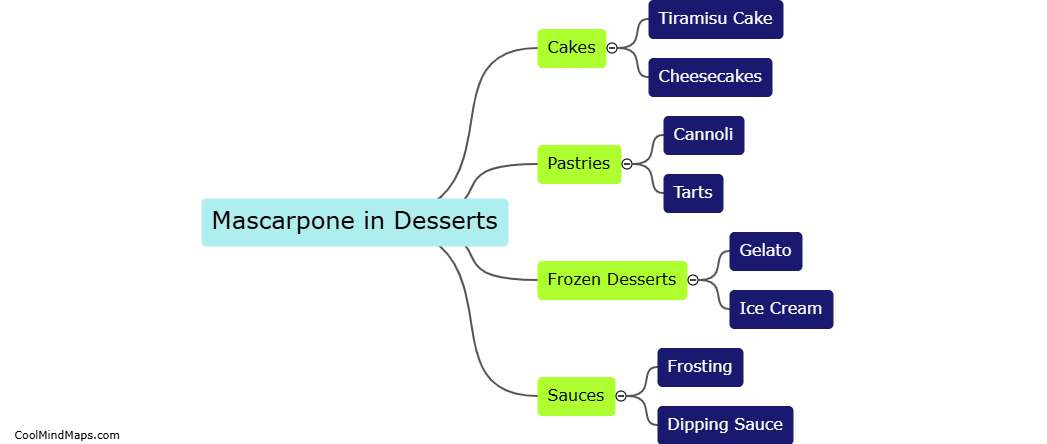
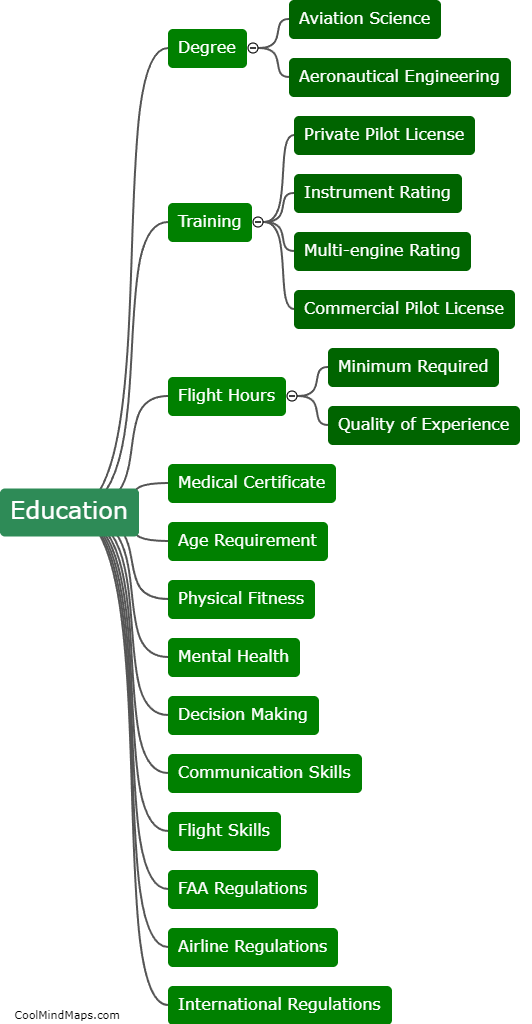
