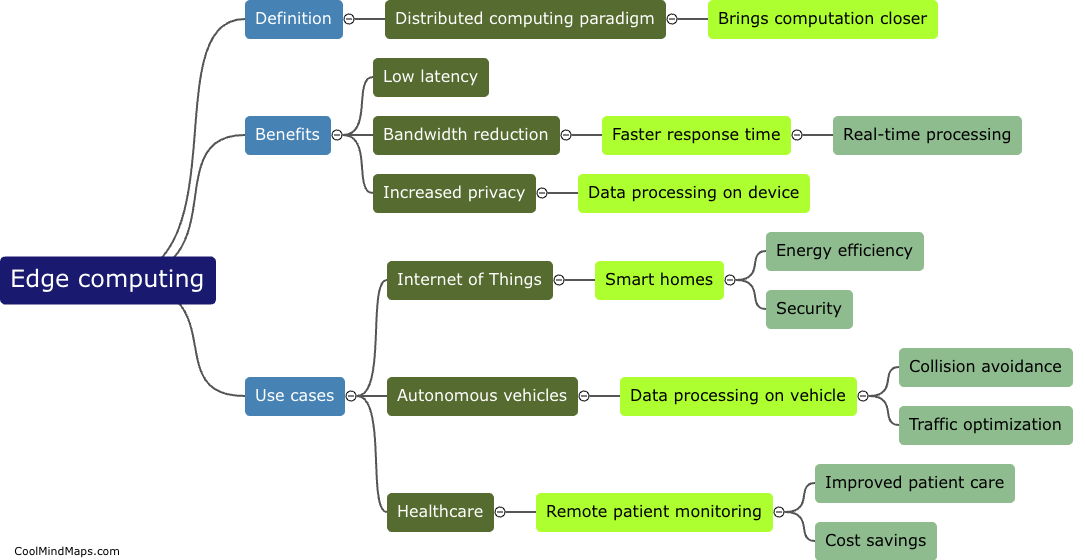
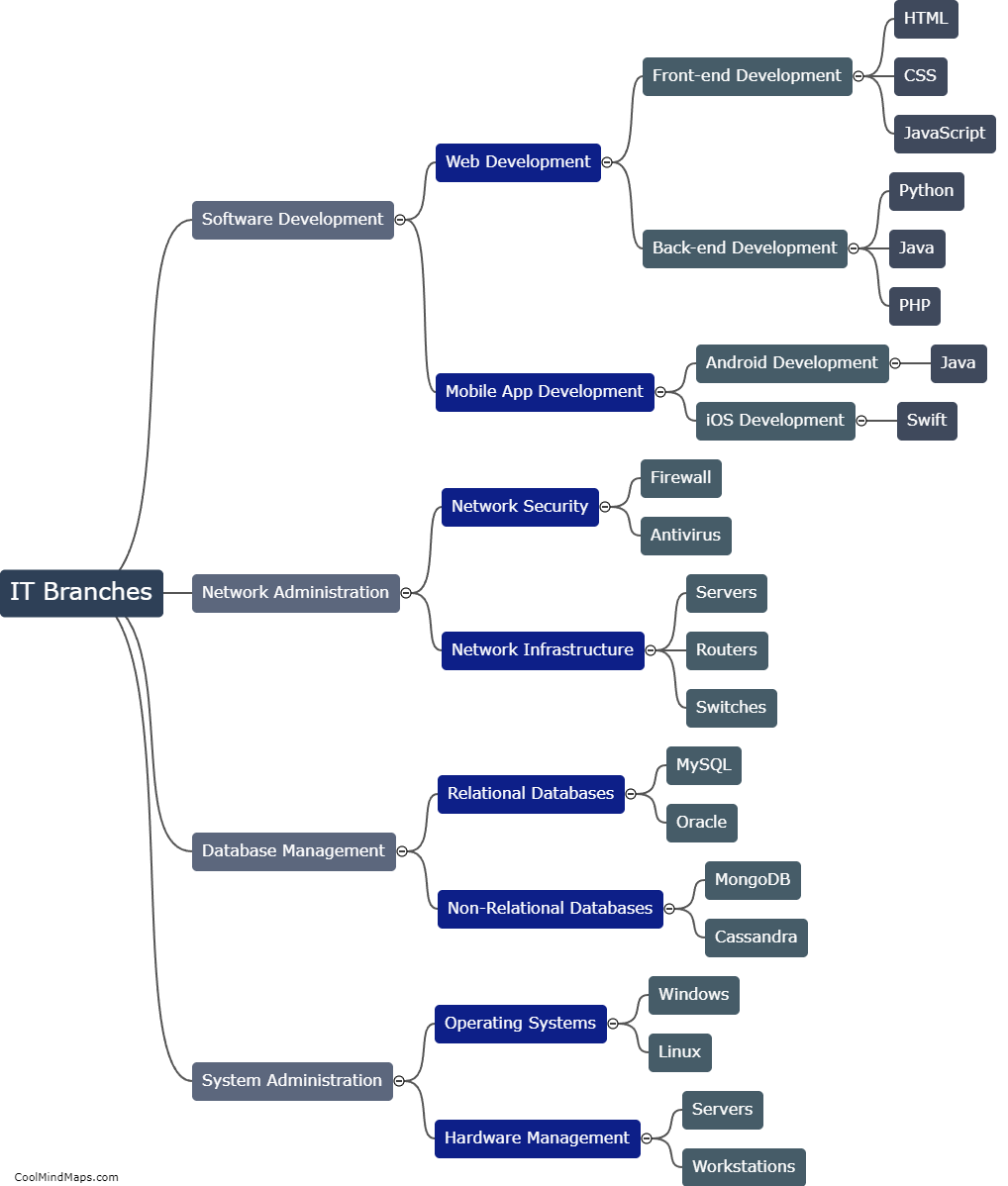
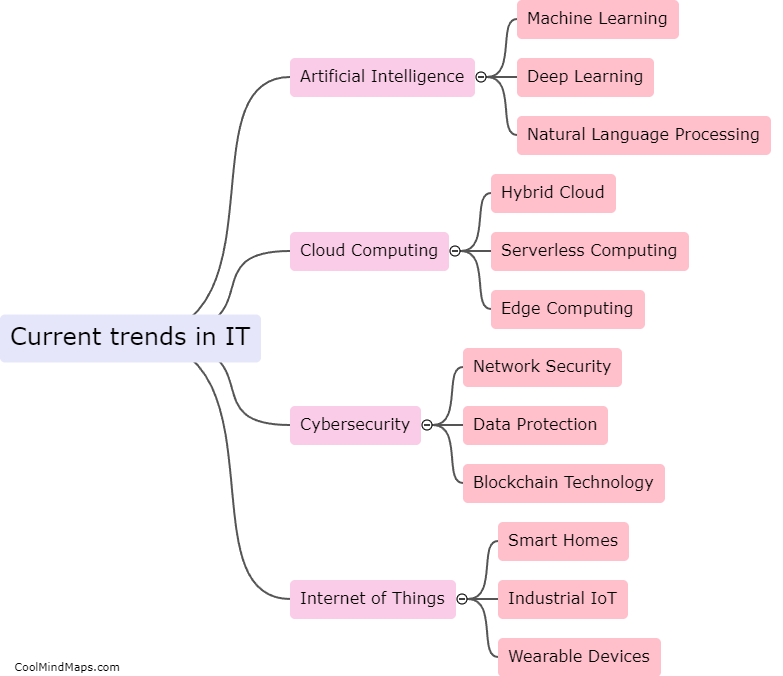
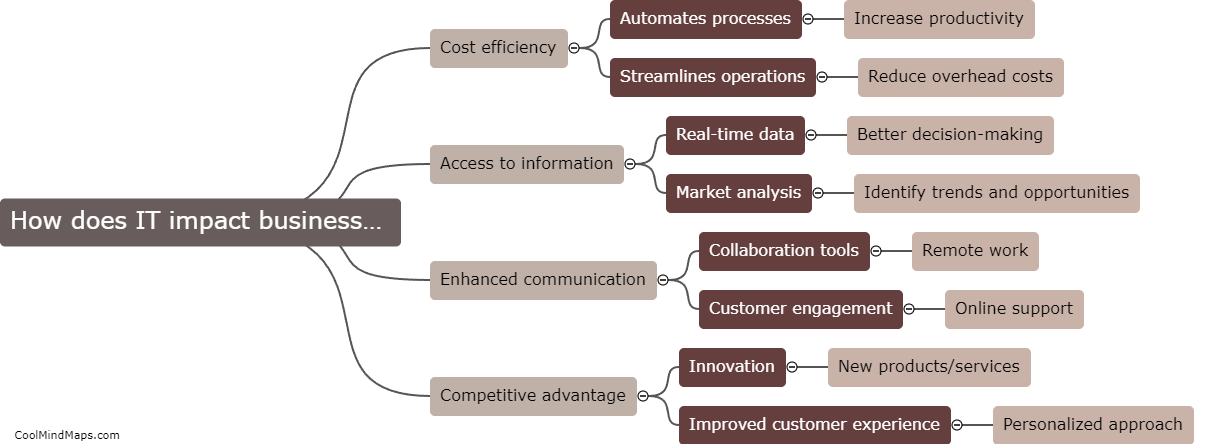
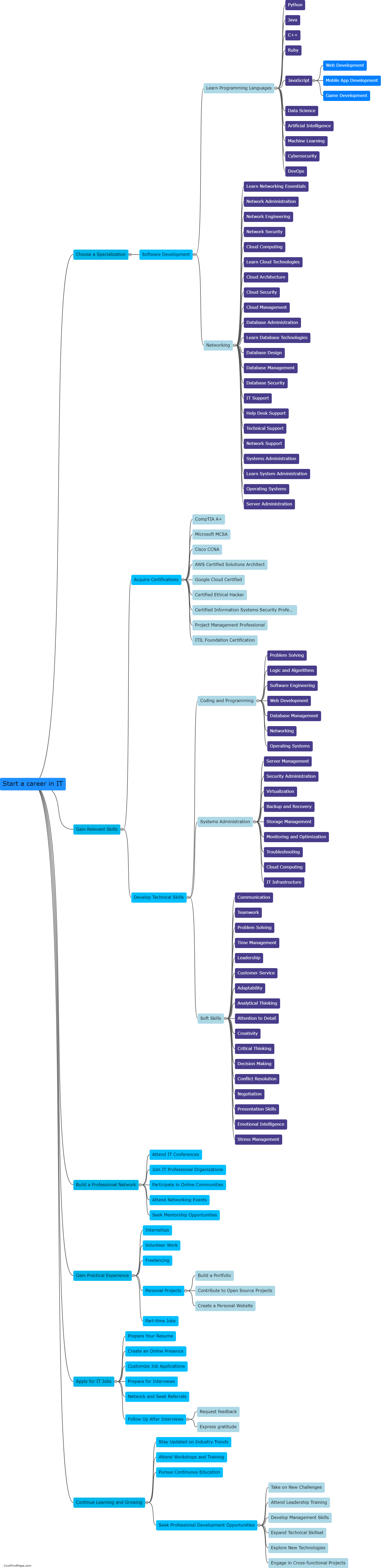
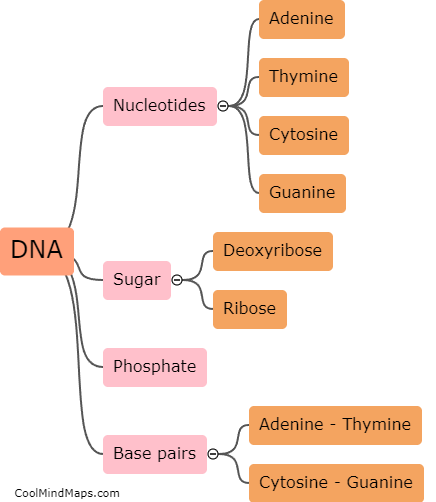
How does DNA replicate?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its genetic material to produce two identical copies of DNA. It is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. The process begins with the unwinding of the double-stranded DNA molecule, catalyzed by enzymes known as helicases. The unwound DNA strands then act as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands. DNA polymerase enzymes attach to the separated strands, adding nucleotides that match the template strand's sequence. This occurs in a semi-conservative manner, where each new DNA molecule formed consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. The replication process is highly accurate due to proofreading mechanisms that ensure the fidelity of DNA synthesis. Overall, DNA replication is a complex and precise mechanism crucial for the maintenance and propagation of genetic information.

This mind map was published on 5 October 2023 and has been viewed 115 times.