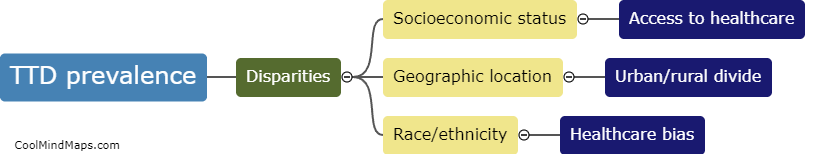
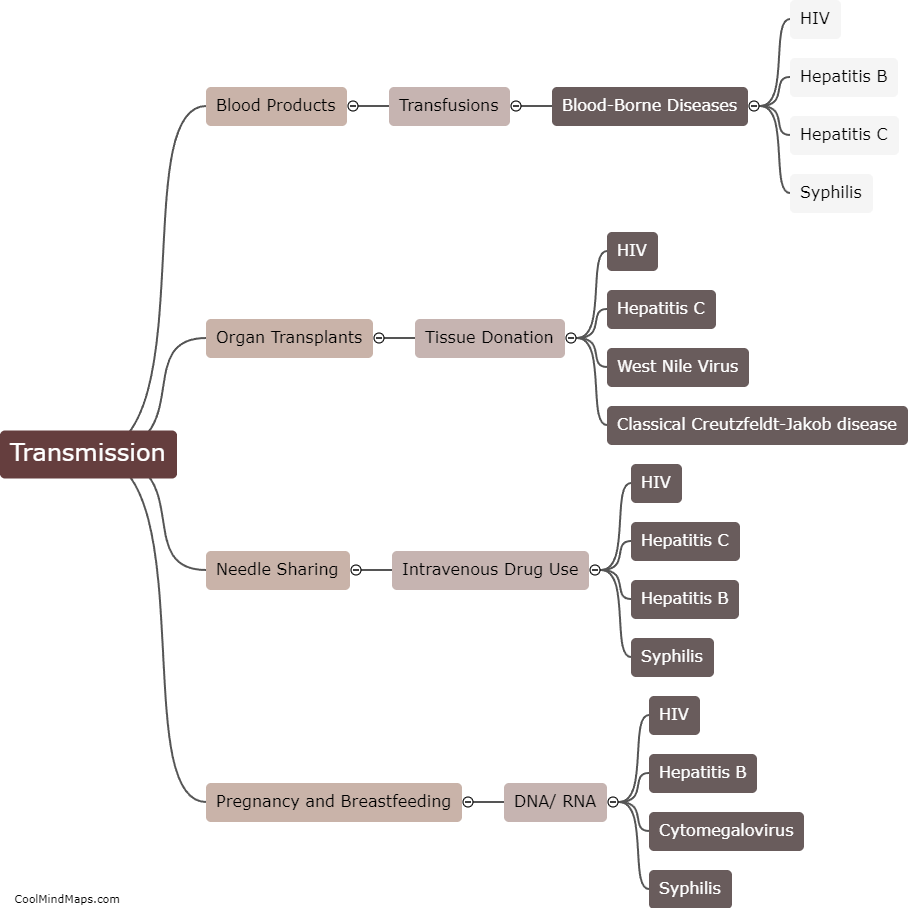
How are transfusion-transmitted diseases transmitted?
