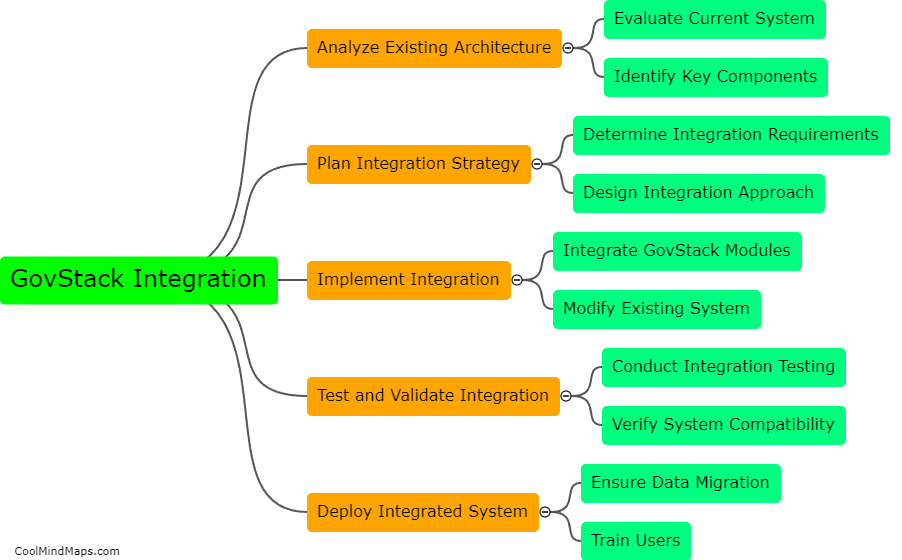
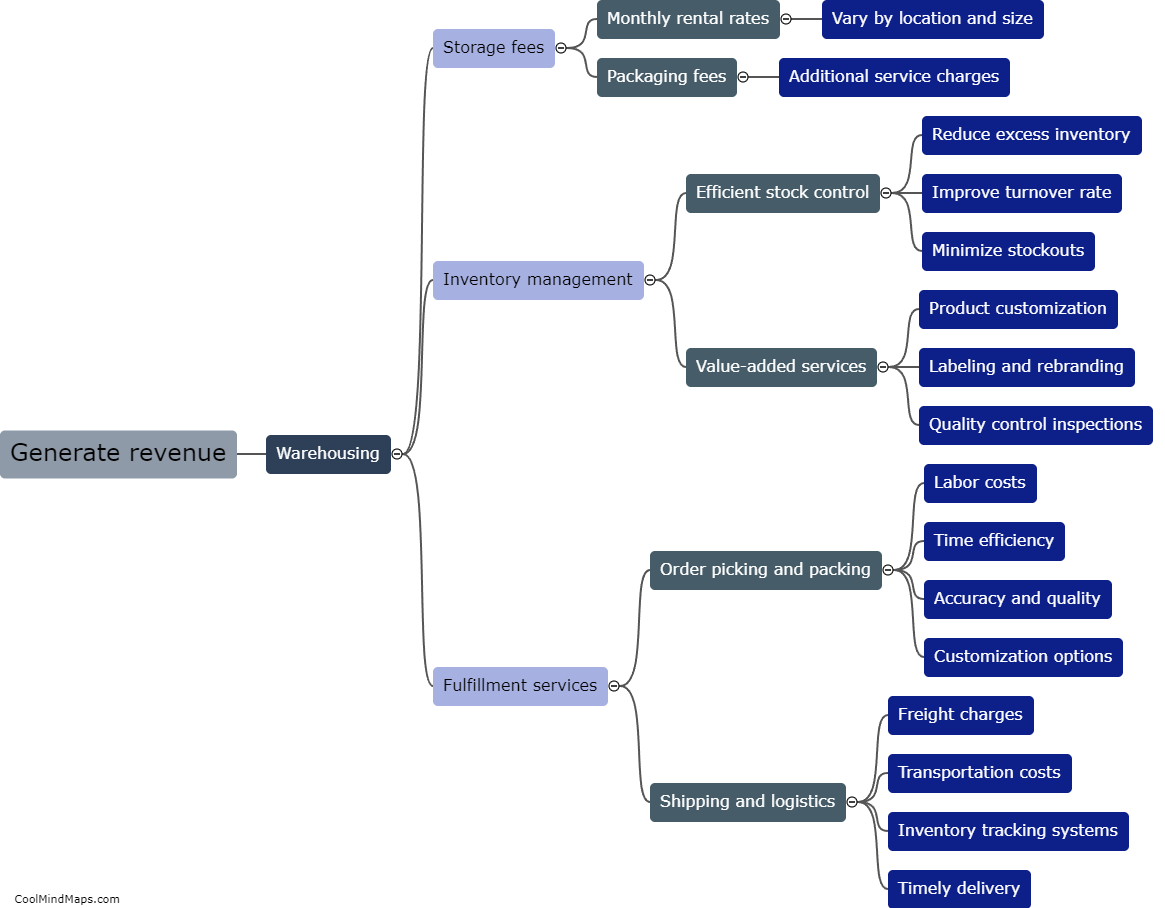
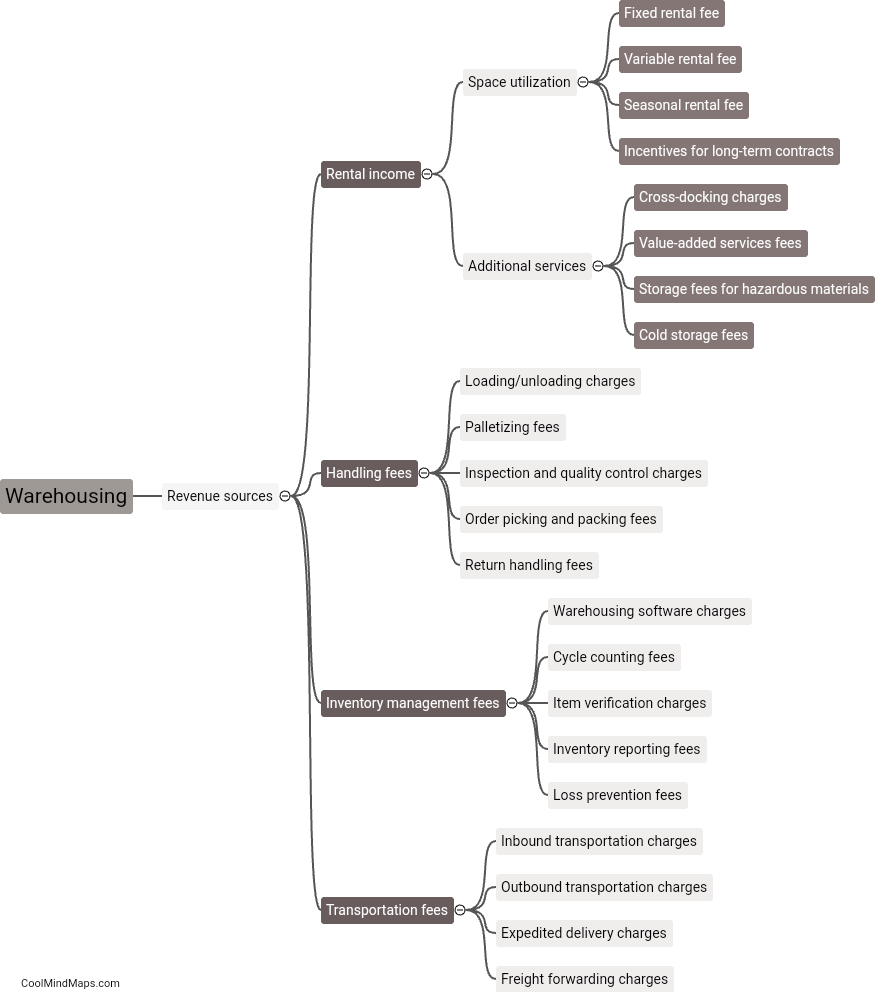
