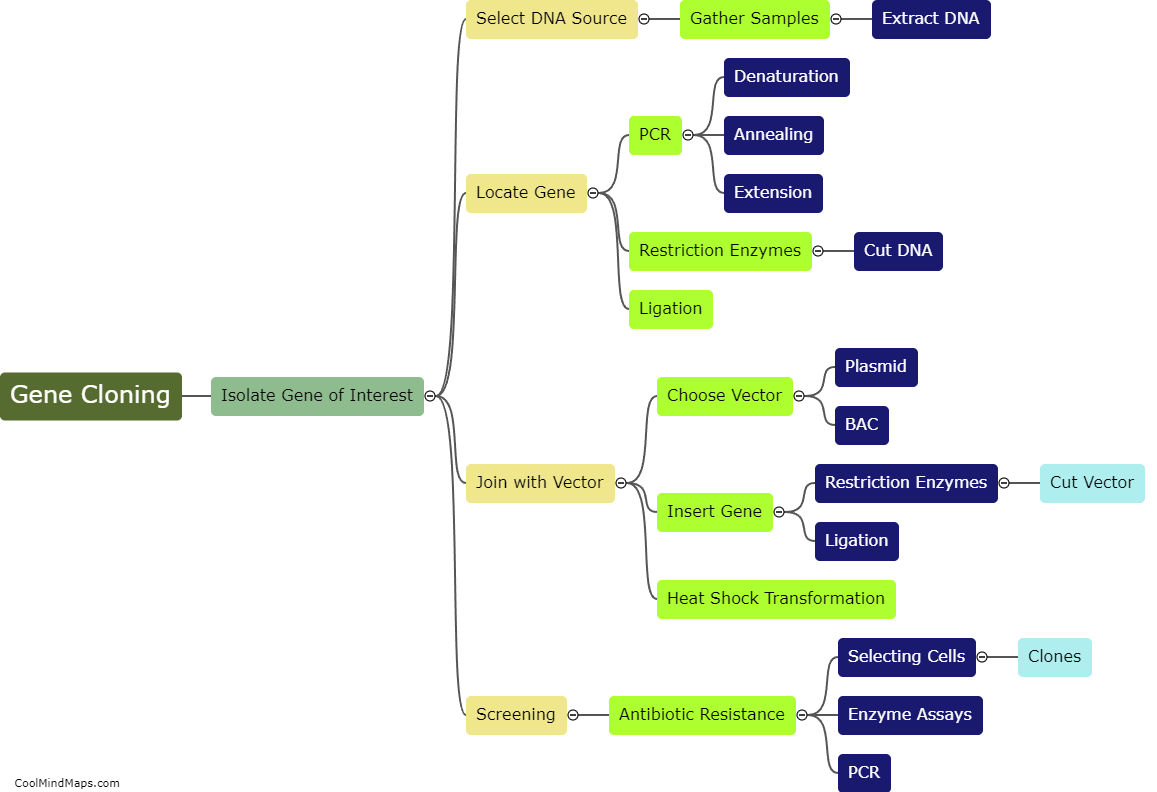
What are the steps involved in gene cloning?
Gene cloning is a process of isolating a specific DNA fragment and creating multiple copies of it. The first step in gene cloning is to select a target DNA sequence, which is then isolated using enzymes that cut the DNA at specific sites. The isolated DNA is then inserted into a vector, which is often a plasmid, using enzymes called ligases. The resulting recombinant DNA molecule is then introduced into a host cell, which can be bacteria, yeast or mammalian cells, and allowed to multiply. Once the host cells have multiplied, the cloned DNA can be isolated and purified. The process of gene cloning requires a number of sophisticated tools such as restriction enzymes, ligases, DNA polymerase, and PCR machines.
This mind map was published on 16 May 2023 and has been viewed 101 times.