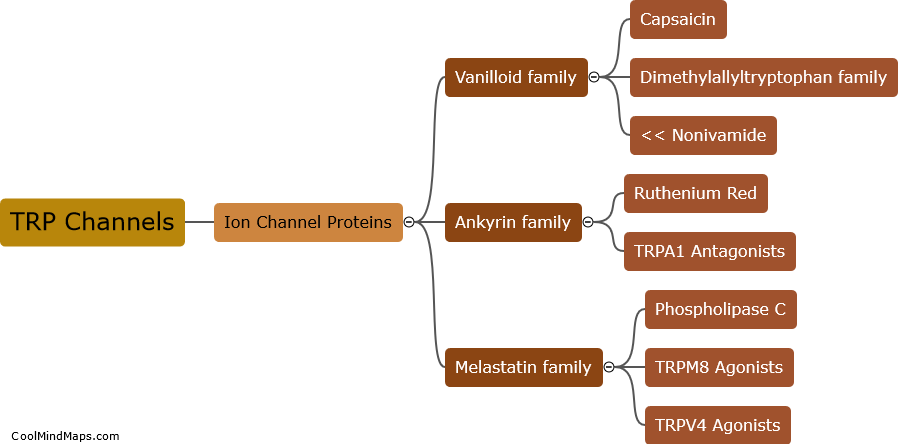
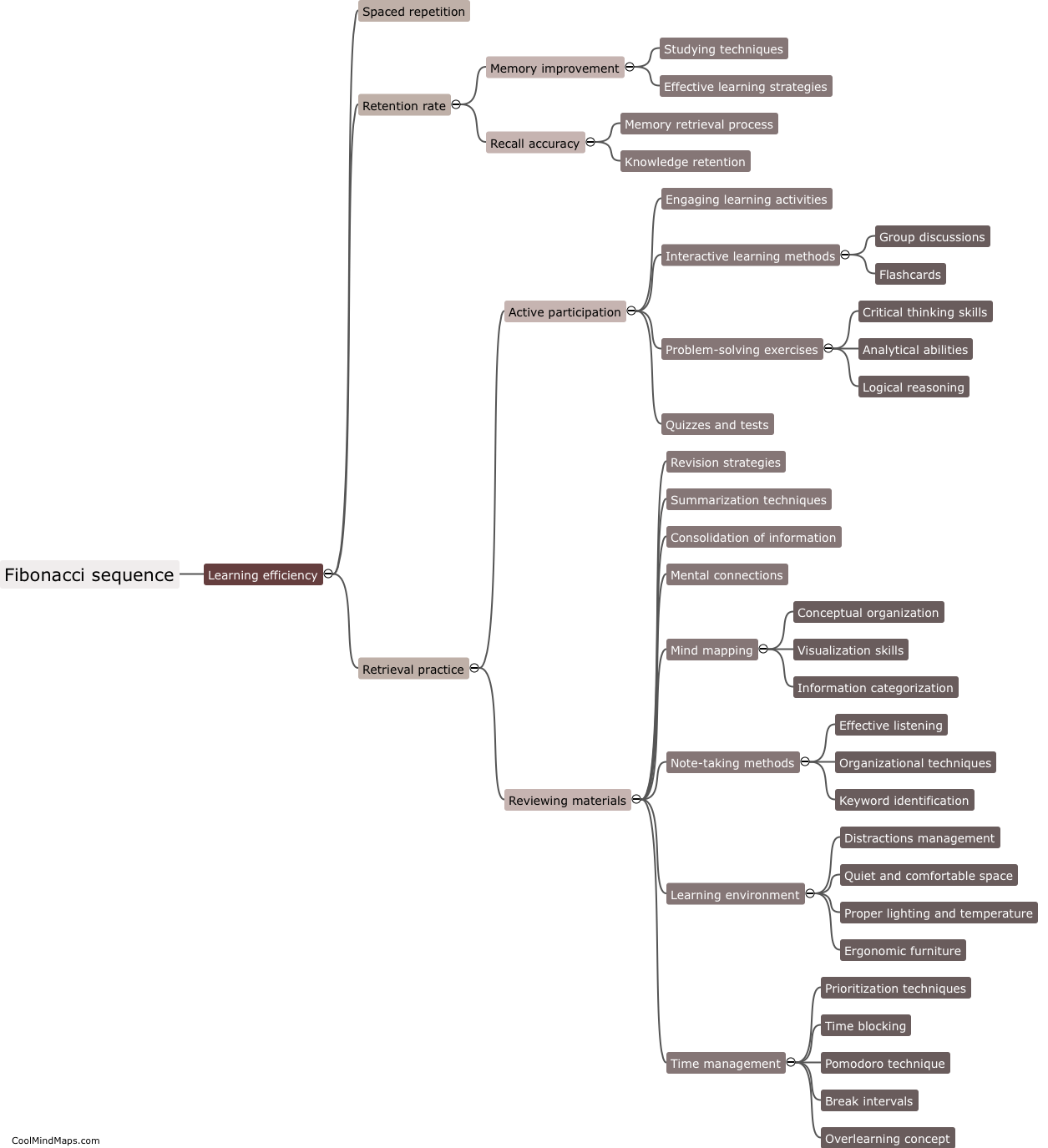
