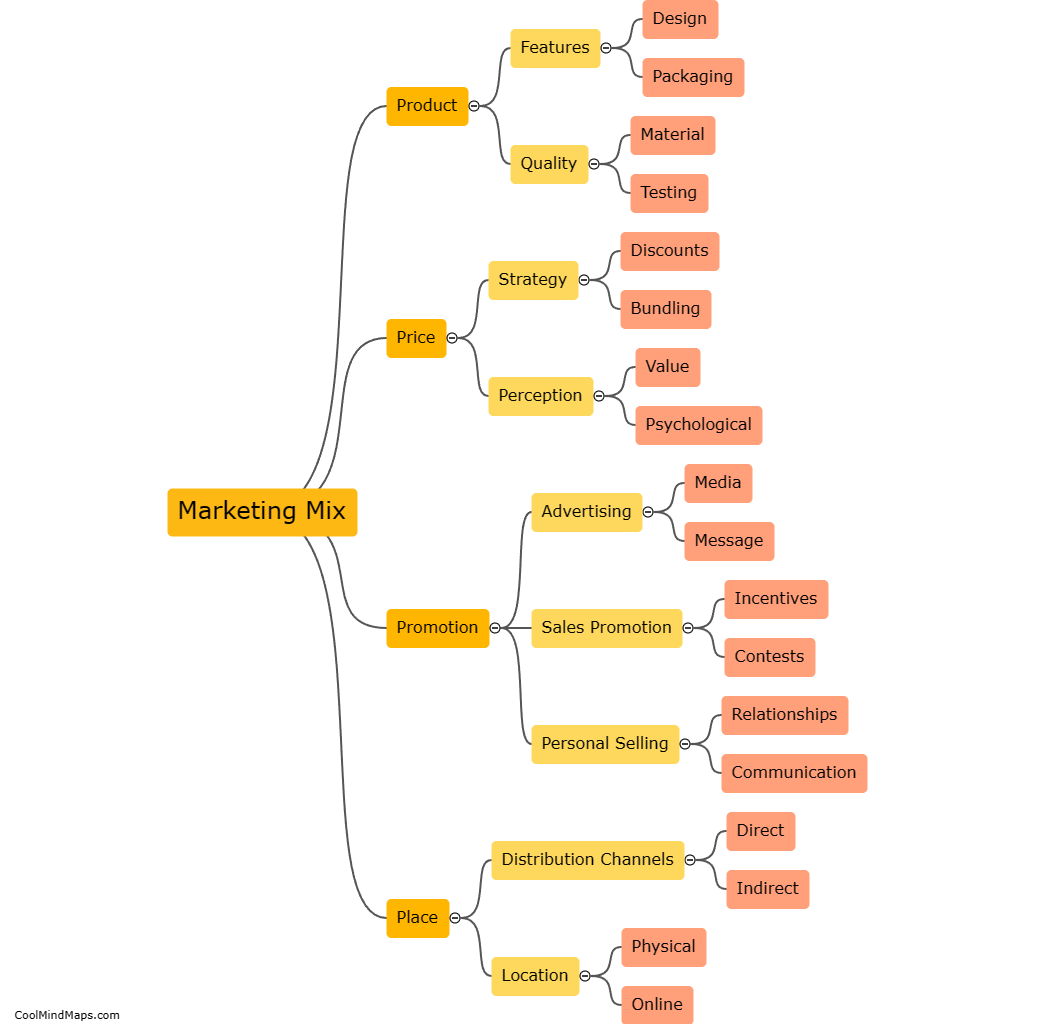
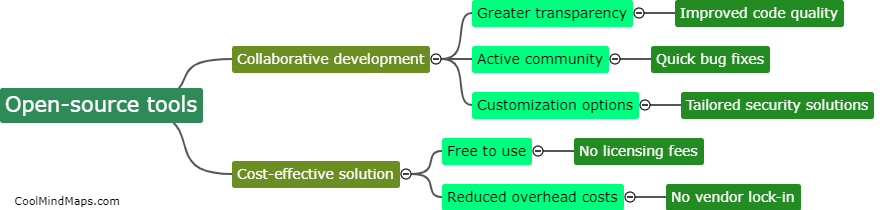
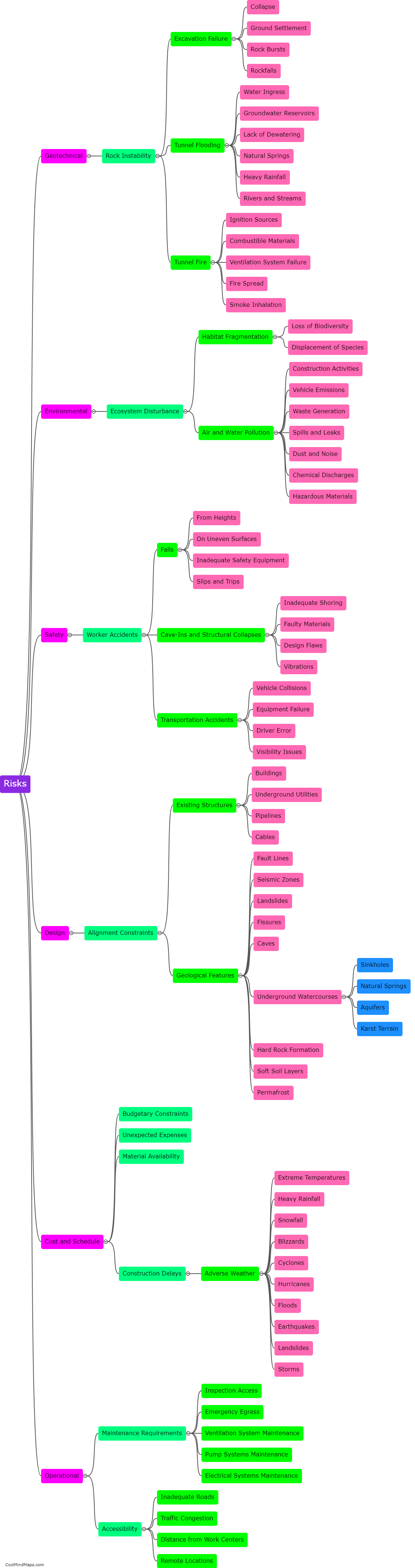
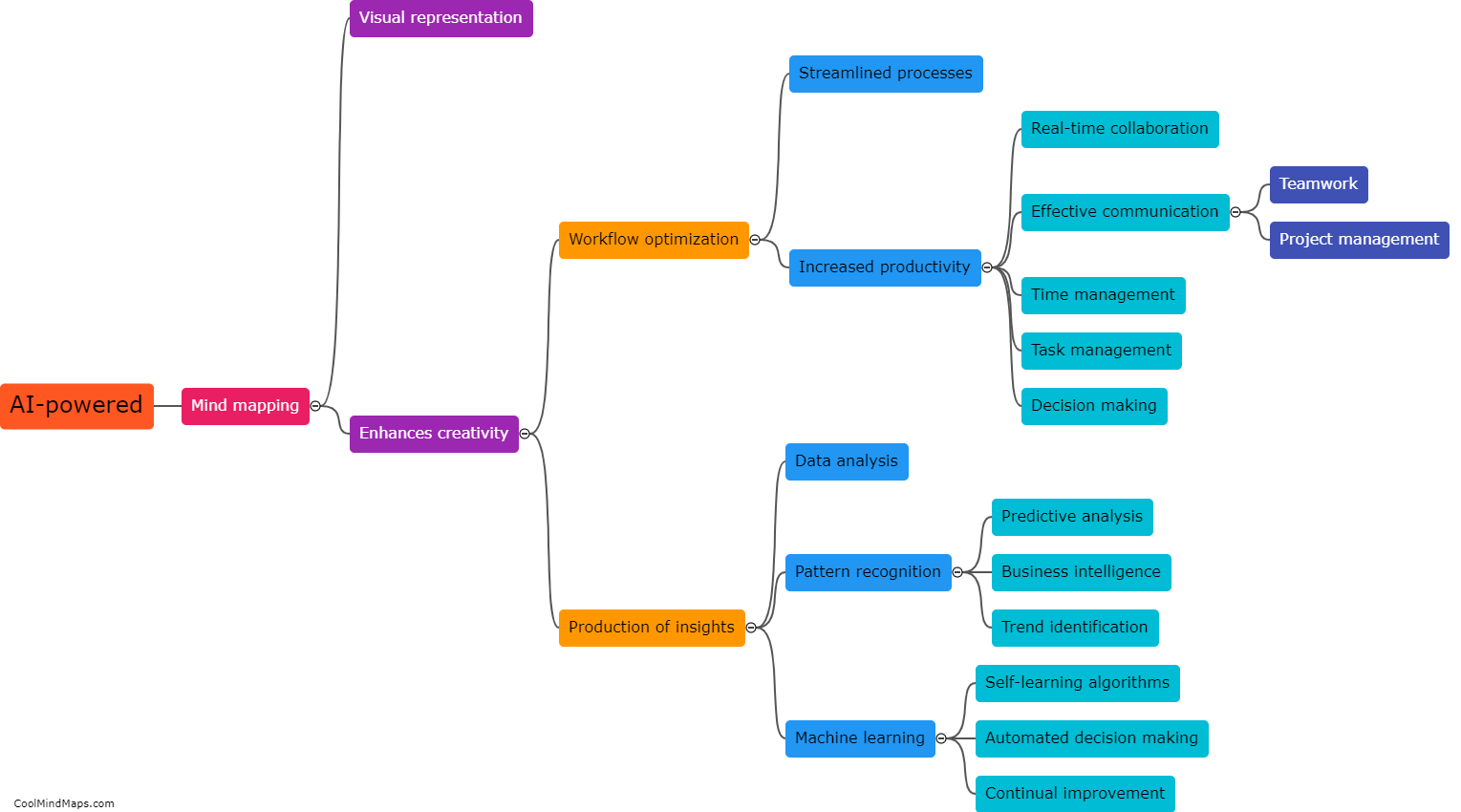
How does the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex contribute to risk assessment?
