What is the Constitution of Trinidad and Tobago?
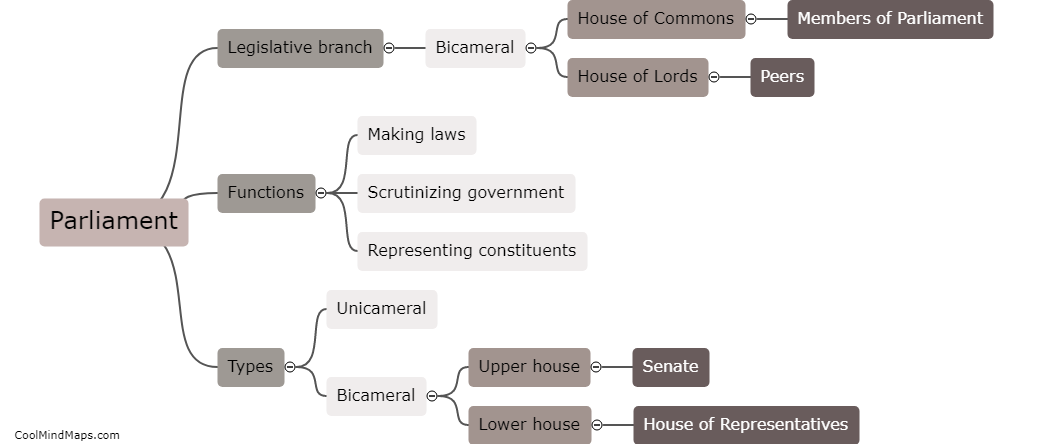
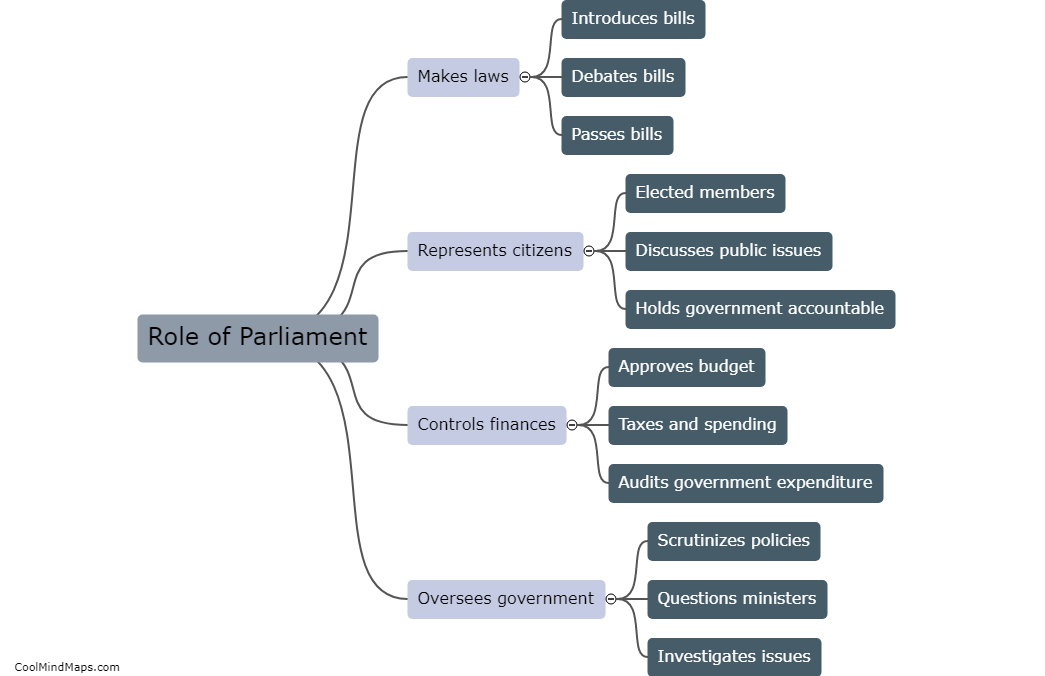
The Constitution of Trinidad and Tobago is the supreme law of the twin-island nation, providing the framework for governance and outlining the rights and responsibilities of citizens, government officials, and institutions. It was adopted in September 1976, following the nation's attainment of Republican status, and has undergone several amendments since then. The Constitution is divided into a preamble and ten parts, covering topics such as citizenship, fundamental human rights and freedoms, the executive branch, the judiciary, the Parliament, and local government. It is pivotal to the functioning of Trinidad and Tobago's democracy and serves as a vital guide for the country's legal system and decision-making processes.

This mind map was published on 15 June 2023 and has been viewed 182 times.