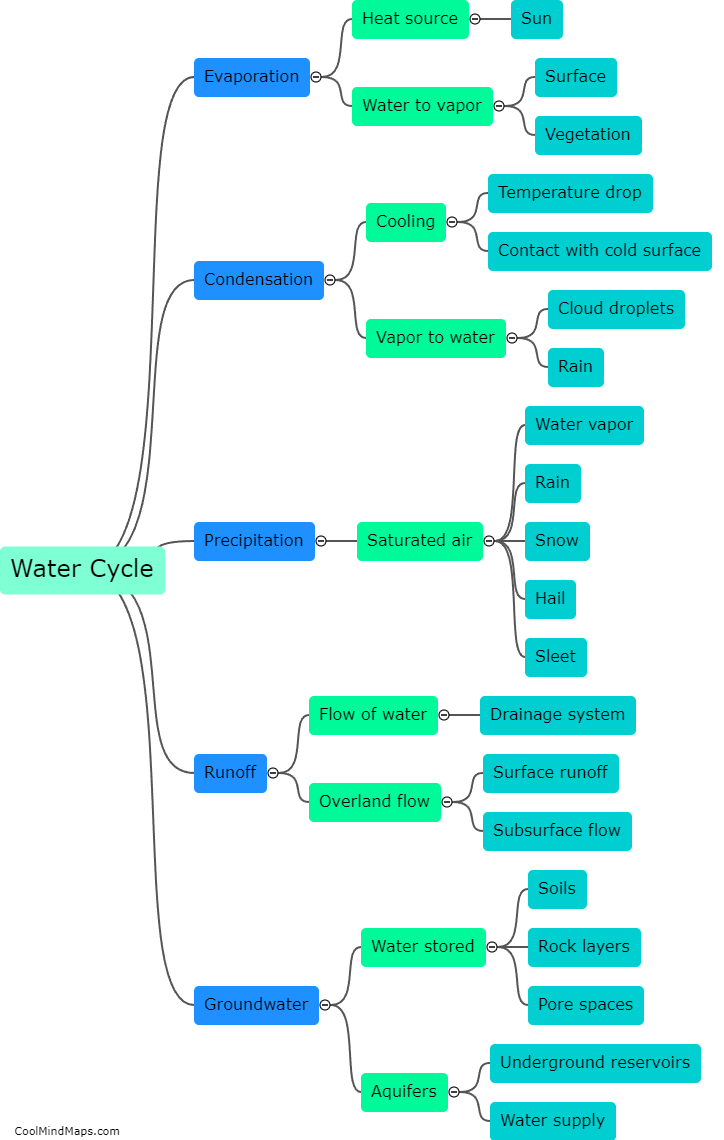
What are the steps of the water cycle?
