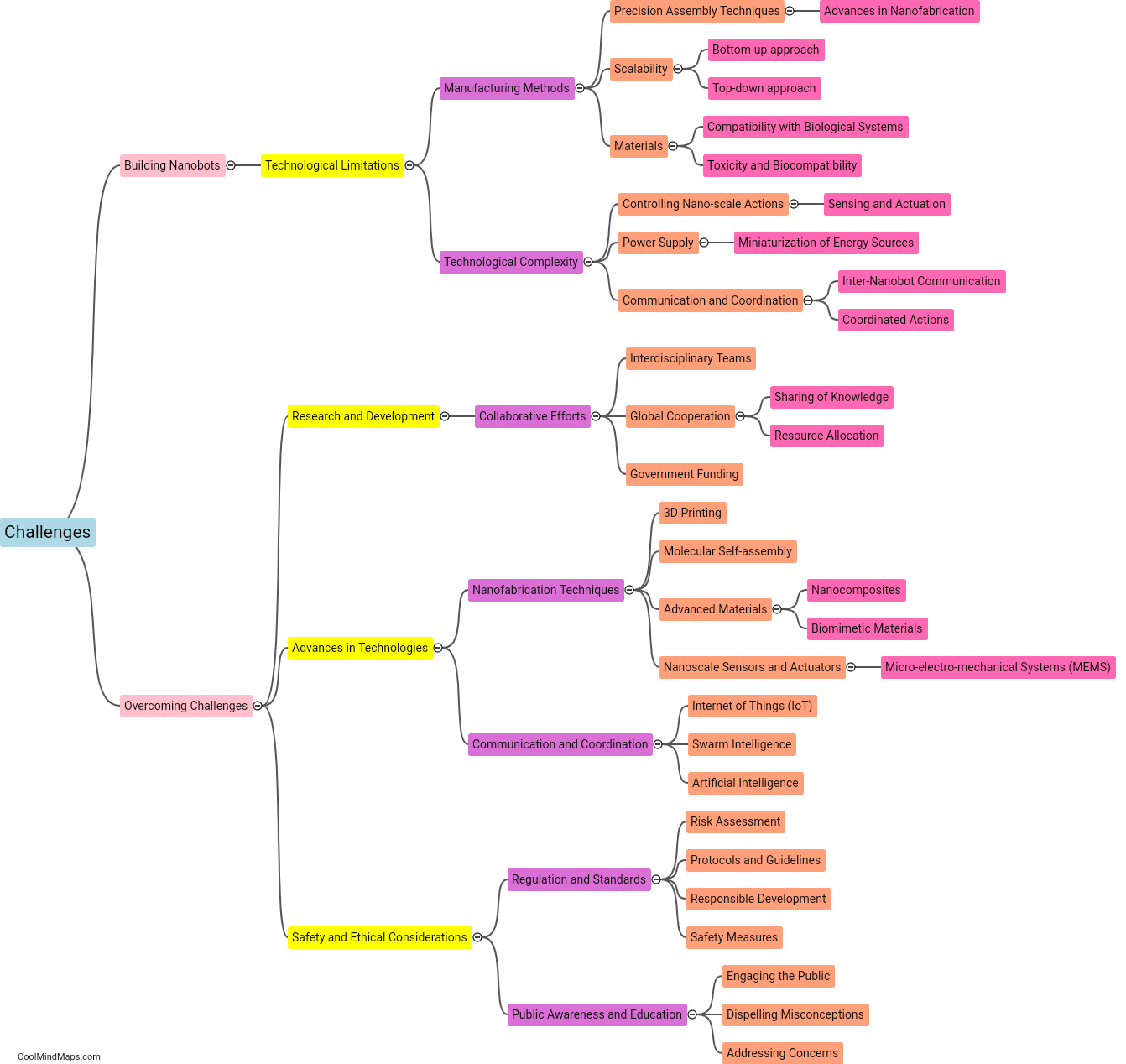
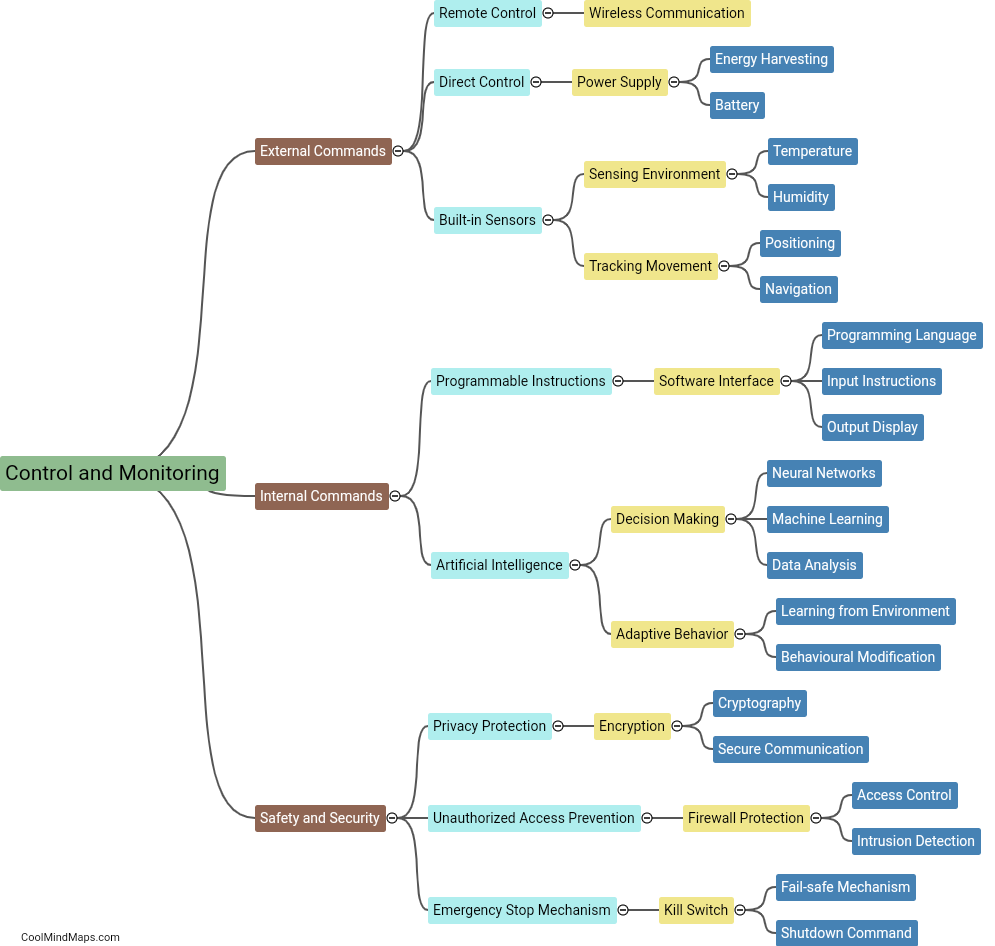
Nanobots, which are minute robots designed to perform specific tasks at the nanoscale, can be controlled and monitored using various techniques. One approach is to utilize external systems such as magnetic fields, acoustic waves, or optical signals to direct their movement or activation. Magnetic fields can be employed to guide nanobots, while acoustic waves can be used for both control and monitoring purposes. Additionally, nanobots can be equipped with light-sensitive materials that react to specific wavelengths, allowing them to be controlled and monitored using optical signals. Other methods involve implanting sensors within the nanobots to monitor their position, activity, or even physiological changes in the body. These sensors can transmit data wirelessly or through wired connections, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of nanobot behavior. The development of control and monitoring systems for nanobots is a critical aspect of their potential use in various fields, including medicine, manufacturing, and environmental monitoring.
This mind map was published on 21 July 2023 and has been viewed 119 times.