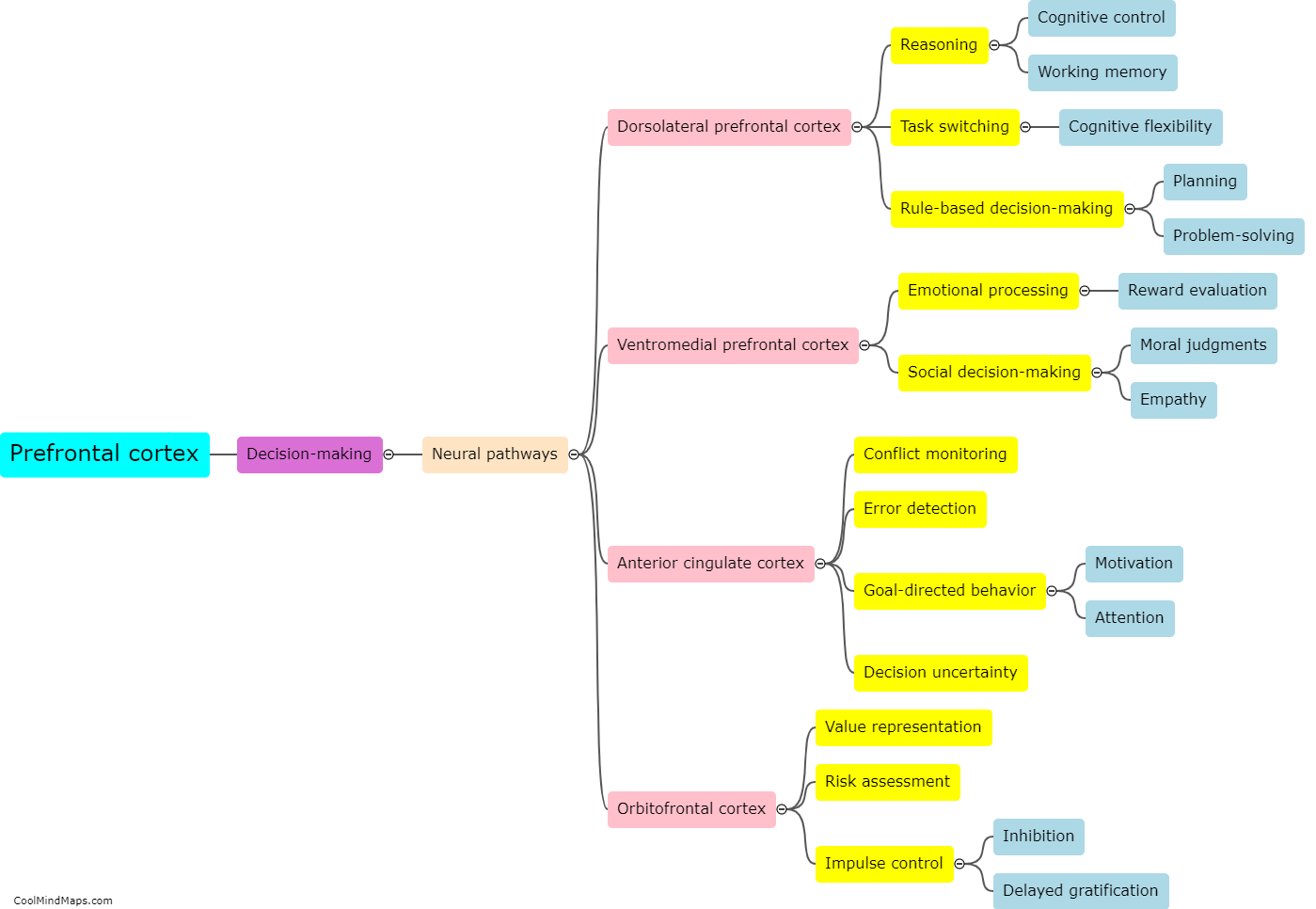
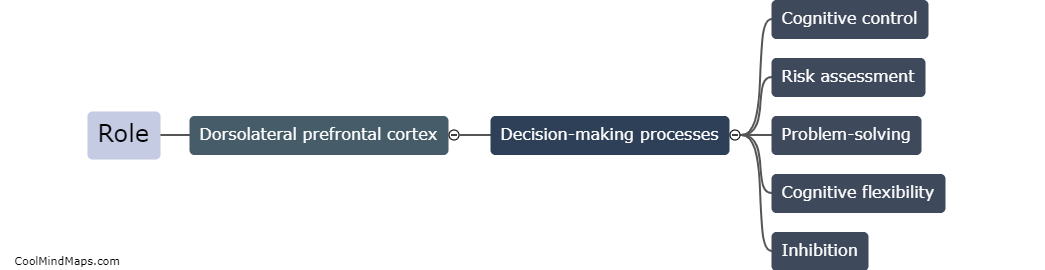
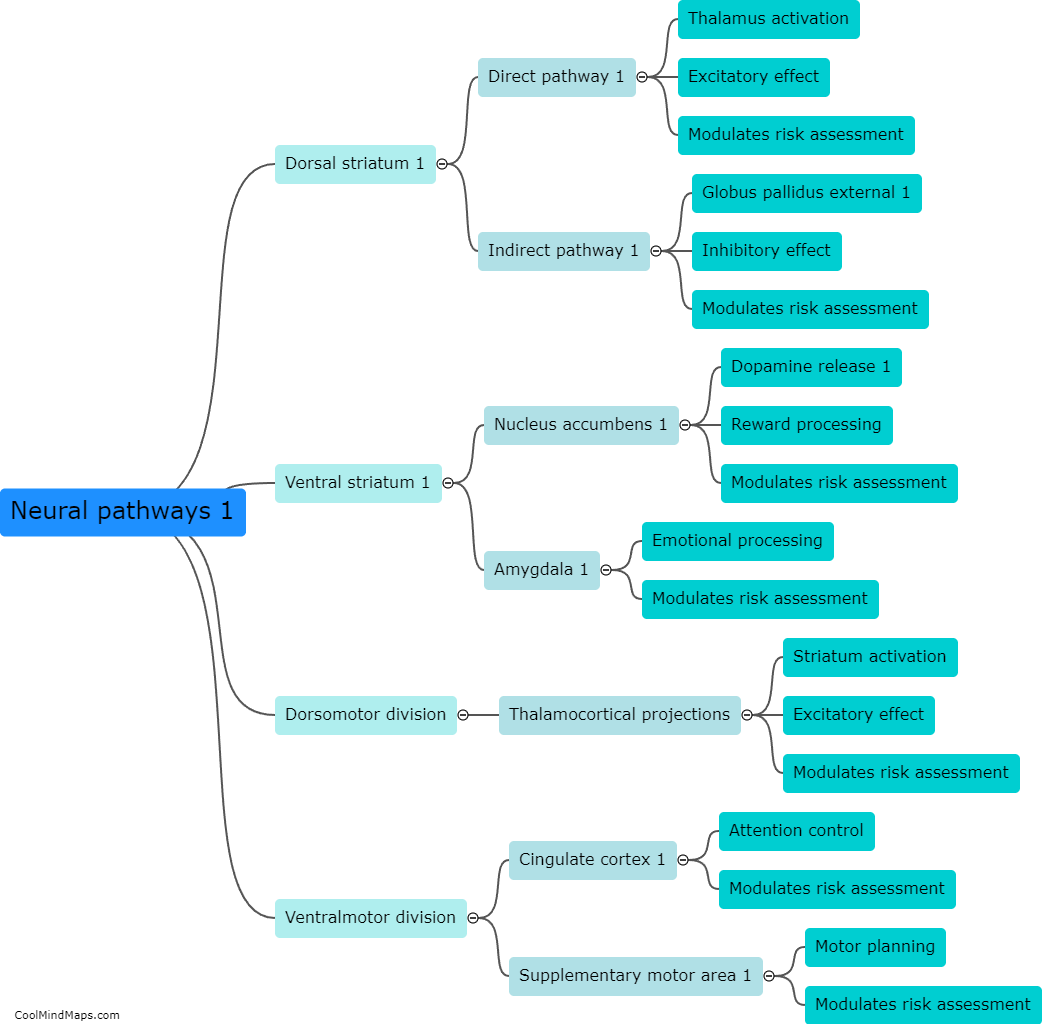
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) is a region of the brain located in the frontal lobes, and it plays a crucial role in risk assessment. It is responsible for higher-order cognitive processes, such as executive functions, decision-making, and working memory, which are all necessary for evaluating and weighing potential risks. Through its connections with other brain regions involved in emotional processing and reward systems, the DLPFC helps individuals assess potential risks by considering both the immediate consequences and long-term outcomes of their actions. It aids in inhibiting impulsive and risky behaviors, allowing individuals to make more informed and cautious decisions. Dysfunction in the DLPFC can lead to impaired risk assessment, which may contribute to impulsive behaviors and taking unnecessary risks.

This mind map was published on 20 October 2023 and has been viewed 149 times.