What role does DNA play in autoimmune diseases?
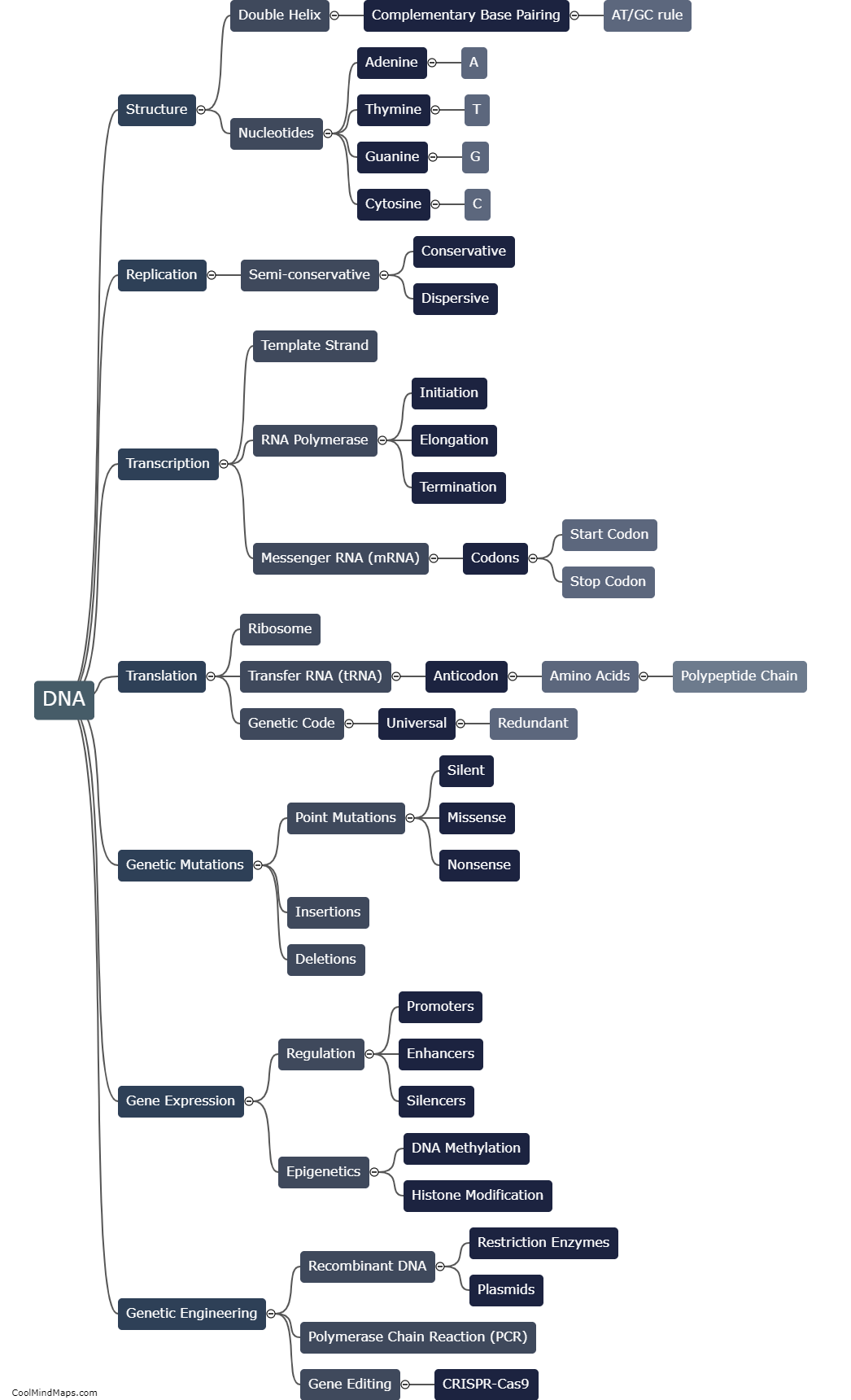
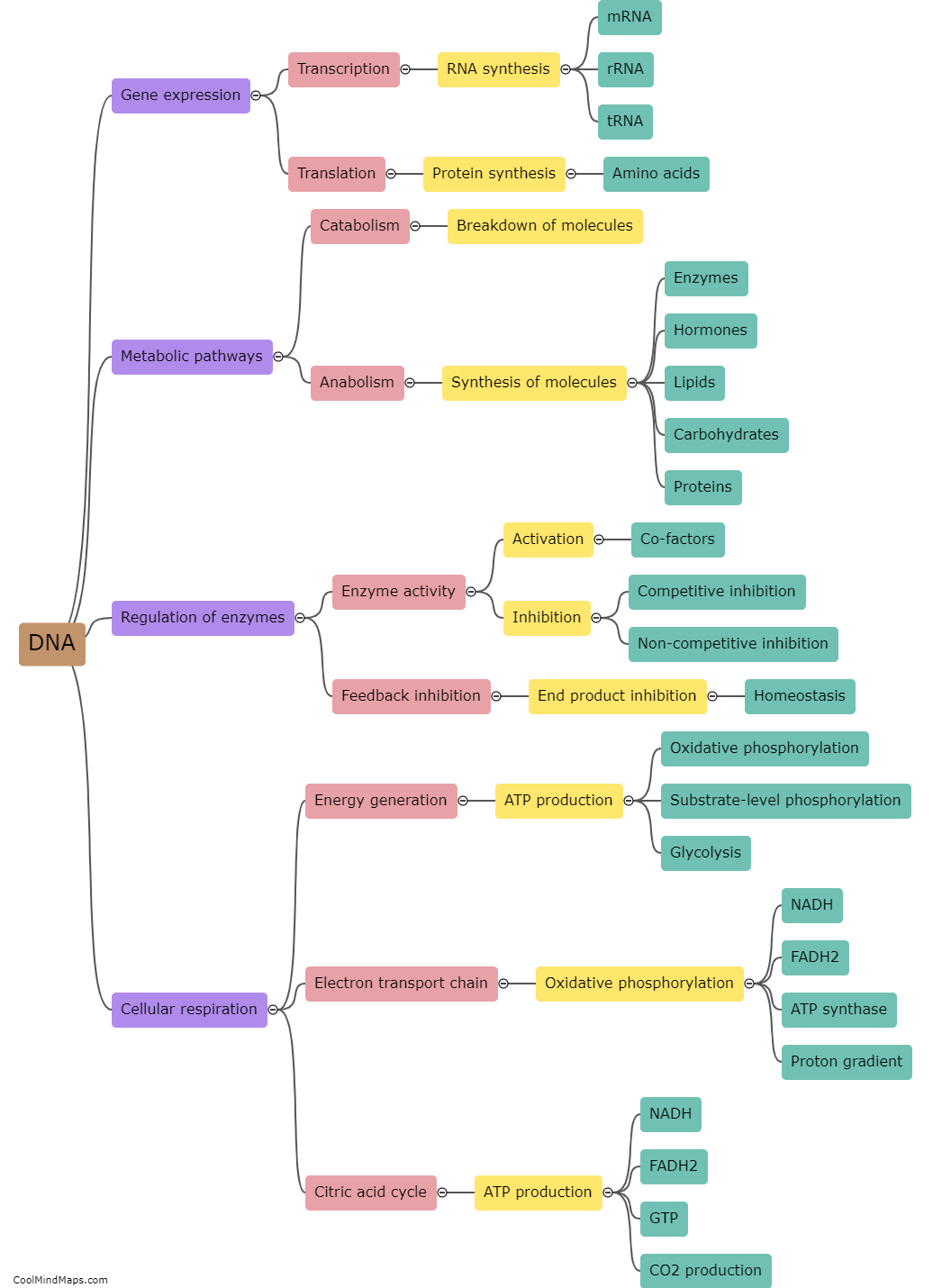
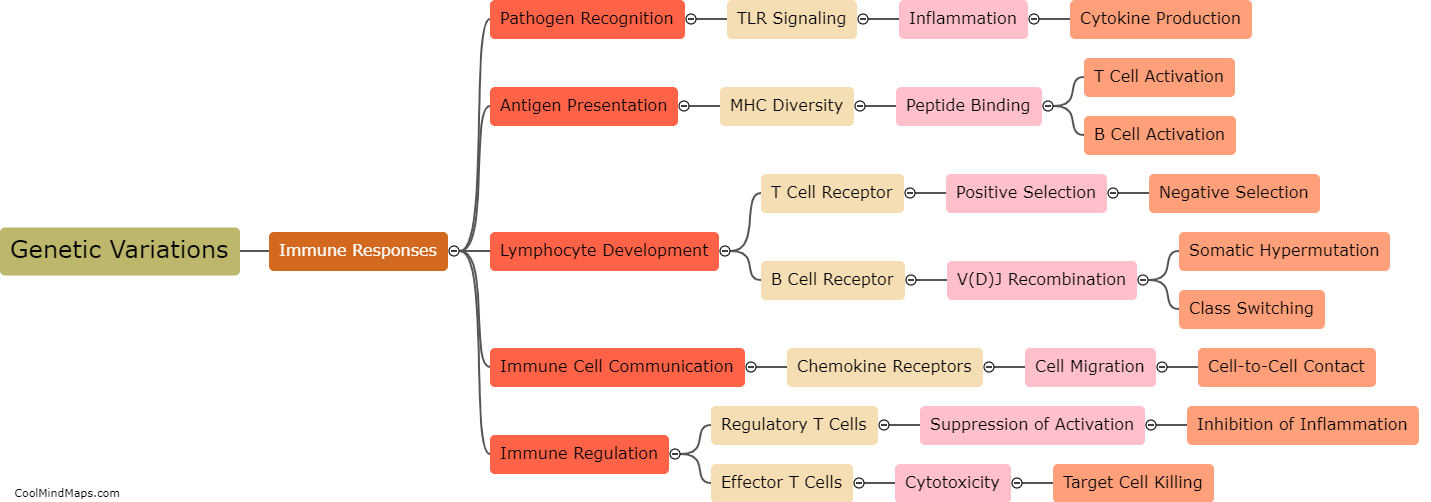
DNA plays a crucial role in autoimmune diseases as it is involved in determining an individual's susceptibility to these conditions. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, and genetic factors are known to contribute significantly to their development. Specific variations or mutations in DNA can affect the functioning of immune cells, leading to an abnormal immune response and the development of autoimmune diseases. Genetic studies have identified various genes associated with autoimmune diseases, such as those involved in immune cell regulation, antigen presentation, and immune response signaling. Understanding the role of DNA in autoimmune diseases can aid in identifying individuals at higher risk, improving diagnosis and treatment strategies, and ultimately developing targeted therapies.

This mind map was published on 27 November 2023 and has been viewed 77 times.