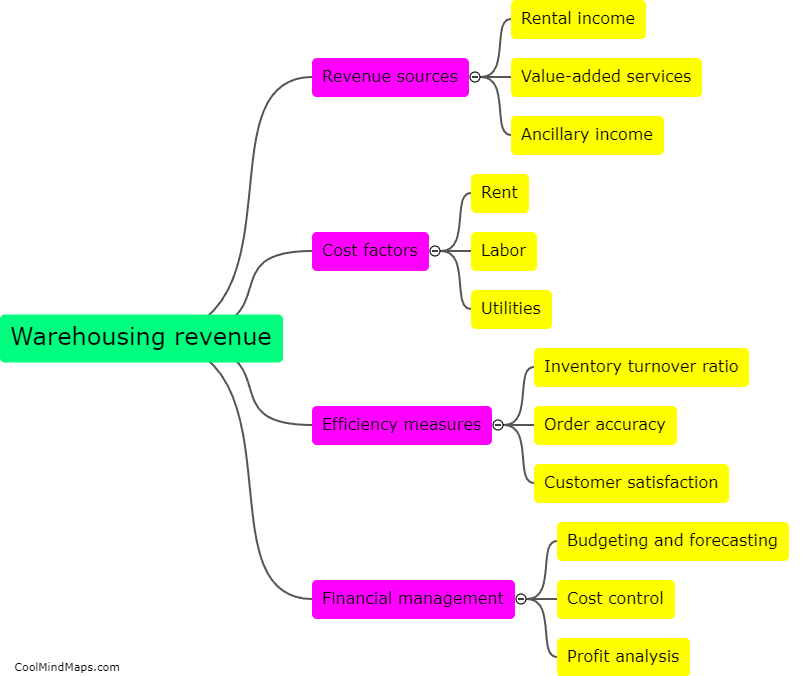
What are the main metabolic processes in cellular respiration?
