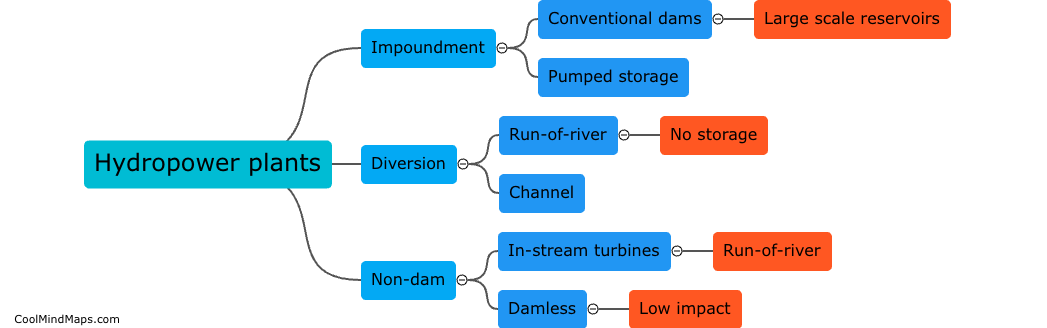
Types of hydropower plants?
There are three main types of hydropower plants: conventional, pumped storage, and run-of-river. Conventional hydropower plants use the force of flowing water to turn a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. Pumped storage plants store energy by pumping water into a reservoir during low-demand periods and releasing it to generate electricity during high-demand periods. Run-of-river plants do not require a reservoir and instead use the natural flow of the river to generate electricity, often with minimal impact on the environment. Each type of hydropower plant has its own benefits and considerations depending on location and energy needs.
This mind map was published on 24 May 2024 and has been viewed 106 times.