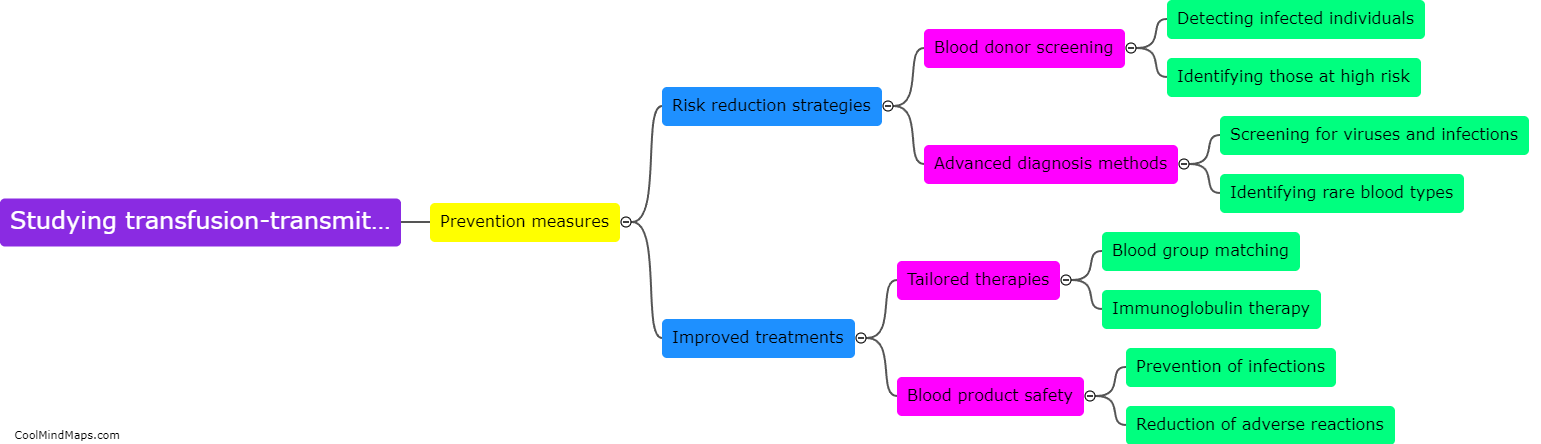
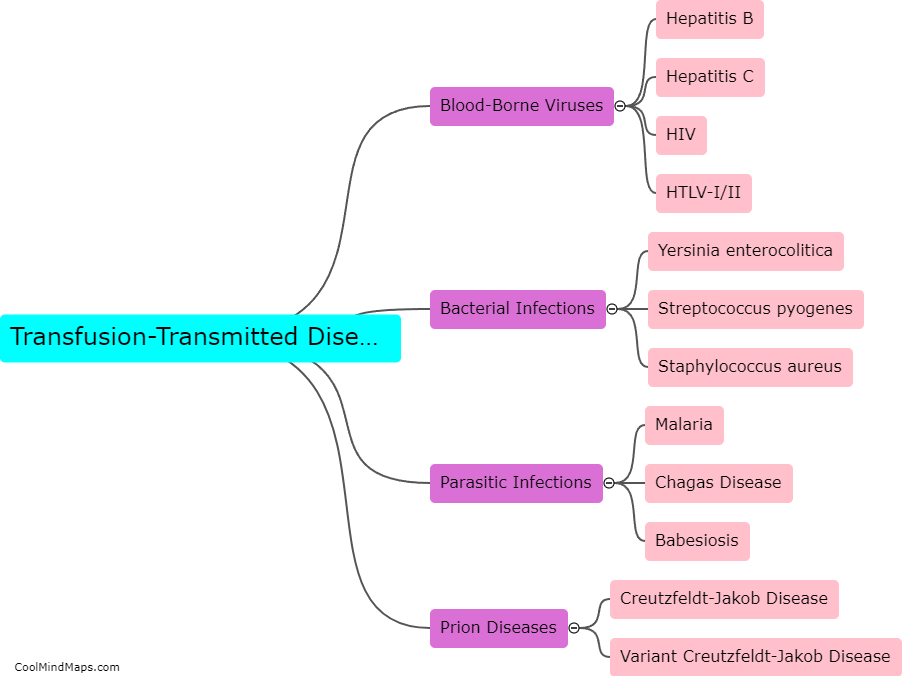
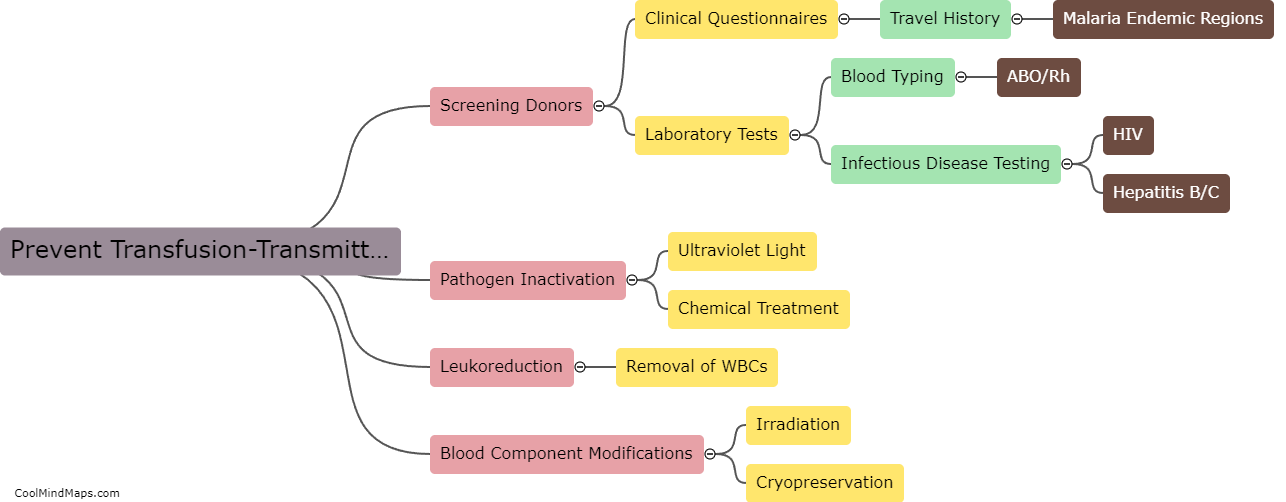
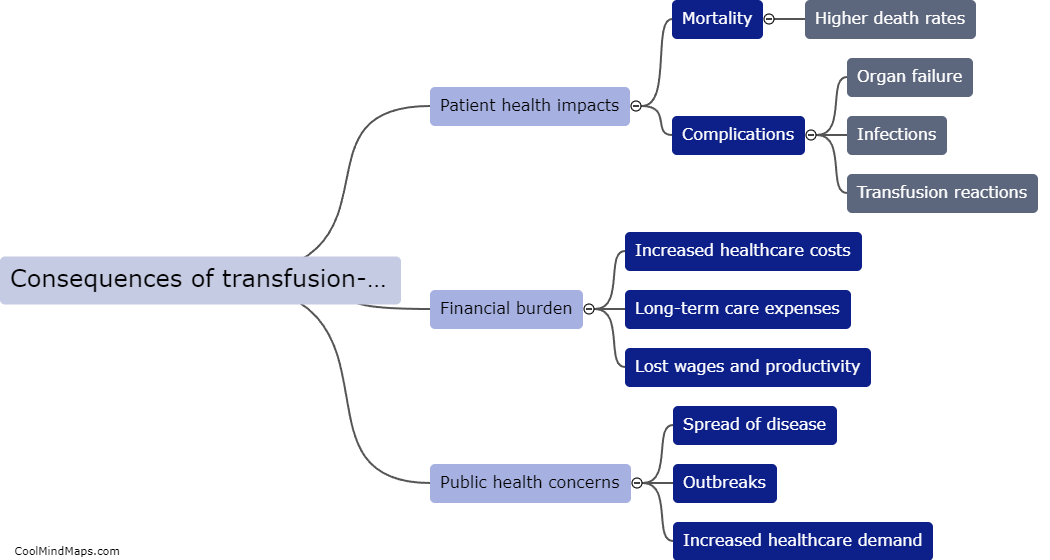
Transfusion-transmitted diseases (TTD) are infectious diseases that can be transmitted through blood transfusions. Various pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites can be transmitted through donated blood or blood components. When a recipient receives blood or blood components from an infected donor, the pathogens can enter the recipient's bloodstream and cause illness. TTD can be prevented through screening of donated blood, effective blood testing, and proper blood processing procedures. Nonetheless, the risk of TTD transmission is still present and can be mitigated through rigorous screening, testing, and processing procedures.
This mind map was published on 25 June 2023 and has been viewed 127 times.