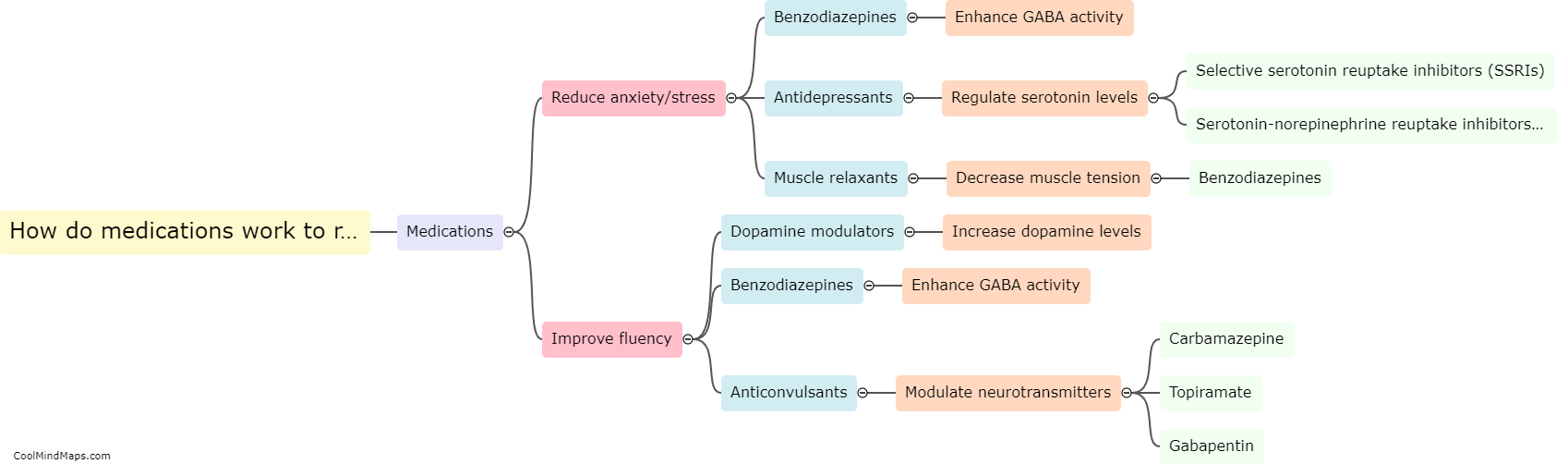
How do these medications work to reduce stuttering?
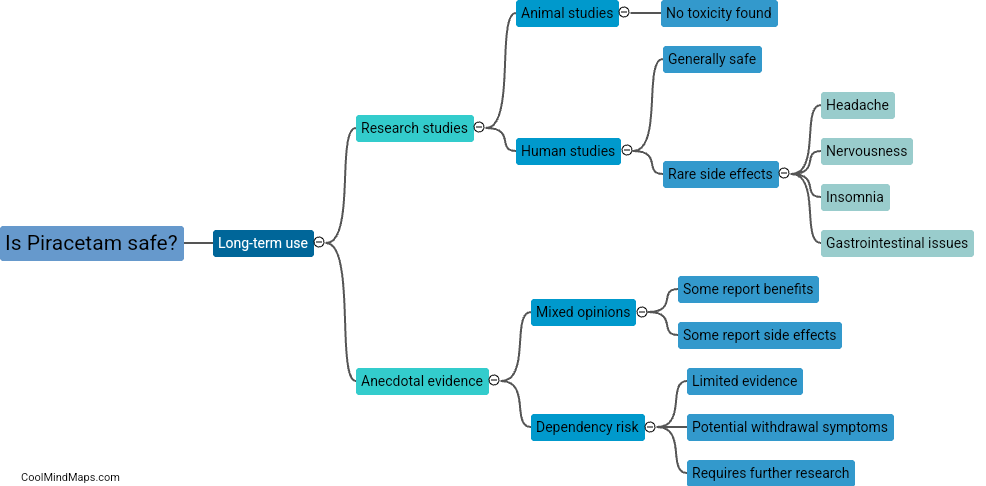
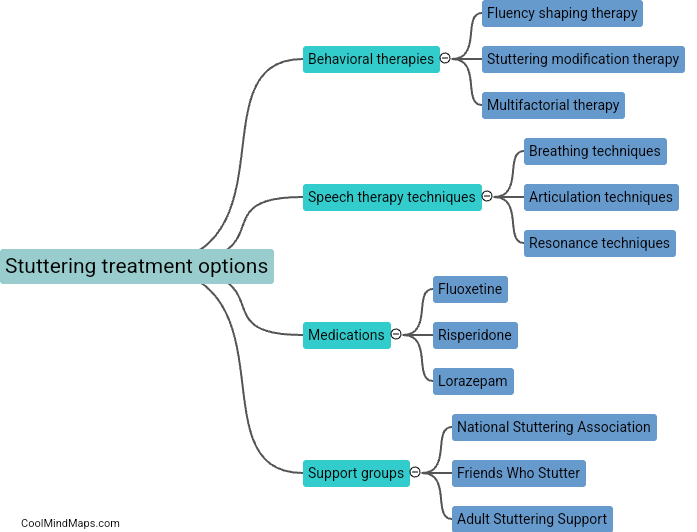
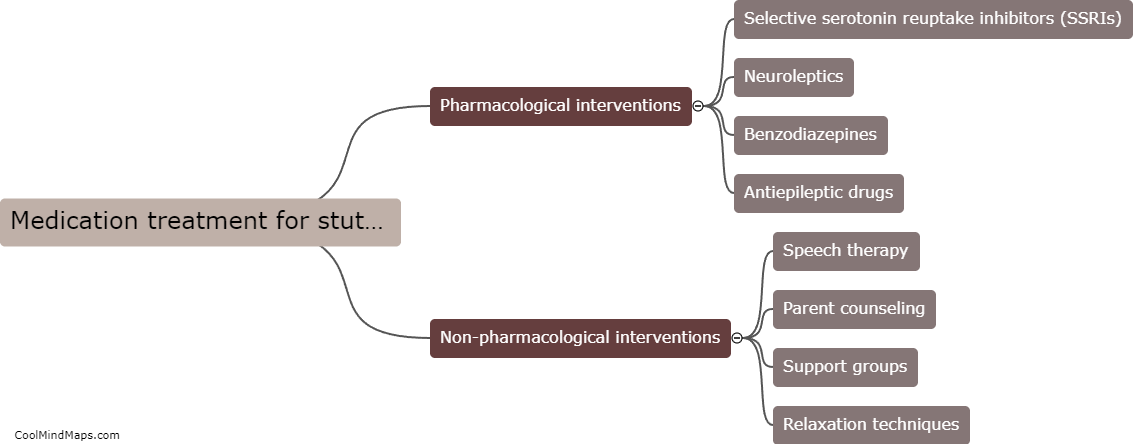
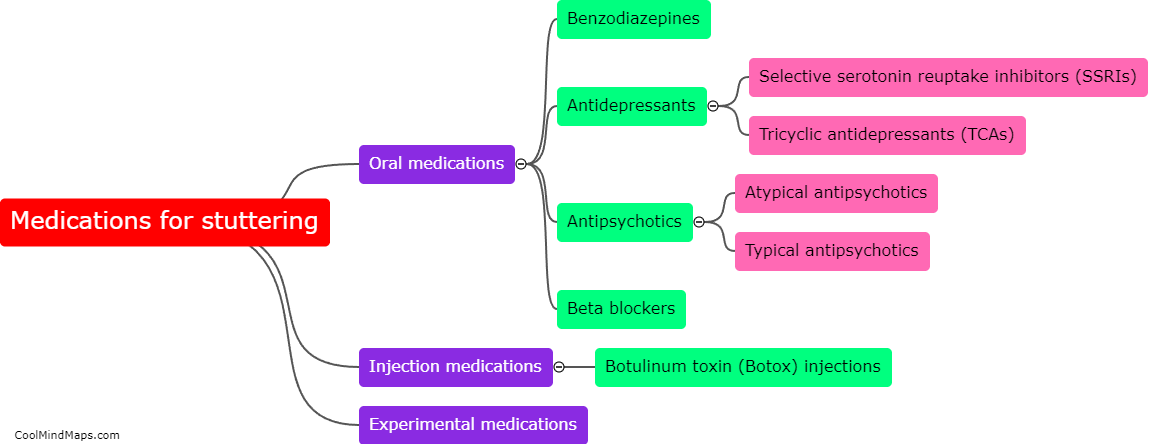
Medications used to reduce stuttering, such as antipsychotics, antidepressants, and benzodiazepines, primarily target the brain's neurotransmitters and their receptors. These medications work by altering the balance of chemicals in the brain to regulate the transmission of nerve signals associated with speech production. Antipsychotics like clozapine and risperidone, which act by blocking dopamine receptors, have been found to reduce the severity of stuttering symptoms. Similarly, medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including fluoxetine and paroxetine, increase the availability of serotonin in the brain, regulating mood and potentially improving speech fluency. Benzodiazepines like clonazepam work by enhancing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity in the brain, which helps to reduce anxiety and subsequently may alleviate stuttering symptoms. However, it is important to note that medications are typically used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for stuttering, which may also include speech therapy and other interventions.
This mind map was published on 26 October 2023 and has been viewed 103 times.