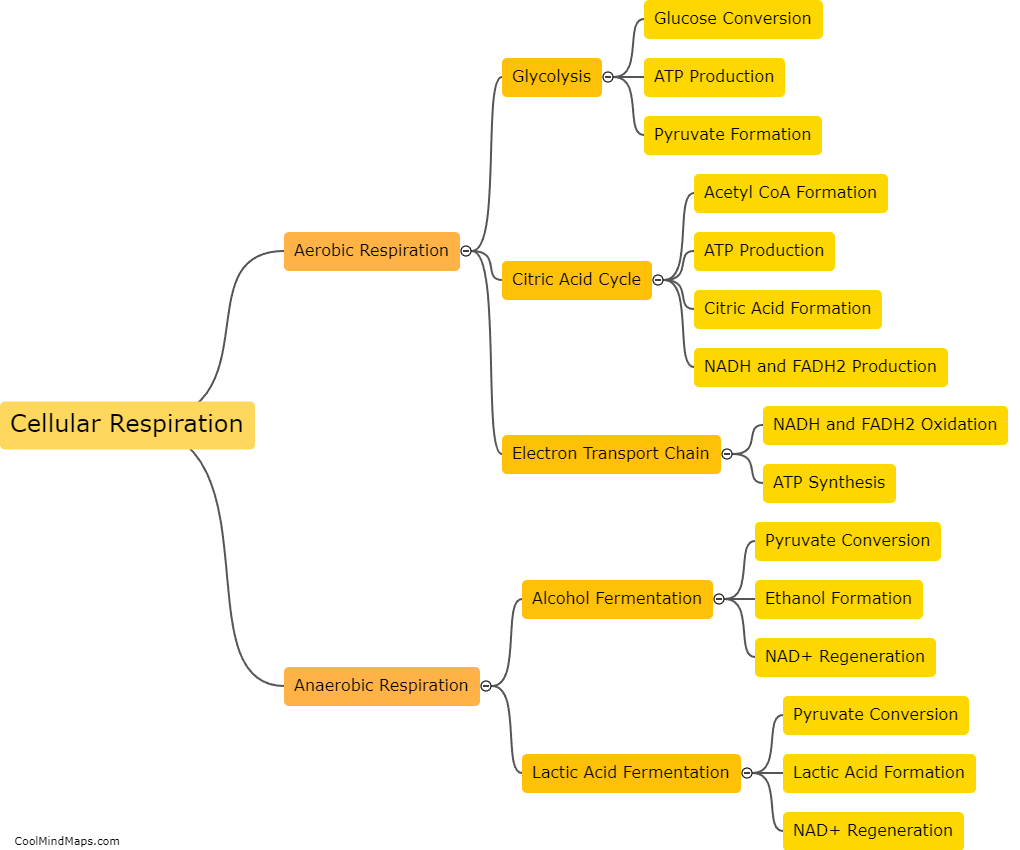
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The main metabolic processes involved in cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and high-energy molecules of NADH. The citric acid cycle takes place within the mitochondria and involves the further breakdown of pyruvate, generating more ATP, NADH, and FADH2. Finally, oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the electron transport chain to generate a large amount of ATP through chemiosmosis. Overall, these metabolic processes in cellular respiration play a crucial role in providing cells with the energy they need to carry out their various functions.
This mind map was published on 10 September 2023 and has been viewed 109 times.