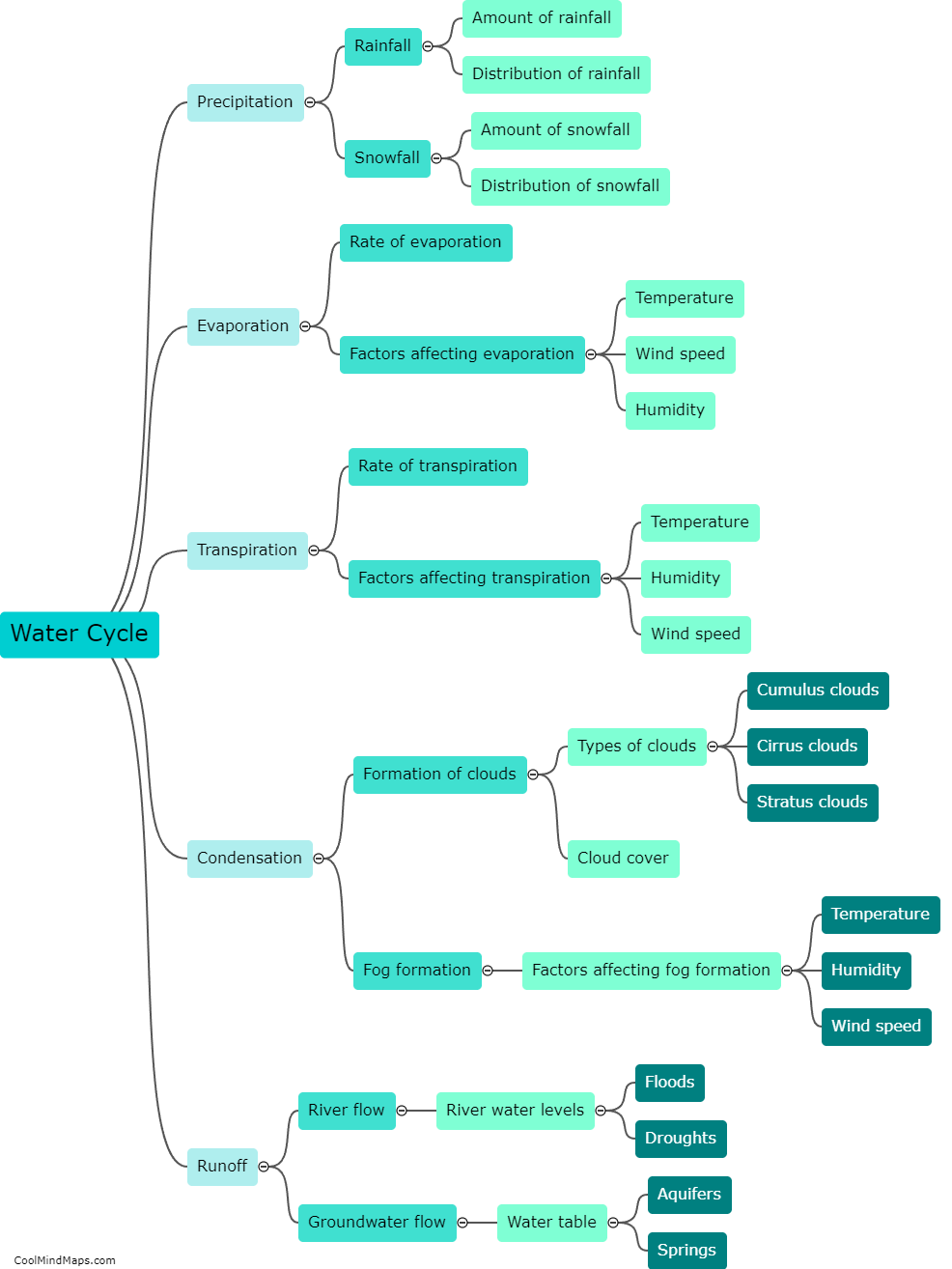
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. It consists of several key steps. Firstly, evaporation occurs when water from oceans, lakes, or other sources turns into water vapor due to heat from the sun. This vapor then rises into the atmosphere. The second step is condensation, where the water vapor cools and changes back into liquid form, forming clouds. Next, precipitation occurs as water droplets in the clouds combine and fall to the ground as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. The fourth step is surface runoff, where the precipitation flows over the land's surface and collects in rivers, lakes, and oceans. Some of this water is then absorbed into the ground through infiltration, becoming groundwater. The final step is transpiration, where plants release water vapor from their leaves into the atmosphere. This completes the water cycle, a vital process that helps sustain life on Earth.
This mind map was published on 27 November 2023 and has been viewed 81 times.