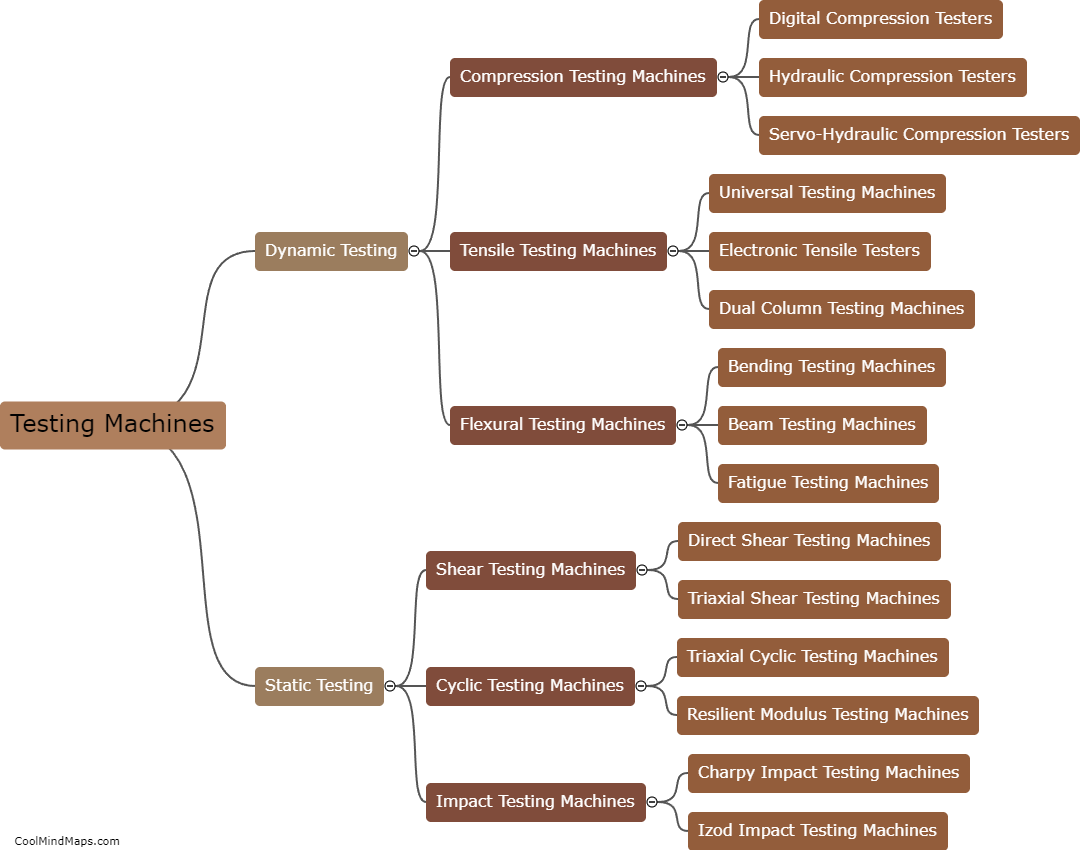
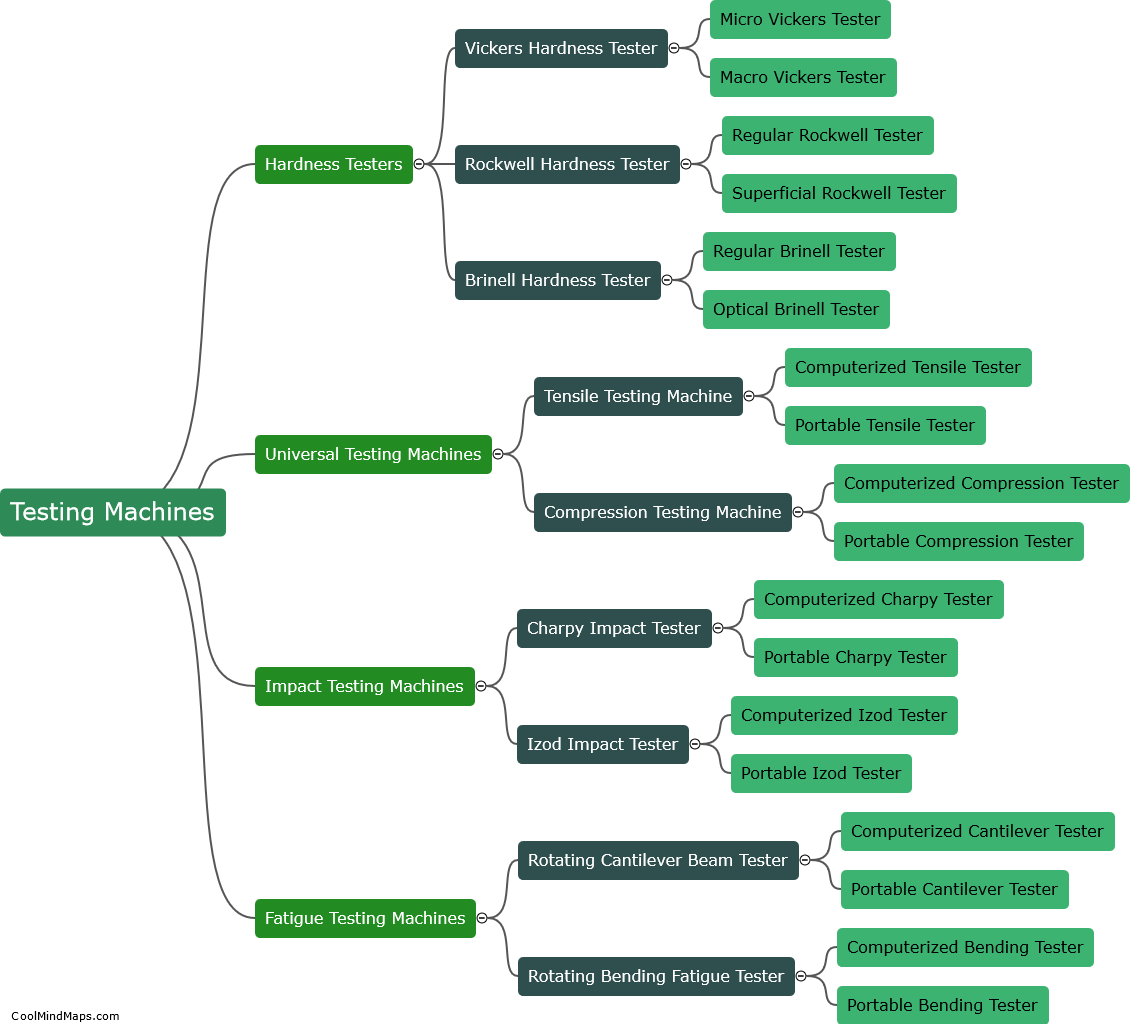
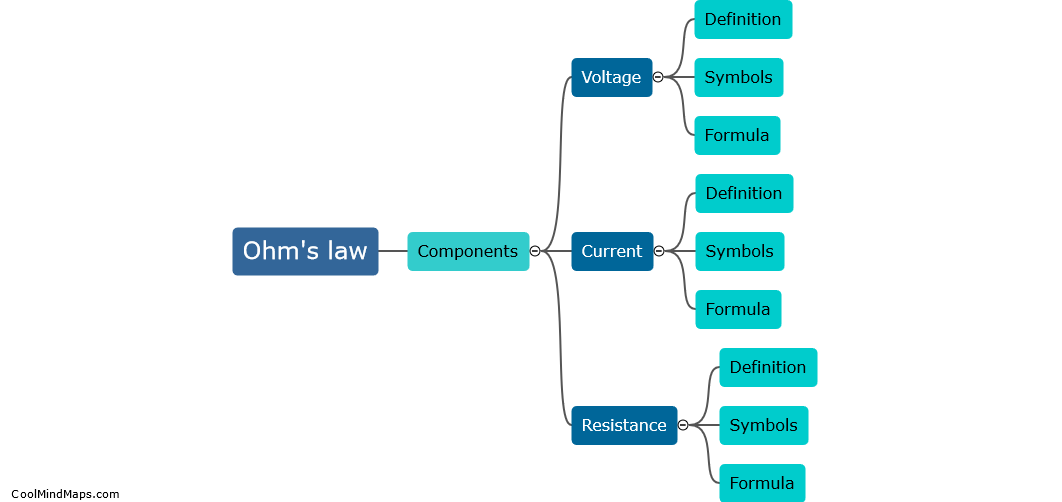
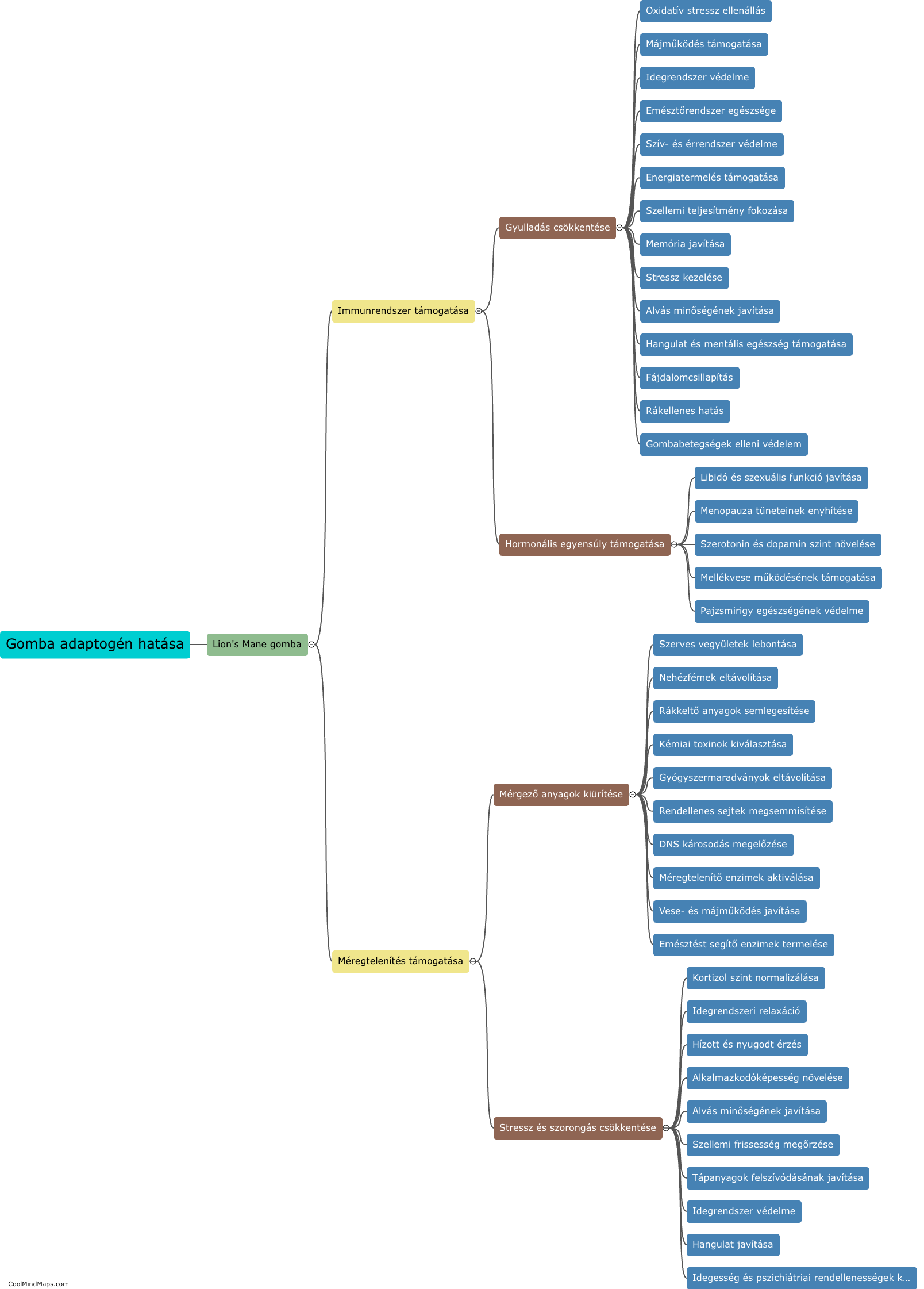
How do you calculate voltage in Ohm's law?
In Ohm's law, voltage can be calculated by multiplying the current flowing through a component by its resistance. The formula for voltage is V = I * R, where V represents the voltage, I represents the current, and R represents the resistance. This equation implies that voltage is directly proportional to the current and resistance. Therefore, if either the current or resistance increases, the voltage across the component will also increase. Similarly, decreasing the current or resistance will result in a decrease in voltage. Ohm's law is a fundamental principle in electrical circuit analysis, used to determine the voltage drop across a resistor or to calculate the voltage supplied by a source.

This mind map was published on 2 August 2023 and has been viewed 124 times.